1. Introduction
In recent years, 3D printing has revolutionized manufacturing processes across various industries. This innovative technology has made it possible to create complex objects with exceptional precision and efficiency. One significant advancement within the realm of 3D printing is the use of metal powders as the printing material. This article explores the fascinating world of 3d printing metal powders, examining its benefits, applications, challenges, and future prospects.
2. What is 3D Printing?
Before delving into the specifics of 3d printing metal powders, it’s essential to understand the fundamentals of 3D printing itself. Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D printing is a process that constructs three-dimensional objects layer by layer from a digital model. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods that involve subtractive techniques, such as cutting or drilling, 3D printing builds objects from scratch using additive processes.

3. Advantages of 3D Printing
3D printing offers several advantages over conventional manufacturing methods, making it an increasingly popular choice in various industries. Some key advantages include:
3.1 Rapid Prototyping
One of the significant benefits of 3D printing is its ability to rapidly produce prototypes. Traditional prototyping methods often involve time-consuming and expensive processes. However, with 3D printing, designers and engineers can quickly create physical prototypes, enabling them to test and refine their designs more efficiently.
3.2 Cost-Effectiveness
3D printing can be a cost-effective manufacturing solution, especially for small-scale production or customized products. It eliminates the need for complex tooling and molds, reducing upfront costs. Additionally, 3D printing allows for on-demand production, eliminating excess inventory and storage costs.
3.3 Design Freedom
Traditional manufacturing methods often impose limitations on design due to manufacturing constraints. With 3D printing, designers have unparalleled freedom to create intricate and complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve using conventional methods. This design freedom enables greater innovation and creativity in product development.
3.4 Complex Geometries
3D printing excels at fabricating objects with complex internal and external geometries. This capability is particularly valuable in industries such as aerospace, where lightweight yet robust structures are crucial. By using metal powders in 3D printing, engineers can create intricate parts with internal channels, lattice structures, and optimized geometries.
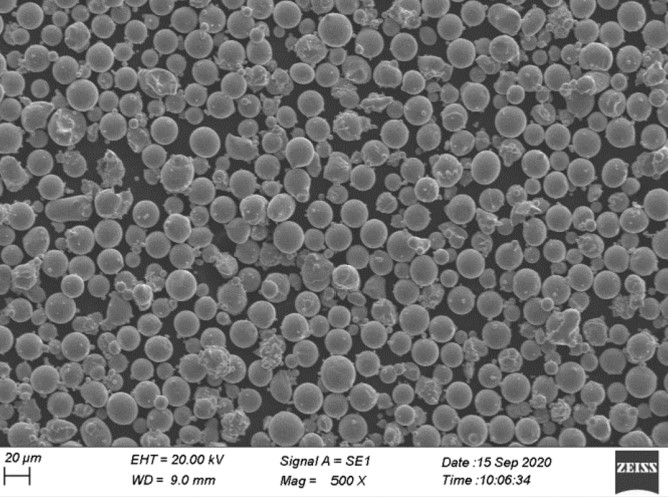
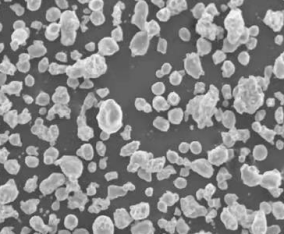
4. 3d printing metal powders
Now that we have a foundational understanding of 3D printing, let’s explore the realm of 3d printing metal powders. This approach involves using metal powders as the printing material in the additive manufacturing process. It opens up a wide range of possibilities for creating metal parts with exceptional strength, durability, and intricate details.
4.1 Understanding Metal Powders
Metal powders used in 3D printing are typically fine particles of metals or metal alloys. These powders are specifically designed and processed for optimal flowability and compatibility with the printing process. Common metals used in 3D printing include stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, nickel alloys, and cobalt-chrome alloys. Each metal powder has its own unique properties, such as strength, corrosion resistance, and heat conductivity, making them suitable for different applications.
