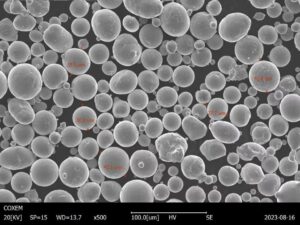
Introduction: Why Spherical Powder is a Game Changer in Modern Manufacturing
Imagine trying to fill a jar with marbles and pebbles. The marbles, smooth and uniform, glide into place effortlessly, leaving minimal gaps. Now, imagine doing the same with irregularly shaped pebbles. You’d struggle to pack them tightly, right? This is the principle behind spherical powder—tiny, uniform particles that flow and pack efficiently, revolutionizing industries from aerospace to biomedical engineering.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of spherical powder. We’ll explore its various types, delve into its unique properties, and discuss why it’s the material of choice for high-precision manufacturing. We’ll also compare different models, outline their specific uses, and guide you through the pros and cons of each. Whether you’re a seasoned engineer or just curious about cutting-edge materials, this guide has something for you.
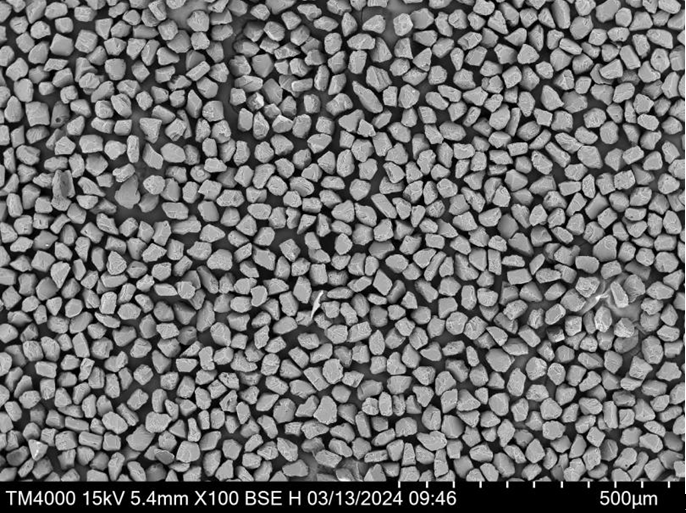

Overview of Spherical Powder
What Exactly is Spherical Powder?
Spherical powder consists of fine, round particles that are typically created using processes like atomization. These powders are highly sought after due to their superior flowability and packing density compared to irregularly shaped particles. Whether you’re talking about metals, ceramics, or polymers, if it’s spherical, it’s more efficient to work with.
Why Shape Matters
The spherical shape is more than just aesthetically pleasing. It’s the key to achieving uniform coatings, precision in additive manufacturing, and even consistency in products like pharmaceuticals. When it comes to manufacturing, uniformity and predictability are everything. Imagine baking a cake with ingredients of all different shapes and sizes—some parts would cook faster, others slower, leading to an uneven result. Spherical powder ensures that every ‘ingredient’ is uniform, resulting in a superior final product.
Composition of Spherical Powder
Types of Spherical Powder and Their Compositions
Different industries require different types of spherical powders, each with its unique composition tailored to specific applications. Here’s a closer look at some of the most common types:
| Type of Spherical Powder | Primary Composition | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium Spherical Powder | Titanium (Ti) | High strength, lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Aerospace, biomedical implants |
| Aluminum Spherical Powder | Aluminum (Al) | Excellent conductivity, lightweight | Automotive, electronics, additive manufacturing |
| Copper Spherical Powder | Copper (Cu) | High thermal and electrical conductivity | Electronics, heat sinks, conductive coatings |
| Stainless Steel Spherical Powder | Iron (Fe), Chromium (Cr), Nickel (Ni) | Corrosion resistance, durability | Medical devices, automotive, tools |
| Nickel Spherical Powder | Nickel (Ni) | High temperature and corrosion resistance | Aerospace, energy, additive manufacturing |
| Cobalt-Chromium Spherical Powder | Cobalt (Co), Chromium (Cr) | Biocompatibility, wear resistance | Medical implants, dental, aerospace |
| Tungsten Spherical Powder | Tungsten (W) | High density, heat resistance | Radiation shielding, aerospace, defense |
| Iron Spherical Powder | Iron (Fe) | Magnetic properties, affordability | Magnetic materials, automotive, additive manufacturing |
| Zinc Spherical Powder | Zinc (Zn) | Corrosion resistance, galvanizing properties | Galvanizing, die-casting, electronics |
| Silicon Spherical Powder | Silicon (Si) | Semiconductor properties, heat resistance | Electronics, solar cells, additive manufacturing |
Understanding the Composition and Its Impact on Performance
The composition of a spherical powder directly impacts its performance in different applications. For instance, titanium’s biocompatibility and strength make it ideal for medical implants, while aluminum’s lightweight nature is perfect for automotive parts. By understanding these compositions, manufacturers can select the right powder for their specific needs.
