Electrode Induction Melting Inert Gas Atomisation (EIGA) is a fascinating and highly technical process used in the production of high-quality metal powders. This technique is particularly valued for its ability to produce powders with excellent purity, uniform particle size distribution, and specific particle morphologies, which are essential in various advanced manufacturing applications. In this extensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of EIGA, explore specific metal powder models, and provide detailed insights into its properties, applications, and advantages.
Overview of Electrode Induction Melting Inert Gas Atomisation
Electrode Induction Melting Inert Gas Atomisation is a process that involves the melting of a metal electrode using induction heating, followed by atomisation of the molten metal into fine particles using an inert gas. This method is highly regarded for producing powders that are free from contamination, which is crucial in applications such as additive manufacturing, powder metallurgy, and advanced ceramics.
Key Features of EIGA:
- Purity: The process minimizes contamination, ensuring high-purity metal powders.
- Particle Size Control: Allows precise control over particle size distribution.
- Spherical Particles: Produces spherical particles, enhancing flowability and packing density.
- Versatility: Can be used with a wide range of metals and alloys.

Composition and Properties of EIGA Powders
Understanding the composition and properties of EIGA powders is essential for selecting the right material for specific applications. Below, we explore the compositions and properties of various metal powders produced using EIGA.
Types and Compositions of EIGA Powders:
| Metal Powder | Composition | Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) | 90% Titanium, 6% Aluminum, 4% Vanadium | High strength, lightweight, corrosion-resistant |
| Nickel Alloy (Inconel 718) | 50-55% Nickel, 17-21% Chromium, 4.75-5.5% Niobium, plus Iron, Molybdenum, Titanium | High temperature resistance, corrosion-resistant |
| Stainless Steel (316L) | 16-18% Chromium, 10-14% Nickel, 2-3% Molybdenum, balance Iron | Corrosion-resistant, good mechanical properties |
| Cobalt-Chromium Alloy (CoCrMo) | 60-65% Cobalt, 26-30% Chromium, 5-7% Molybdenum | High wear resistance, biocompatible |
| Aluminum Alloy (AlSi10Mg) | 85-90% Aluminum, 9-11% Silicon, 0.2-0.4% Magnesium | Lightweight, good mechanical properties, castable |
| Copper (Cu) | >99% Copper | Excellent electrical and thermal conductivity |
| Tungsten (W) | >99% Tungsten | Very high density, high melting point |
| Magnesium Alloy (AZ91D) | 90-93% Magnesium, 8-9% Aluminum, 0.2-1% Zinc | Lightweight, good castability |
| Tool Steel (H13) | 0.32-0.45% Carbon, 4.75-5.5% Chromium, 1.1-1.75% Molybdenum, balance Iron | High wear resistance, good toughness |
| Titanium Aluminide (TiAl) | 45-48% Titanium, 48-51% Aluminum | Lightweight, high temperature strength |
Characteristics of EIGA Powders:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Particle Morphology | Spherical, enhancing flowability and packing density |
| Purity | High, due to the inert gas atmosphere preventing oxidation and contamination |
| Particle Size Distribution | Narrow and controllable, critical for precise manufacturing processes |
| Density | High tap and bulk densities, beneficial for powder bed fusion techniques |
| Surface Area | Controlled to optimize sintering and melting processes |
Applications of EIGA Powders
EIGA powders find applications across various industries, each leveraging the unique properties of these high-quality metal powders. Below is a detailed table showcasing different applications.
