Introduction
High purity iron powder is a critical material used in various industries, from metallurgy to electronics. But what exactly makes it so special? How does it differ from regular iron powder? In this guide, we’ll dive deep into the world of high purity iron powder, exploring its composition, characteristics, applications, and much more. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a curious learner, this article is designed to answer all your questions about high purity iron powder.
Overview of High Purity Iron Powder
High purity iron powder is iron powder with a purity level of 99.9% or higher. Its unique properties make it ideal for specialized applications requiring high strength, excellent conductivity, or specific magnetic properties. The production of high purity iron powder involves advanced processes such as atomization or reduction, resulting in a fine powder with consistent particle size and shape.
Key Characteristics of High Purity Iron Powder
- Purity: Typically 99.9% or higher
- Particle Size: Can range from a few micrometers to several hundred micrometers
- Shape: Spherical or irregular, depending on the production method
- Magnetic Properties: High saturation magnetization
- Electrical Conductivity: Excellent due to the high purity level

Composition and Properties of High Purity Iron Powder
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Purity | 99.9% or higher |
| Particle Size | From a few micrometers to several hundred micrometers |
| Shape | Spherical or irregular |
| Magnetic Saturation | High |
| Electrical Conductivity | Excellent due to minimal impurities |
| Density | Varies depending on the particle size and shape |
| Surface Area | Higher in finer powders |
| Oxygen Content | Low, ensuring minimal oxidation |
Types and Models of High Purity Iron Powder
There are various types of high purity iron powder, each tailored to specific applications. The differences between these types lie in their particle size, shape, and production methods. Below, we discuss some of the most common models available on the market:
1. Atomized Iron Powder
Atomized iron powder is produced through the atomization process, where molten iron is dispersed into fine droplets that solidify into powder. This type typically has a spherical shape and is used in applications where flowability and packing density are important.
- Purity: 99.9% or higher
- Applications: Powder metallurgy, magnetic materials, metal injection molding (MIM)
2. Reduced Iron Powder
Reduced iron powder is produced by reducing iron ore or mill scale in a hydrogen atmosphere. It typically has an irregular shape and is used in applications where surface area is critical, such as in chemical reactions or as a catalyst.
- Purity: 99.5% to 99.9%
- Applications: Chemical synthesis, pharmaceutical industry, magnetic materials
3. Electrolytic Iron Powder
Electrolytic iron powder is produced through the electrolysis of iron. This method results in very high purity and a controlled particle size distribution. It is often used in applications requiring high precision and purity.
- Purity: 99.9% or higher
- Applications: Electronics, battery manufacturing, high-performance magnets
4. Carbonyl Iron Powder
Carbonyl iron powder is produced by decomposing iron pentacarbonyl. This method creates ultra-fine spherical particles, often used in applications requiring high magnetization and minimal impurities.
- Purity: 99.9% or higher
- Applications: Electronics, inductors, electromagnetic shielding
5. Water-Atomized Iron Powder
Similar to atomized iron powder, but using water as the dispersing medium, water-atomized iron powder has irregular shapes and is used where a balance between cost and performance is needed.
- Purity: 99.5% to 99.9%
- Applications: Powder metallurgy, automotive parts, metal injection molding (MIM)
6. Gas-Atomized Iron Powder
Gas-atomized iron powder, created using inert gases to disperse the molten iron, typically has a more uniform spherical shape and is used in high-performance applications.
- Purity: 99.9% or higher
- Applications: Aerospace, 3D printing, magnetic materials
7. Ultra-Fine Iron Powder
Ultra-fine iron powder is characterized by its extremely small particle size, often in the nanometer range. It is used in advanced applications such as coatings, inks, and nanotechnology.
- Purity: 99.9% or higher
- Applications: Coatings, nanotechnology, conductive inks
8. High-Density Iron Powder
High-density iron powder is designed for applications requiring maximum packing density and is typically used in high-performance metallurgy.