4.2 Metal Powder Bed Fusion (PBF)
Metal Powder Bed Fusion (PBF) is one of the most commonly used techniques for 3d printing metal powders. It involves selectively melting and fusing metal powders layer by layer using a laser or an electron beam. The powdered material is spread in a thin layer, and the energy source selectively melts the desired areas according to the digital design. Once a layer is complete, the build platform moves down, and a new layer of powder is spread on top, repeating the process until the object is fully formed.
4.3 Direct Energy Deposition (DED)
Another method for 3d printing metal powders is Direct Energy Deposition (DED). In this technique, metal powders are fed through a nozzle, and a laser or an electron beam melts the powder as it is deposited onto a substrate or an existing structure. DED is particularly suitable for repairing or adding material to existing components and for creating large-scale objects. It offers faster printing speeds but may not provide the same level of detail as PBF.

5. Benefits of 3d printing metal powders
3d printing metal powders brings several advantages to the manufacturing industry. Let’s explore some of the key benefits:
5.1 Increased Strength and Durability
Metal parts produced through 3d printing metal powders exhibit excellent mechanical properties, including high strength and durability. The layer-by-layer fusion process allows for precise control over the microstructure of the printed parts, resulting in enhanced mechanical performance. This makes 3D-printed metal parts suitable for demanding applications where strength and reliability are critical.
5.2 Lightweight Structures
One of the significant advantages of 3d printing metal powders is the ability to create lightweight structures without compromising strength. By employing optimized lattice structures or hollow designs, engineers can reduce the weight of metal components while maintaining structural integrity. This is especially valuable in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where lightweighting is essential for fuel efficiency and performance.
5.3 Customization and Personalization
3d printing metal powders enables customization and personalization on a whole new level. It allows for the production of highly complex and unique designs tailored to specific customer requirements. With digital design files, manufacturers can easily modify and adapt the geometry of the printed objects without the need for additional tooling or molds. This flexibility opens up possibilities for personalized products and one-of-a-kind creations.
5.4 Reduced Material Waste
Traditional manufacturing processes often generate significant material waste due to subtractive techniques or limitations in mold design. In contrast, 3d printing metal powders is an additive process, where material is precisely deposited only where needed. This reduces material waste and leads to a more sustainable manufacturing approach. Additionally, unused or excess powder can be recycled and reused, further minimizing waste.
5.5 Time and Cost Savings
The use of 3d printing metal powders can lead to significant time and cost savings in the production process. With traditional manufacturing, creating complex metal parts may involve multiple steps, including machining, assembly, and finishing. 3D printing consolidates these steps into a single process, reducing labor, assembly time, and associated costs. It also eliminates the need for expensive tooling and molds, making it a cost-effective solution, particularly for low-volume production or custom-made components.
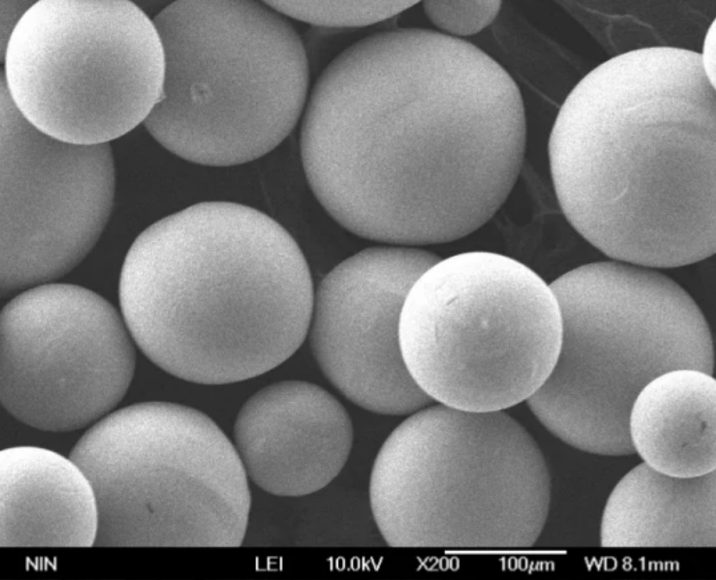

6. Applications of 3D Printing with Metal Powders
The versatility of 3d printing metal powders has resulted in its widespread adoption across various industries. Let’s explore some of the key applications:
6.1 Aerospace and Defense
The aerospace and defense sectors have embraced 3d printing metal powders for manufacturing lightweight yet strong components. It allows for the production of complex geometries, reducing the weight of aircraft and spacecraft while maintaining structural integrity. 3D printing is used for creating engine components, turbine blades, brackets, and other critical parts, enabling faster prototyping and customization for specific mission requirements.
