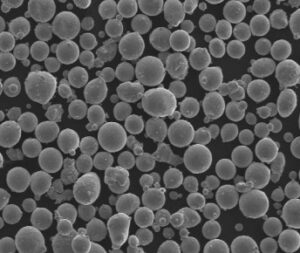
Overview of Molten Metal Deposition (MMD)
Molten Metal Deposition (MMD) is a cutting-edge additive manufacturing technique used to create intricate and high-performance metal parts. This process involves depositing layers of molten metal to build a component from the ground up, offering unparalleled precision and strength. MMD is particularly valued in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical, where the demand for complex and robust components is ever-increasing.
In this guide, we will delve into the specifics of MMD, including the types of metal powders used, their properties, applications, and more. By the end, you’ll have a thorough understanding of why MMD is revolutionizing manufacturing and how it can be applied to various industries.

Types of Metal Powders Used in MMD
Understanding the various metal powders used in MMD is crucial for selecting the right material for specific applications. Below is a detailed overview of ten specific metal powder models commonly used in MMD, along with their compositions and characteristics.
| Metal Powder Model | Composition | Properties | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium Ti-6Al-4V | 90% Titanium, 6% Aluminum, 4% Vanadium | High strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance | Widely used in aerospace, biocompatible for medical implants |
| Stainless Steel 316L | Iron, Chromium, Nickel, Molybdenum | Excellent corrosion resistance, high toughness | Ideal for marine and medical applications |
| Aluminum AlSi10Mg | Aluminum, Silicon, Magnesium | Lightweight, good thermal properties | Suitable for automotive and aerospace components |
| Inconel 718 | Nickel, Chromium, Iron, Niobium | High-temperature resistance, good oxidation resistance | Used in gas turbines and rocket engines |
| Cobalt-Chrome | Cobalt, Chromium | High wear and corrosion resistance, biocompatible | Common in dental and orthopedic implants |
| Tool Steel H13 | Iron, Chromium, Molybdenum, Vanadium | High hardness and toughness | Used in molds and dies for plastic injection molding |
| Copper CuNi2SiCr | Copper, Nickel, Silicon, Chromium | High thermal and electrical conductivity | Used in electrical components and heat exchangers |
| Maraging Steel (1.2709) | Iron, Nickel, Cobalt, Molybdenum | Ultra-high strength, good toughness | Used in tooling and high-performance parts |
| Nickel Alloy 625 | Nickel, Chromium, Molybdenum, Niobium | Excellent corrosion and oxidation resistance | Ideal for marine and chemical processing |
| Bronze CuSn10 | Copper, Tin | Good wear resistance, easy to cast | Used in bearings, bushings, and artistic sculptures |
Applications of Molten Metal Deposition (MMD)
MMD’s versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of applications. Below is a table summarizing the various applications of MMD across different industries.
| Industry | Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Engine components, structural parts | Lightweight, high strength, complex geometries |
| Automotive | Engine parts, chassis components | Improved performance, reduced weight, custom designs |
| Medical | Implants, surgical instruments | Biocompatibility, customization, rapid prototyping |
| Marine | Propellers, structural components | Corrosion resistance, durability |
| Energy | Turbine blades, heat exchangers | High-temperature resistance, efficiency |
| Electronics | Connectors, heat sinks | High conductivity, precision |
| Tooling | Molds, dies | High strength, wear resistance, precision |
| Art and Jewelry | Sculptures, custom jewelry | Intricate designs, material variety |
| Industrial Equipment | Machine components, gears | Durability, strength, custom solutions |
| Construction | Structural elements, fasteners | Strength, corrosion resistance, complex shapes |
Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards
To ensure consistency and quality in MMD, specific standards, sizes, and grades are followed. The table below outlines these specifications.
| Material | Specifications | Sizes (mm) | Grades | Standards |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium Ti-6Al-4V | ASTM B348, AMS 4911 | 1-50 | Grade 5 | ASTM, AMS, ISO |
| Stainless Steel 316L | ASTM A240, AMS 5507 | 0.5-100 | Grade 316L | ASTM, AMS, ISO |
| Aluminum AlSi10Mg | EN 1706, ISO 3522 | 0.5-50 | AlSi10Mg | EN, ISO |
| Inconel 718 | AMS 5662, ASTM B637 | 1-50 | UNS N07718 | AMS, ASTM |
| Cobalt-Chrome | ASTM F75, ISO 5832-4 | 1-20 | CoCrMo | ASTM, ISO |
| Tool Steel H13 | ASTM A681, SAE J437 | 1-100 | H13 | ASTM, SAE |
| Copper CuNi2SiCr | DIN 17670, ASTM B505 | 0.5-100 | CuNi2SiCr | DIN, ASTM |
| Maraging Steel (1.2709) | AMS 6514, DIN 1.2709 | 1-50 | Grade 300 | AMS, DIN |
| Nickel Alloy 625 | AMS 5599, ASTM B443 | 1-50 | UNS N06625 | AMS, ASTM |
| Bronze CuSn10 | ASTM B505, SAE J461 | 1-100 | CuSn10 | ASTM, SAE |





Suppliers and Pricing Details
Knowing where to source metal powders and their cost is vital for budgeting and planning in MMD. Here’s a table with details on suppliers and pricing.