Characteristics of Spherical Powder
Key Properties That Make Spherical Powder Unique
What makes spherical powder stand out in the crowded field of materials science? Here’s a breakdown of the key characteristics:
| Property | Description | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Flowability | The ability of powder to flow smoothly | Essential for additive manufacturing and consistent layer deposition |
| Packing Density | The degree to which particles pack together | Higher density leads to stronger, more uniform materials |
| Surface Area | The total surface area of the particles | Impacts reactivity, especially in chemical processes |
| Purity | The absence of contaminants | Crucial for applications requiring high reliability, like medical implants |
| Sphericity | How close the particle shape is to a perfect sphere | Higher sphericity improves flow and packing characteristics |
Comparing the Characteristics of Different Spherical Powders
Different types of spherical powders exhibit these properties to varying degrees. For example, aluminum spherical powder has excellent flowability and is lightweight, making it perfect for additive manufacturing. In contrast, tungsten powder is extremely dense and heat-resistant, suitable for specialized applications like radiation shielding.
Advantages of Spherical Powder
Why Spherical Powder is Superior in Manufacturing
Using spherical powder offers numerous advantages, especially in industries where precision and efficiency are paramount. Here’s why:
- Improved Flowability: Spherical powders flow like water, filling molds and cavities with ease, which is essential in additive manufacturing and metal injection molding (MIM).
- Higher Packing Density: Because the particles pack together more tightly, the final product is often denser and stronger.
- Better Surface Finish: Spherical particles create smoother surfaces, reducing the need for post-processing.
- Uniform Coatings: In processes like thermal spraying, spherical powders result in more uniform coatings, improving performance and durability.
- Consistency in Composition: The uniformity of the particles ensures that each batch of powder behaves predictably, which is crucial for maintaining quality in production.
Case Study: Spherical Powder in Aerospace Manufacturing
Let’s take a closer look at how spherical powder is revolutionizing the aerospace industry. In the production of turbine blades, for example, the use of nickel spherical powder allows for the creation of parts that can withstand extreme temperatures and stresses. The uniformity of the powder ensures that each blade is identical in composition and structure, which is critical in an industry where even the smallest flaw can lead to catastrophic failure.





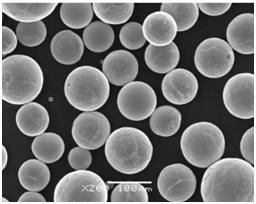
Applications of Spherical Powder
Industry-Specific Uses
Spherical powder’s unique properties make it invaluable across various industries. Here’s how different sectors are leveraging this material:
| Industry | Application | Benefits of Using Spherical Powder |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, rocket components | High strength-to-weight ratio, heat resistance |
| Automotive | Engine components, lightweight structures | Reduced weight, improved fuel efficiency |
| Medical | Implants, prosthetics | Biocompatibility, precision in additive manufacturing |
| Electronics | Conductive inks, components | High electrical conductivity, precision in microfabrication |
| Defense | Armor, ammunition | Density for ballistic protection, consistent quality |
| Energy | Nuclear reactors, solar panels | High temperature resistance, efficiency in energy conversion |
How Spherical Powder is Transforming Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is one of the most exciting fields where spherical powder is making a significant impact. The uniformity and flowability of these powders are perfect for creating intricate designs and complex geometries that would be impossible with traditional manufacturing methods. For instance, in the production of custom medical implants, spherical titanium powder is used to create structures that perfectly match the patient’s anatomy, improving outcomes and reducing recovery times.