6.2 Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, 3d printing metal powders is utilized for producing lightweight, high-performance parts. This technology enables the creation of intricate designs that enhance fuel efficiency and optimize vehicle performance. Applications include engine components, exhaust manifolds, brackets, and customized parts for specialized vehicles. 3D printing also facilitates rapid prototyping and accelerates the development of new automotive designs.
6.3 Medical Field
3d printing metal powders has revolutionized the medical field by enabling the production of patient-specific implants and surgical instruments. It offers a personalized approach to healthcare, allowing for customized implants tailored to an individual’s anatomy. Metal 3D-printed implants exhibit excellent biocompatibility and can be designed to provide optimal fit and functionality. Additionally, 3D printing aids in creating anatomical models and surgical guides, improving surgical planning and patient outcomes.
6.4 Jewelry and Fashion
The jewelry industry has embraced 3d printing metal powders as a means of creating intricate and unique designs. This technology allows jewelry designers to push the boundaries of creativity, producing highly detailed and customized pieces. 3D-printed metal jewelry offers intricate filigree work, complex patterns, and precise stone settings. The fashion industry also benefits from 3D-printed metal accessories and embellishments, providing designers with endless possibilities for innovative and avant-garde designs.
6.5 Manufacturing and Tooling
3d printing metal powders is also utilized in the manufacturing sector for producing tooling and molds. Complex tooling and dies can be quickly created using 3D printing, reducing lead times and costs associated with traditional methods. Additive manufacturing enables the production of customized fixtures, jigs, and assembly aids that enhance productivity on the factory floor. By leveraging 3D printing, manufacturers can streamline their processes, improve efficiency, and respond swiftly to changing production needs.

7. Challenges and Limitations of 3D Printing with Metal Powders
While 3d printing metal powders offers numerous advantages, there are challenges and limitations to consider:
7.1 High Equipment Cost
The initial investment required for 3d printing metal powders can be substantial. Specialized printers capable of handling metal powders and the associated post-processing equipment can be costly. Additionally, the need for safety measures, such as handling metal powders in controlled environments, further adds to the equipment cost. However, as the technology advances and becomes more widespread, the cost of equipment is expected to decrease.
7.2 Limited Material Availability
Although there is a growing range of metal powders available for 3D printing, the selection may still be limited compared to conventional manufacturing materials. Certain metals or alloys may not be readily available in powder form, limiting the choice of materials for specific applications. However, ongoing research and development efforts are expanding the range of metal powders, providing more options for 3D printing with metals.
7.3 Post-Processing Requirements
After the 3D printing process, metal parts often require post-processing to achieve the desired surface finish and mechanical properties. This may involve additional steps such as heat treatment, machining, polishing, or surface coating. Post-processing adds time and cost to the overall manufacturing process and requires specialized equipment and expertise. However, advancements in post-processing techniques, such as improved automation and integrated finishing solutions, are addressing these challenges and streamlining the post-processing phase.
7.4 Surface Finish and Resolution
Achieving a high-quality surface finish and fine resolution can be a challenge in 3D printing with metal powders. The layer-by-layer nature of the printing process can result in visible layer lines or rough surfaces. Improving surface finish often requires additional post-processing steps, such as polishing or machining. Resolution limitations can affect the level of detail and intricacy achievable in the printed parts. However, advancements in printing technologies and the development of finer metal powders are addressing these limitations and improving surface finish and resolution.
