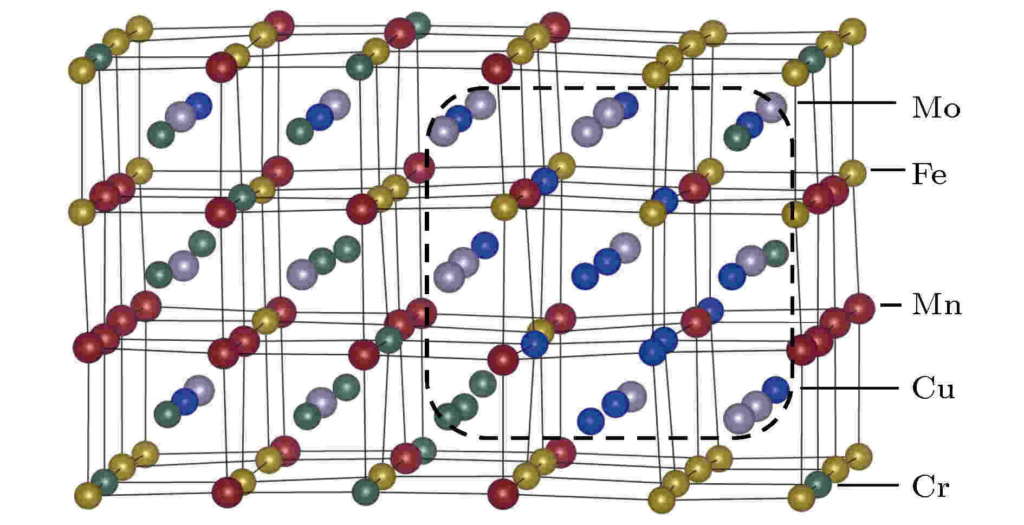
High-entropy alloys (HEA for short) are alloys formed from five or more metals in equal or approximately equal amounts. High entropy alloy powders have broad application prospects as raw materials for the preparation of blocks, coatings, thin-film materials, and other functional materials.
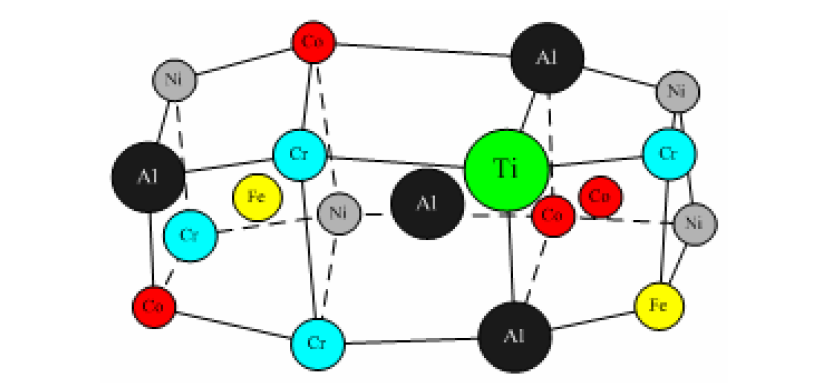
High Entropy Alloy (HEA) alloys are made up of 5 or more elements in equal or near-equal atomic ratios, each containing between 5% and 35% of each element. This concept is a break with the traditional design of alloys based on one or two elements. This concept is a break from the traditional design of alloys based on one or two elements and opens up a whole new path for alloy development.
Ultra-fine high entropy alloy powders with homogeneous structures can not only be used to prepare blocks and coatings but also to replace other high-temperature alloy powders used under special conditions for 3D printing, laser cladding, laser alloying, laser repair, laser quenching, and 3D rapid prototyping technologies, which greatly reduce material losses in machining and achieve low cost and high performance of products. Current The main methods of preparing ultra-fine high entropy alloy powders are mechanical alloying and gas/water atomization.
Mechanical Alloying (MA) is a powder preparation technique in which metal or alloy powders are alloyed in a high energy ball mill through prolonged and intense impact and collision between the powder particles and the grinding balls, resulting in repeated cold welding and fracture of the powder particles, leading to the diffusion of atoms in the powder particles, thus obtaining an alloyed powder.
The working principle of the vacuum atomization powder making device is that the metal or metal alloy is melted under vacuum conditions, and under the condition of gas protection, the metal liquid is atomized and broken into a large number of fine metal droplets by the high-pressure airflow through the nozzle in the process of flowing down through the insulated intermediate ladle and guide tube, and the fine droplets are formed into spheres and solidified into particles under the action of surface tension in the flight process to achieve the powder making The fine droplets are formed into spheres and solidified into particles under surface tension during flight to achieve powder production.