Applications and Uses of EIGA Powders:
| Industry | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, structural components | High strength-to-weight ratio, temperature resistance |
| Medical | Implants, prosthetics, dental applications | Biocompatibility, corrosion resistance |
| Automotive | Engine components, heat exchangers | Lightweight, high performance |
| Electronics | Conductive inks, heat sinks | Excellent electrical conductivity |
| Energy | Fuel cells, battery components | High efficiency, reliability |
| Additive Manufacturing | 3D printing of complex geometries | Design flexibility, reduced material waste |
| Powder Metallurgy | Sintered parts, bearings | High density, uniform microstructure |
| Coatings | Thermal spray coatings, wear-resistant coatings | Enhanced surface properties, durability |




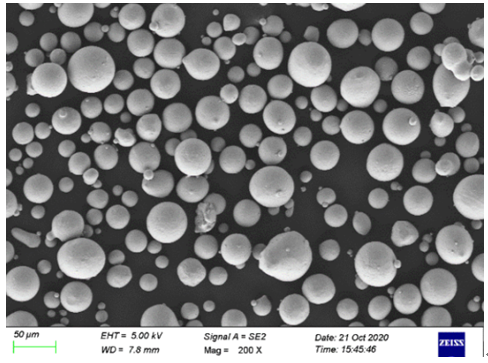
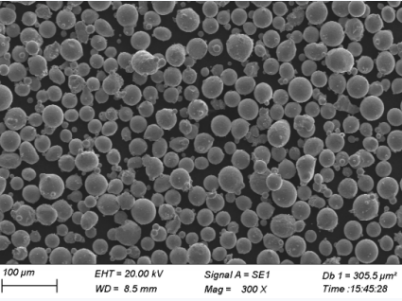
Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards
When selecting EIGA powders for specific applications, it is crucial to understand the specifications, sizes, grades, and standards associated with these materials.
Specifications and Standards for EIGA Powders:
| Metal Powder | Particle Size Range (µm) | Standard Grades | Relevant Standards |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V | 15-45, 45-90 | Grade 5 | ASTM F2924 |
| Inconel 718 | 15-45, 45-106 | AMS 5662 | AMS 5662, ASTM B637 |
| 316L Stainless Steel | 15-45, 45-106 | ASTM F138 | ASTM A276, F138 |
| CoCrMo | 15-45, 45-106 | ASTM F75 | ASTM F75 |
| AlSi10Mg | 15-45, 45-106 | EN AC-43400 | EN 1706 |
| Copper | 15-45, 45-106 | OFHC | ASTM B216 |
| Tungsten | 15-45, 45-106 | W1, W2 | ASTM B777 |
| AZ91D Magnesium | 15-45, 45-106 | ASTM B93/B93M | ASTM B93/B93M |
| H13 Tool Steel | 15-45, 45-106 | ASTM A681 | ASTM A681 |
| Titanium Aluminide | 15-45, 45-106 | Custom | ISO 5832-3 |
Suppliers and Pricing Details
Identifying reputable suppliers and understanding pricing details is vital for sourcing high-quality EIGA powders. Below is a table outlining some key suppliers and indicative pricing.
Suppliers and Pricing of EIGA Powders:
| Supplier | Metal Powder | Price Range (USD/kg) | Contact Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| Praxair Surface Technologies | Ti-6Al-4V | $200 – $300 | Praxair Website |
| Carpenter Additive | Inconel 718 | $150 – $250 | Carpenter Additive Website |
| GKN Hoeganaes | 316L Stainless Steel | $100 – $200 | GKN Hoeganaes Website |
| HC Starck Solutions | CoCrMo | $200 – $300 | HC Starck Solutions Website |
| ECKART America | AlSi10Mg | $50 – $100 | ECKART Website |
| AMETEK Specialty Metal Products | Copper | $50 – $100 | AMETEK SMP Website |
| Advanced Powder & Coatings Ltd. | Tungsten | $300 – $500 | Advanced Powder & Coatings Website |
| Zhongnuo Advanced Material | AZ91D Magnesium | $50 – $100 | Zhongnuo Website |
| Kennametal | H13 Tool Steel | $100 – $200 | Kennametal Website |
| ATI Metals | Titanium Aluminide | $300 – $500 | ATI Metals Website |
Comparing Pros and Cons of EIGA Powders
Evaluating the advantages and limitations of EIGA powders helps in making informed decisions for specific applications.