- Purity: 99.7% to 99.9%
- Applications: Aerospace, automotive, heavy machinery
9. Magnetic Iron Powder
Magnetic iron powder is specially processed to enhance its magnetic properties and is used in applications such as inductors, transformers, and magnetic shielding.
- Purity: 99.9% or higher
- Applications: Transformers, inductors, magnetic shielding
10. Spray-Formed Iron Powder
Spray-formed iron powder is created using a rapid solidification process, resulting in a unique microstructure that provides enhanced mechanical properties.
- Purity: 99.8% to 99.9%
- Applications: Tooling, structural parts, high-performance alloys
Applications of High Purity Iron Powder
High purity iron powder is utilized in a wide range of industries due to its exceptional properties. Its applications span from traditional metallurgy to cutting-edge electronics and nanotechnology.
Table: Applications of High Purity Iron Powder
| Application Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Powder Metallurgy | Used to create high-strength, precision parts through sintering and other processes. |
| Electronics | Essential in the manufacture of components like inductors, capacitors, and transformers. |
| Magnetic Materials | Used to produce high-performance magnets for various applications, including motors and sensors. |
| Chemical Synthesis | Serves as a catalyst in chemical reactions and is used in the production of synthetic materials. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Employed in the manufacturing of certain drug formulations due to its high purity. |
| Nanotechnology | Used in advanced materials and coatings, often at the nanoscale level. |
| Battery Manufacturing | Used in the production of high-performance batteries, especially in the cathode and anode materials. |
| Additive Manufacturing | Essential for 3D printing and other additive manufacturing techniques, providing fine, uniform powders. |
| Electromagnetic Shielding | Utilized in creating materials that protect electronic devices from electromagnetic interference. |
| High-Performance Alloys | Added to alloys to improve their mechanical properties, especially in aerospace and automotive applications. |




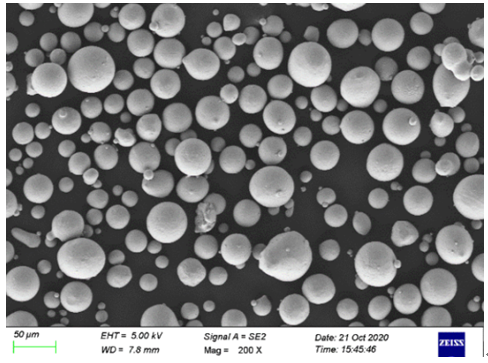

Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards
When selecting high purity iron powder, it’s crucial to understand the specifications, sizes, grades, and standards that apply. These parameters can vary depending on the intended application, and knowing the right choice can significantly impact performance.
Table: Specifications of High Purity Iron Powder
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Purity Levels | 99.5% to 99.9% or higher |
| Particle Size Range | From nanometers (nm) to several hundred micrometers (µm) |
| Grade Standards | ASTM, ISO, JIS, depending on the industry |
| Shapes Available | Spherical, irregular, flake |
| Production Method | Atomization, reduction, electrolytic, carbonyl |
| Density Range | Depends on particle size and shape; typically 2.5-7.8 g/cm³ |
| Magnetic Properties | High saturation magnetization, low coercivity |
| Conductivity | High electrical conductivity due to minimal impurities |
Table: Grades of High Purity Iron Powder
| Grade | Purity Level | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Grade A | 99.9% or higher | Electronics, medical devices, high-performance magnets |
| Grade B | 99.7% to 99.9% | Powder metallurgy, chemical synthesis |
| Grade C | 99.5% to 99.7% | Additive manufacturing, automotive components |
| Grade D | 99.0% to 99.5% | General metallurgy, tooling, structural parts |
Suppliers and Pricing Details of High Purity Iron Powder
The availability and cost of high purity iron powder can vary significantly depending on the supplier, region, and specific product requirements. Below is a guide to some of the leading
suppliers and their pricing details.