The novel properties of high entropy alloy powders, such as superb specific strength, excellent mechanical properties at high temperatures, excellent toughness, and fracture strength at low temperatures, superb magnetic properties, and superconductivity, pave the way for high entropy alloy powders to be used in aerospace, transportation, energy, electronics, biomedical, molds, precision shear tools, and other applications. High entropy alloy powders are used as hydrogen storage materials, radiation protection materials, diffusion barrier layers for electrons, precision shear, electromagnetic shielding materials, thermal spray materials, hard, low coefficient of friction and biological coatings, binders, and soft magnetic and hot spot materials.
With recent advanced developments in powder technology, improvements in printing processes and printed product performance have led to the use of high entropy alloy powders in 3D printing. The rapid solidification of DEDs and PBFs results in superior properties of printed HEA products compared to conventional manufacturing processes, resulting from the grain refinement caused by rapid solidification. 3D printing allows material selection, design, and free fabrication of lightweight materials, individual design, and nano-assembly to be combined. The need for new material development and structural optimization of high entropy alloy powders has facilitated the printing of HEA products that can achieve the complex shapes required for applications in aerospace, energy, molds, tools, and other fields.
High entropy alloy powder materials can be used widely.
High entropy alloy powder materials can be used on the one hand to prepare blocks, coatings, thin-film materials, but also as a substitute for other high-temperature alloy powders used under special conditions for 3D printing, laser cladding, laser alloying, laser repair, laser quenching, and 3D rapid prototyping. laser repair, laser quenching, and three-dimensional rapid prototyping technologies.
The material loss in machining can be greatly reduced, thus realizing the products’ low cost and high performance. On the other hand, nano-high entropy alloy powder materials can also be used as functional materials in catalysis, surface plasmon resonance, electronics, magnetism, energy storage, and high entropy alloy nanomaterials can be used as functional materials in the fields of catalysis, surface plasmon resonance, electronics, magnetics, energy storage, and bio/plasma imaging.
High entropy alloy powders can be used as raw materials for the preparation of blocks, plates, coatings, or films with excellent overall mechanical, physical, and chemical properties. The high entropy alloy powder can be used as a raw material for the preparation of blocks, sheets, coatings, or films. Considering the practicality, processability, and environmental friendliness of high-entropy alloys, they are promising as raw materials for structural and functional materials. The high entropy alloy powders have a wide range of applications as raw materials for the production of structural and functional materials. The high entropy alloys have a great potential for use as raw materials for structural and functional materials.
Frequently Asked Questions (Supplemental)
1) Which preparation route is best for High Entropy Alloy Powder used in PBF/LPBF?
- Gas or plasma atomization under high‑purity inert atmospheres. These routes yield spherical, satellite‑free particles with narrow PSD (typically 15–45 μm for LPBF) and low oxygen/nitrogen—critical for density and crack resistance.
2) Can mechanically alloyed (MA) HEA powders be used for AM?
- Yes, primarily for DED or cold spray where irregular particles are acceptable. For PBF, MA powders often need post‑spheroidization (plasma spheroidization) and de‑oxidation to meet flow and O/N specs.
3) What O/N/H targets are recommended for HEA powders in AM?
- Application‑specific, but common targets are O ≤0.05–0.10 wt%, N ≤0.02 wt%, H ≤0.002 wt% for crack‑sensitive systems. Verify by inert‑gas fusion (ASTM E1019).
4) How do composition ranges affect printability and properties?
- Cantor‑type FCC (e.g., CoCrFeMnNi) shows good ductility and low‑temperature toughness; BCC/B2‑lean (e.g., Al‑containing HEAs) improve high‑temperature strength but can be more crack‑prone, often requiring preheat, scan strategy tuning, or HIP.
5) Can High Entropy Alloy Powder be recycled between builds?
- With sieving, removal of spatter/oxides, and blend‑back controls, limited reuse is feasible. Track PSD, flow, apparent/tap density, and interstitials via a powder passport. Set site‑specific cycle limits based on tensile/fatigue trends and CT porosity.
2025 Industry Trends and Data
- Atomization upgrades: More suppliers use vacuum induction melting + inert gas atomization with argon recirculation and in‑line O2/H2O scrubbing to cut interstitials in HEA powders.
- Qualification accelerators: Digital powder passports tied to in‑situ melt‑pool imaging shorten allowables development for HEA components in aerospace and energy.
- Preheat and multi‑laser control: Elevated build‑plate preheats and harmonized gas‑flow ducts reduce cracking in Al‑rich or BCC HEAs; multi‑laser synchronization improves overlap quality.
- Function‑first alloys: Hydrogen storage, wear‑/corrosion‑resistant clads, and radiation‑tolerant parts drive adoption of Co‑/Cr‑lean, Fe‑Ni‑Mn‑based HEAs due to cost and ESG pressures.