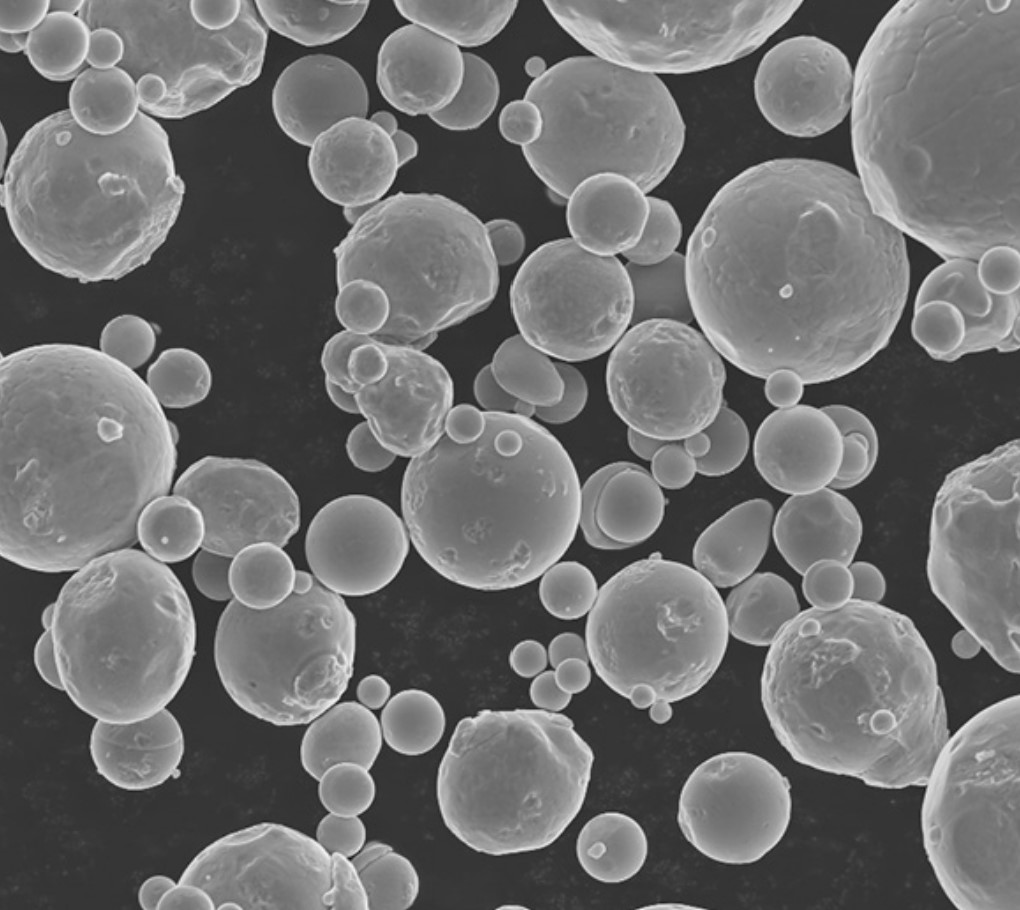

8. Future Trends and Innovations
The field of 3d printing metal powders is constantly evolving, with ongoing research and innovation driving its future prospects. Here are some trends and advancements to look out for:
8.1 Improved Material Options
Researchers and manufacturers are continually developing new metal powders to expand the range of materials available for 3D printing. This includes the development of high-performance alloys, exotic metals, and composite materials. These advancements will unlock new possibilities for applications in industries such as aerospace, healthcare, and advanced engineering.
8.2 Enhanced Printing Techniques
Printing techniques for 3d printing metal powders are continuously improving, with a focus on faster printing speeds, improved accuracy, and finer resolution. Innovations in laser and electron beam technologies are enabling greater control over the printing process, resulting in higher quality and more intricate metal parts.
8.3 Integration with Other Technologies
3d printing metal powders is being integrated with other technologies to further enhance its capabilities. For example, combining 3D printing with advanced robotics, machine learning, or artificial intelligence can optimize process parameters, increase efficiency, and enable real-time monitoring and quality control.