Table: Suppliers and Pricing of High Purity Iron Powder
| Supplier | Location | Product Range | Price Range (per kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Höganäs AB | Sweden | Atomized, reduced, electrolytic powders | $50 – $200 |
| JFE Steel Corporation | Japan | High purity iron powder for electronics and metallurgy | $80 – $250 |
| Rio Tinto Metal Powders | Canada | Gas-atomized, water-atomized powders | $60 – $180 |
| BASF | Germany | Carbonyl iron powder, ultra-fine powders | $100 – $300 |
| GKN Powder Metallurgy | USA | High-density, magnetic iron powders | $70 – $220 |
| Mitsui Mining & Smelting | Japan | Spray-formed, ultra-high purity powders | $90 – $280 |
| CNPC Powder Group | China | Reduced, atomized, electrolytic powders | $40 – $150 |
| Kobe Steel | Japan | Specialty grades for advanced applications | $110 – $320 |
| Sandvik Materials Technology | Sweden | High-performance iron powders for aerospace and automotive | $120 – $350 |
| American Elements | USA | Nanoparticles, ultra-fine powders | $200 – $500 |
Advantages and Limitations of High Purity Iron Powder
Like any material, high purity iron powder comes with its own set of advantages and limitations. Understanding these can help in selecting the right type for your application.
Table: Advantages and Limitations of High Purity Iron Powder
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| High Strength | Ideal for applications requiring robust mechanical properties |
| Excellent Magnetic Properties | Perfect for magnetic materials and electromagnetic shielding |
| High Purity | Reduces impurities, enhancing conductivity and performance |
| Versatile Applications | Can be used in a wide range of industries from electronics to pharmaceuticals |
| Customization | Available in various grades, sizes, and shapes to suit specific needs |
| Cost | Higher purity levels can be expensive |
| Production Complexity | Requires advanced production methods, which can limit availability |
| Limited Suppliers | Not as widely available as lower-grade iron powders |
| Oxidation Sensitivity | High purity iron can be more prone to oxidation, requiring careful storage |
Comparing High Purity Iron Powder with Other Metal Powders
How does high purity iron powder stack up against other types of metal powders? Let’s compare it to some commonly used alternatives:
Table: Comparison of High Purity Iron Powder with Other Metal Powders
| Metal Powder | Purity Level | Applications | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Purity Iron Powder | 99.5% to 99.9% or higher | Electronics, metallurgy, chemical synthesis | High strength, excellent magnetic properties, high conductivity | Higher cost, sensitive to oxidation |
| Aluminum Powder | 99.0% to 99.8% | Lightweight alloys, pyrotechnics, coatings | Lightweight, good conductivity, corrosion resistance | Lower strength, less magnetic properties |
| Copper Powder | 99.9% or higher | Conductive inks, electronics, brazing | Excellent conductivity, good thermal properties | Higher cost, prone to oxidation |
| Nickel Powder | 99.0% to 99.9% | High-performance alloys, batteries | Corrosion resistance, good magnetic properties | Expensive, limited availability |
| Stainless Steel Powder | 95% to 99.5% | Tooling, 3D printing, structural parts | Corrosion resistance, high strength | Heavier, less conductive than pure metals |
| Titanium Powder | 99.5% to 99.9% | Aerospace, medical implants, additive manufacturing | High strength-to-weight ratio, biocompatible | Very expensive, difficult to process |
| Cobalt Powder | 99.0% to 99.9% | Superalloys, batteries, magnetic materials | High-temperature resistance, good magnetic properties | Expensive, limited availability |
| Silver Powder | 99.9% or higher | Electronics, medical devices, conductive inks | Best electrical conductivity, antimicrobial properties | Extremely expensive, prone to tarnishing |
| Zinc Powder | 99.0% to 99.5% | Galvanization, batteries, pharmaceuticals | Good corrosion resistance, inexpensive | Lower strength, lower conductivity |
| Magnesium Powder | 99.0% to 99.5% | Lightweight alloys, pyrotechnics, batteries | Very lightweight, good machinability | Highly reactive, flammable |
How to Choose the Right High Purity Iron Powder for Your Application
Choosing the right high purity iron powder for your application can be a complex decision. Here are some key factors to consider:
1. Purity Level
The required purity level depends on your application. For instance, in electronics and pharmaceuticals, where impurities can significantly affect performance, you’ll need iron powder with 99.9% or higher purity. On the other hand, for general metallurgy, a slightly lower purity level might suffice.