| Supplier | Location | Materials Available | Pricing (USD/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| EOS GmbH | Germany | Ti-6Al-4V, 316L, AlSi10Mg, Inconel 718 | 150-400 |
| Carpenter Technology | USA | Cobalt-Chrome, H13, Maraging Steel | 200-500 |
| Sandvik | Sweden | 316L, CuNi2SiCr, Inconel 625 | 100-300 |
| AP&C | Canada | Ti-6Al-4V, 316L, AlSi10Mg | 180-350 |
| GKN Hoeganaes | USA | Bronze CuSn10, 316L, Maraging Steel | 120-400 |
| Praxair | USA | Ti-6Al-4V, 316L, Inconel 718, CuNi2SiCr | 200-450 |
| Höganäs AB | Sweden | Stainless Steels, Tool Steels, Bronzes | 150-400 |
| LPW Technology | UK | 316L, AlSi10Mg, Inconel 625 | 180-360 |
| Arcam AB | Sweden | Ti-6Al-4V, CoCrMo, Inconel 718 | 250-500 |
| Tekna Plasma Systems | Canada | 316L, Ti-6Al-4V, Inconel 718 | 200-450 |
Advantages and Limitations of MMD
Every technology comes with its pros and cons. Here’s a detailed comparison of the advantages and limitations of MMD.
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | High accuracy in creating complex geometries | Requires precise control and calibration |
| Material Properties | Excellent mechanical properties and performance | Limited to specific metals and alloys |
| Customization | Highly customizable designs | Design complexity can increase cost and time |
| Speed | Faster production for small to medium batches | Slower for large-scale production |
| Cost | Reduced material waste, cost-effective for prototypes | High initial investment in equipment |
| Strength and Durability | Produces strong, durable parts | Some materials may require post-processing |
| Sustainability | Minimal waste, recyclable materials | Energy-intensive process |
| Versatility | Wide range of applications across industries | Not suitable for all types of components |
| Integration | Can be integrated with other manufacturing processes | Requires specialized knowledge and skills |
| Innovation | Enables innovative designs and rapid prototyping | Limited by current technological advancements |
Key Characteristics of Molten Metal Deposition (MMD)
Let’s explore the key characteristics of MMD that make it a unique and valuable manufacturing process.
Precision and Accuracy
One of the standout features of MMD is its precision. By depositing molten metal layer by layer, MMD can achieve intricate details that traditional methods might miss. This high level of accuracy is essential for industries where even the slightest deviation can lead to significant issues, such as in aerospace or medical applications.
Material Versatility
MMD is compatible with a variety of metals and alloys, each offering unique properties. Whether it’s the high strength-to-weight ratio of titanium or the excellent corrosion resistance of stainless steel, MMD can cater to diverse needs, making it a highly versatile manufacturing technique.
Strength and Durability
The components produced through MMD are known for their superior strength and durability. This is particularly beneficial in industries like automotive and aerospace, where parts are subjected to extreme conditions and must maintain their integrity over time.
Customization and Flexibility
MMD allows for significant customization, enabling manufacturers to produce parts tailored to specific requirements. This flexibility is invaluable in applications where bespoke solutions are necessary, such as custom medical implants or specialized aerospace components.
Efficiency and Sustainability
MMD is an efficient process that minimizes waste, as it only uses the material needed to create the part. Additionally, many of the materials used in MMD are recyclable, contributing to the sustainability of the manufacturing process.
FAQ
What is Molten Metal Deposition (MMD)?
Q: What exactly is Molten Metal Deposition (MMD)?
A: Molten Metal Deposition (MMD) is an additive manufacturing process that builds metal parts layer by layer using molten metal. It allows for precise, complex geometries and high-performance components.
How does MMD compare to other additive manufacturing methods?
Q: How does MMD differ from other 3D printing techniques?
A: Unlike other additive manufacturing methods that might use plastic or resin, MMD uses metal, providing superior strength and durability. It is particularly useful for applications requiring high-performance metal parts.
What materials can be used in MMD?
Q: What types of metals and alloys are commonly used in MMD?
A: Common metals used in MMD include Titanium Ti-6Al-4V, Stainless Steel 316L, Aluminum AlSi10Mg, Inconel 718, and Cobalt-Chrome, among others. Each material offers unique properties suitable for different applications.
What are the benefits of using MMD?
Q: Why should I consider using MMD for manufacturing?
A: MMD offers high precision, excellent material properties, customization, efficiency, and sustainability. It is particularly beneficial for producing complex and high-performance parts.
Are there any limitations to MMD?
Q: What are the drawbacks or limitations of MMD?
A: While MMD is highly versatile and precise, it can be expensive to set up and requires specialized knowledge. Additionally, it may not be suitable for all types of components, and some materials may need post-processing.
How can I get started with MMD?
Q: What do I need to start using MMD for my projects?
A: To get started with MMD, you’ll need access to an MMD machine, the appropriate metal powders, and knowledge of the process. Partnering with experienced suppliers and manufacturers can also help streamline the adoption of MMD.
Where can I source metal powders for MMD?
Q: Where can I buy metal powders for MMD, and what should I consider?
A: Metal powders for MMD can be sourced from suppliers such as EOS GmbH, Carpenter Technology, and Sandvik. Consider factors like material properties, cost, and supplier reliability when making your choice.