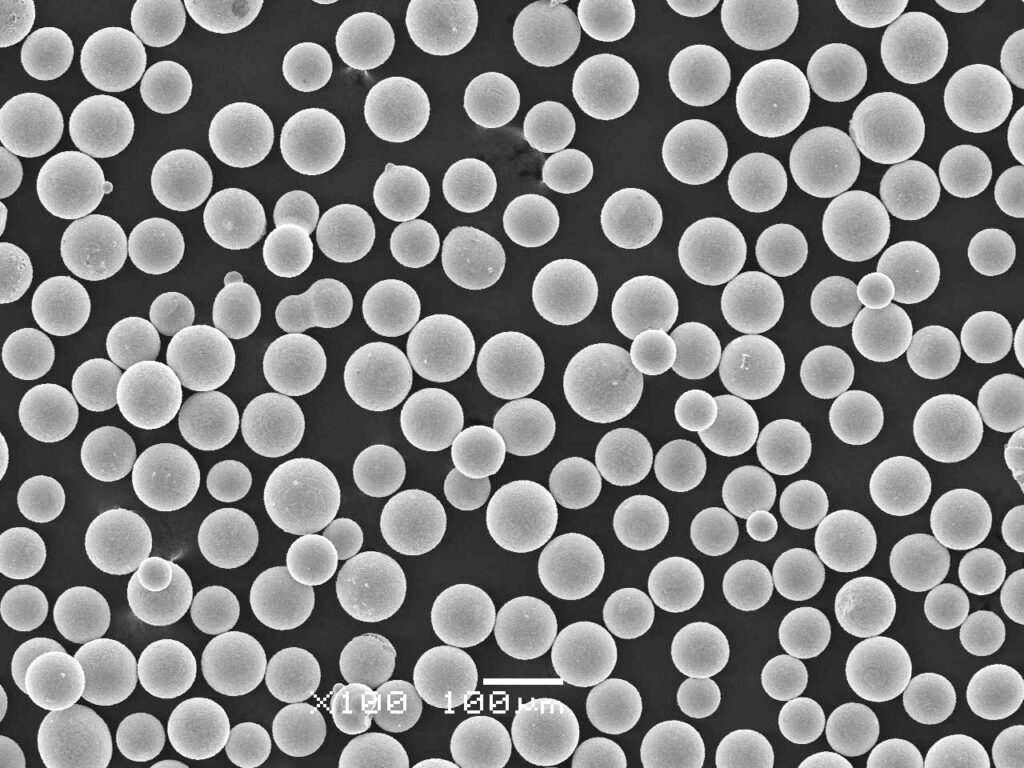
9. Conclusion
3D printing with metal powders has emerged as a game-changing technology in the manufacturing industry. It offers numerous benefits, including design freedom, rapid prototyping, customized production, and lightweight yet durable structures. Applications span various sectors, including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, jewelry, and manufacturing. While challenges such as equipment cost, limited material availability, and post-processing requirements exist, ongoing research and innovation are addressing these limitations. The future of 3d printing metal powders holds promise with improved materials, enhanced printing techniques, and integration with other technologies, paving the way for further advancements in additive manufacturing.
FAQs
1. Can 3D-printed metal parts be as strong as conventionally manufactured metal parts?
Yes, 3D-printed metal parts can exhibit similar strength and even surpass conventionally manufactured parts. The layer-by-layer fusion process allows for precise control over the microstructure, resulting in excellent mechanical properties.
2. What are the cost implications of 3d printing metal powders?
While the initial equipment cost for 3D printing with metal powders can be high, it can lead to cost savings in other areas such as tooling, customization, and on-demand production. It is a cost-effective solution for low-volume production or complex geometries.
3. Are there any size limitations for 3d printing metal powders?
The size limitations depend on the specific 3D printing technology and equipment being used. However, advancements are being made to enable the printing of larger objects, and the scalability of the technology is continuously improving.
4. What safety considerations are involved in handling metal powders for 3D printing?
Metal powders can be flammable and potentially hazardous. Proper safety protocols, such as working incontrolled environments with adequate ventilation and wearing appropriate personal protective equipment, should be followed when handling metal powders for 3D printing. It is important to adhere to safety guidelines provided by the equipment manufacturers and consult with experts in the field.