2. Particle Size and Shape
The particle size and shape can influence the powder’s flowability, packing density, and surface area. Spherical powders are generally preferred in applications requiring good flowability, like metal injection molding, while irregular particles might be better for chemical synthesis due to their higher surface area.
3. Magnetic Properties
If your application involves magnetic materials, focus on iron powders with high magnetic saturation and low coercivity. Magnetic iron powders and carbonyl iron powders are often the best choices for such applications.
4. Production Method
The production method can affect both the cost and the properties of the iron powder. For example, atomized powders are generally more expensive but offer better flowability and packing density, while reduced powders might be more cost-effective but less uniform.
5. Cost and Availability
Finally, consider your budget and the availability of the specific grade of high purity iron powder. While high-purity, specialty powders offer superior performance, they also come at a higher cost and may have limited suppliers.
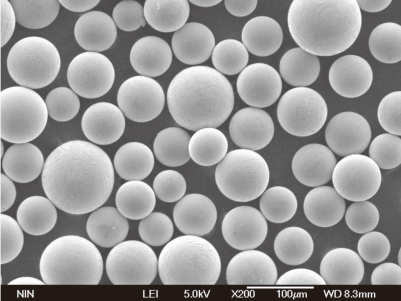
FAQs
What is high purity iron powder?
High purity iron powder is a fine iron powder with a purity level of 99.9% or higher. It is used in various applications requiring specific properties such as high strength, excellent conductivity, or magnetic characteristics.
How is high purity iron powder made?
High purity iron powder can be produced through several methods, including atomization, reduction, electrolysis, and decomposition of iron pentacarbonyl. The choice of method depends on the desired particle size, shape, and purity level.
What are the common applications of high purity iron powder?
High purity iron powder is used in industries such as electronics, powder metallurgy, magnetic materials, chemical synthesis, pharmaceuticals, and additive manufacturing. Its applications range from high-performance magnets to advanced battery materials.
What is the difference between atomized and reduced iron powder?
Atomized iron powder is produced by dispersing molten iron into fine droplets, resulting in spherical particles, while reduced iron powder is made by reducing iron ore in a hydrogen atmosphere, resulting in irregularly shaped particles. Atomized powders are preferred for their flowability, while reduced powders are used for their higher surface area.
How do I choose the right high purity iron powder for my needs?
Consider factors such as the required purity level, particle size and shape, magnetic properties, production method, and cost. Your specific application will determine the best choice of high purity iron powder.
Where can I buy high purity iron powder?
High purity iron powder is available from various suppliers worldwide, including Höganäs AB, JFE Steel Corporation, Rio Tinto Metal Powders, BASF, and GKN Powder Metallurgy. Prices vary depending on the grade, purity level, and supplier.
What are the advantages of using high purity iron powder?
High purity iron powder offers advantages such as high strength, excellent magnetic properties, high conductivity, and versatility in applications. However, it also comes with limitations such as higher cost and sensitivity to oxidation.
Can high purity iron powder be used in 3D printing?
Yes, high purity iron powder is used in additive manufacturing, including 3D printing, where its fine particle size and consistent properties are essential for producing high-quality parts.
What is the price range for high purity iron powder?
The price of high purity iron powder can range from $40 to $500 per kilogram, depending on the purity level, particle size, production method, and supplier.
What are the magnetic properties of high purity iron powder?
High purity iron powder typically exhibits high saturation magnetization and low coercivity, making it suitable for use in magnetic materials and electromagnetic shielding.