- Binder jetting maturation: Fine HEA powders with sinter‑HIP routes reach near‑wrought density for complex heat‑exchanger and tooling inserts.
| KPI (High Entropy Alloy Powder & AM), 2025 | 2023 Baseline | 2025 Typical/Target | Why it matters | Sources/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPBF density post‑HIP (HEAs) | 99.5–99.8% | 99.8–99.95% | Fatigue, leak‑tightness | OEM/peer‑reviewed data |
| Chamber O2 during build (ppm) | ≤1000 | 100–300 | Oxide/soot control | Machine vendor guidance |
| Satellite count (≥5 μm per 100 particles) | 4–6 | 2–3 | Flow, spread consistency | SEM image analysis |
| Typical LPBF PSD (μm) | 20–63 | 15–45 | Packing, melt stability | ISO/ASTM 52907 |
| Qualified powder reuse cycles | 3–5 | 5–8 | Cost, consistency | Plant case studies |
| Binder‑jet HEA final density with HIP | 98–99% | 99–99.5% | Mechanical reliability | OEM notes |
| Reported recycled content in HEA lots | — | 10–25% | ESG, cost | EPD/LCA reports |
Authoritative resources:
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (metal powder characterization), 52904 (LPBF practice), 52910 (design for AM): https://www.iso.org
- ASTM B822/B214 (PSD), B212/B213 (density/flow), E1019 (O/N/H), F3302 (AM process control): https://www.astm.org
- ASM Handbook: Additive Manufacturing; High‑Entropy Alloys overview: https://dl.asminternational.org
- NIST AM Bench datasets and in‑situ monitoring: https://www.nist.gov/ambench
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: LPBF of Cantor‑Type HEA with Elevated Preheat for Cryogenic Components (2025)
- Background: An energy OEM needed ductile cryogenic brackets with low defect rates using CoCrFeMnNi High Entropy Alloy Powder.
- Solution: Gas‑atomized spherical powder (15–45 μm, O 0.06 wt%); build‑plate preheat 400–500°C; island hatch with contour pass; stress‑relief + HIP; shot peen and electropolish.
- Results: Post‑HIP density 99.92%; −196°C Charpy impact +18% vs. wrought baseline; CT porosity <0.05%; dimensional scatter −20%.
Case Study 2: DED Cladding of Wear‑Corrosion Resistant Al‑Containing HEA on Pump Shafts (2024)
- Background: A chemical processor required simultaneous wear and chloride corrosion resistance on shafts.
- Solution: Mechanically alloyed AlCoCrFeNi powder, plasma‑spheroidized; DED with interpass temperature control; post‑clad temper; slurry erosion and salt‑spray validation.
- Results: 3× wear life vs. 316L overlay; corrosion rate reduced 40% in 3.5% NaCl; downtime −25% over 12 months.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Yong Zhang, Materials Scientist, City University of Hong Kong (HEA research)
- Viewpoint: “Controlling stacking fault energy via Mn/Ni balance in FCC HEAs enables exceptional cryogenic toughness—powder cleanliness preserves that advantage in AM.”
- Dr. Tresa Pollock, Distinguished Professor, UC Santa Barbara
- Viewpoint: “For HEAs in AM, solidification pathway control—via scan strategy and preheat—is as critical as composition for avoiding hot cracking.”
- Dr. Martina Zimmermann, Head of Additive Materials, Fraunhofer IWM
- Viewpoint: “Powder passports linked to in‑situ layer imaging and CT benchmarks are accelerating HEA adoption in regulated sectors.”
Affiliation links:
- CityU Hong Kong: https://www.cityu.edu.hk
- UC Santa Barbara: https://www.ucsb.edu
- Fraunhofer IWM: https://www.iwm.fraunhofer.de
Practical Tools/Resources
- Standards/QC: ISO/ASTM 52907; ASTM B212/B213/B214/B822; ASTM E1019; ASTM F3302 for AM process control
- Metrology: LECO inert‑gas fusion for O/N/H (https://www.leco.com); laser diffraction PSD; SEM/EDS for morphology and segregation; CT for porosity; EBSD for texture/grain size
- Simulation: Thermo‑Calc/DICTRA and CALPHAD‑based HEA thermodynamics; Ansys/Simufact Additive for scan and distortion; nTopology for lattice and conformal channels
- Databases/Guides: NIST AM Bench; ASM Handbook; open HEA datasets and CALPHAD assessed systems (various journals)
- Process playbooks: Preheat and parameter windows for Al‑rich HEAs; HIP + surface finishing sequences for FCC HEAs targeting cryogenic service
Last updated: 2025-08-22
Changelog: Added 5 FAQs targeting preparation routes, interstitial targets, and reuse; introduced 2025 trend KPI table with references; included two case studies (LPBF Cantor‑type HEA with preheat; DED Al‑containing HEA clads); added expert viewpoints with affiliations; compiled standards, metrology, simulation, and database resources for High Entropy Alloy Powder.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ISO/ASTM standards update, major OEMs publish new O/N/H limits for HEA powders, or new datasets on preheat strategies and HEA binder‑jet densification are released.