Comparing Different Models of Spherical Powder
Detailed Comparison of 10 Spherical Powder Models
When selecting spherical powder for a specific application, it’s essential to compare different models based on their properties, composition, and cost. Below is a table that compares ten different models of spherical powder, highlighting their unique features and ideal uses:
| Model | Material | Properties | Best For | Price Range (per kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V | Titanium alloy | High strength, biocompatible | Medical implants, aerospace | $350 – $450 |
| AlSi10Mg | Aluminum alloy | Lightweight, good thermal properties | Automotive, aerospace | $100 – $150 |
| 316L | Stainless steel | Corrosion-resistant, durable | Medical devices, tools | $50 – $70 |
| CuNi2SiCr | Copper alloy | High electrical conductivity, strength | Electronics, heat sinks | $200 – $300 |
| CoCrMo | Cobalt-Chromium-Molybdenum | Biocompatible, wear-resistant | Dental implants, orthopedic devices | $400 – $500 |
| NiCr20TiAl | Nickel alloy | High temperature resistance, strength | Aerospace, energy | $600 – $750 |
| Fe2O3 | Iron oxide | Magnetic properties, affordable | Electronics, magnetic materials | $20 – $40 |
| WNiFe | Tungsten-Nickel-Iron | High density, radiation shielding | Defense, aerospace | $500 – $600 |
Specifications and Standards for Spherical Powder
Key Specifications and Standards for Spherical Powder
When selecting spherical powder for various applications, it’s essential to consider the specifications and standards that ensure quality and performance. Here’s a detailed overview:
| Specification | Description | Common Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size | Diameter of the powder particles, typically measured in micrometers (µm) | ASTM B330, ISO 3290 |
| Particle Shape | Sphericity or roundness of the particles | ASTM B212, ISO 19530 |
| Bulk Density | Mass of the powder per unit volume | ASTM B329, ISO 3953 |
| Apparent Density | Density of the powder as it appears in bulk | ASTM B212, ISO 3923 |
| Purity | Percentage of the main material vs. contaminants | ASTM E18, ISO 9001 |
| Flowability | How easily the powder flows through a funnel or chute | ASTM B213, ISO 4490 |
| Chemical Composition | The elements or compounds present in the powder | ASTM E1621, ISO 6892 |
Common Sizes and Grades of Spherical Powder
Different applications require specific sizes and grades of spherical powder. Here’s a table outlining some common sizes and grades:
| Size (µm) | Grade | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|
| 10 – 20 | Fine | Precision coatings, additive manufacturing |
| 20 – 50 | Medium | Automotive components, medical implants |
| 50 – 100 | Coarse | Industrial applications, large-scale manufacturing |
Suppliers and Pricing for Spherical Powder
Top Suppliers and Pricing Details
Here’s a snapshot of some prominent suppliers of spherical powder and their pricing:
| Supplier | Type of Powder | Price Range (per kg) | Website |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ametek | Titanium, Aluminum | $300 – $500 | ametek.com |
| Sandvik | Stainless Steel, Cobalt | $50 – $200 | home.sandvik |
| Höganäs | Iron, Nickel, Copper | $100 – $400 | hoganas.com |
| ARC Group | Tungsten, Zinc | $200 – $600 | arc-group.com |
| Elementum | Silicon, Molybdenum | $150 – $400 | elementum3d.com |
Pricing Factors
The price of spherical powder can vary based on several factors:
- Material Type: Premium materials like titanium and cobalt-chromium alloys are more expensive than standard metals like iron or aluminum.
- Particle Size: Finer powders tend to be more costly due to the additional processing required.
- Purity: High-purity powders usually command higher prices.
Comparing the Pros and Cons of Spherical Powder
Advantages and Limitations of Spherical Powder
When it comes to spherical powders, here’s what you need to know about their benefits and potential drawbacks:
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Flowability | Smooth, efficient flow for manufacturing | May require specific handling techniques |
| Packing Density | Higher density results in stronger materials | Dense powders can be harder to process |
| Surface Finish | Superior surface finish with minimal post-processing | Higher cost due to processing requirements |
| Uniformity | Consistent quality and performance | Production of uniform spherical powder can be expensive |
| Cost | Economical for high-volume production | Initial investment in high-quality powders can be high |
Detailed Comparison: Spherical Powder vs. Irregular Powder
- Spherical Powder: Offers superior flowability and packing density. Ideal for precision manufacturing and high-quality coatings. However, the processing can be more expensive.
- Irregular Powder: Typically cheaper but can lead to inconsistent flow and packing issues. Better suited for applications where precision is less critical.

FAQ
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is spherical powder used for? | Spherical powder is used in a variety of applications including additive manufacturing, automotive components, medical implants, and electronics. Its uniformity ensures high quality and precision in these fields. |
| How is spherical powder manufactured? | Spherical powder is typically produced using atomization techniques, where molten metal or other materials are rapidly cooled to form spherical particles. Other methods include gas atomization and water atomization. |
| What are the benefits of using spherical powder in 3D printing? | Spherical powder provides excellent flowability and packing density, leading to more consistent layer deposition and better final product quality in 3D printing. |
| How does the particle size affect the performance of spherical powder? | Finer particles provide better resolution and surface finish but may be more difficult to handle. Coarser particles are easier to handle but may not offer the same level of detail and finish. |
| Can spherical powder be recycled? | Yes, many types of spherical powder can be recycled, particularly in additive manufacturing. However, the recycling process must ensure that the powder maintains its quality and characteristics. |
| What is the typical cost of spherical powder? | The cost varies widely depending on the material, particle size, and purity. Prices can range from $20 per kg for common materials to over $750 per kg for specialized alloys. |
| Where can I purchase spherical powder? | Spherical powder can be purchased from specialized suppliers such as Ametek, Sandvik, Höganäs, ARC Group, and Elementum. Prices and availability will vary based on the type and specifications of the powder. |