Advantages and Limitations of EIGA Powders:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| High Purity | EIGA minimizes contamination, producing high-purity powders. |
| Uniform Particle Size | Allows for precise control over particle size distribution. |
| Spherical Particles | Enhances flowability and packing density, crucial for additive manufacturing. |
| Versatile Material Range | Can produce powders from a wide range of metals and alloys. |
| Low Oxygen Content | The inert gas atmosphere reduces oxidation, maintaining material integrity. |
| Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
| Cost | EIGA powders can be more expensive compared to other methods. |
| Complexity | The process requires sophisticated equipment and expertise. |
| Production Volume | May be limited in the volume of powder that can be produced in a single batch. |
| Energy Consumption | High energy requirements due to induction melting. |
Detailed Insights and Examples
Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) vs. Inconel 718:
Titanium Ti-6Al-4V and Inconel 718 are two prominent metal powders used in high-performance applications. Ti-6Al-4V, known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, is extensively used in aerospace and biomedical fields. In contrast, Inconel 718, with its superior high-temperature strength and oxidation resistance, is preferred for aerospace components that operate in extreme environments. When comparing the two, Ti-6Al-4V is lighter and more suitable for weight-sensitive applications, whereas Inconel 718 offers better performance in high-temperature conditions.
Stainless Steel 316L vs. Aluminum Alloy (AlSi10Mg):
Stainless Steel 316L and Aluminum Alloy AlSi10Mg are commonly used in additive manufacturing. 316L is favored for its corrosion resistance and mechanical properties, making it ideal for medical and marine applications. On the other hand, AlSi10Mg, being lightweight and castable, is excellent for automotive and aerospace applications where reducing weight is crucial. The choice between these materials often boils down to the specific application requirements, with 316L offering durability and AlSi10Mg providing weight savings.
Cobalt-Chromium Alloy (CoCrMo) for Medical Applications:
Cobalt-Chromium Alloy (CoCrMo) is widely used in medical applications, particularly in implants and prosthetics, due to its high wear resistance and biocompatibility. The alloy’s ability to withstand the body’s harsh environment without degrading makes it a top choice for long-term implants. Additionally, its mechanical properties are well-suited for load-bearing applications, ensuring reliability and longevity in medical devices.

FAQ
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is Electrode Induction Melting Inert Gas Atomisation? | EIGA is a process that involves melting a metal electrode using induction heating and atomizing the molten metal into fine particles using an inert gas. |
| What metals can be processed using EIGA? | A wide range of metals and alloys, including titanium, nickel, stainless steel, cobalt-chromium, aluminum, copper, tungsten, magnesium, tool steel, and titanium aluminide. |
| What are the benefits of using EIGA powders? | EIGA powders offer high purity, uniform particle size, spherical morphology, and low oxygen content, making them ideal for advanced manufacturing applications. |
| How does EIGA compare to other powder production methods? | EIGA provides superior purity and particle control compared to methods like gas atomisation or water atomisation, though it may be more expensive and complex. |
| What are common applications of EIGA powders? | Applications include aerospace components, medical implants, automotive parts, electronics, energy systems, additive manufacturing, powder metallurgy, and coatings. |
| What factors should be considered when selecting EIGA powders? | Key factors include the specific application requirements, desired material properties, particle size distribution, purity, and cost. |
| Can EIGA powders be used in additive manufacturing? | Yes, EIGA powders are highly suitable for additive manufacturing due to their controlled particle size distribution and high purity, which enhance the quality of printed parts. |
| What is the typical particle size range for EIGA powders? | Particle sizes typically range from 15 to 106 microns, depending on the application and requirements. |
| Are there any limitations to using EIGA powders? | Limitations include higher costs, complexity of the process, limited production volumes, and high energy consumption. |
| Where can I buy EIGA powders? | Reputable suppliers include Praxair Surface Technologies, Carpenter Additive, GKN Hoeganaes, HC Starck Solutions, ECKART America, AMETEK Specialty Metal Products, Advanced Powder & Coatings Ltd., Zhongnuo Advanced Material, Kennametal, and ATI Metals. |
Conclusion
Electrode Induction Melting Inert Gas Atomisation is a cutting-edge technology that plays a pivotal role in the production of high-quality metal powders. Its ability to produce powders with exceptional purity, precise particle size distribution, and spherical morphology makes it indispensable in advanced manufacturing sectors such as aerospace, medical, and additive manufacturing. By understanding the composition, properties, applications, and advantages of EIGA powders, industries can leverage this technology to achieve superior performance and innovation in their products.
Whether you are an engineer, researcher, or manufacturer, this comprehensive guide provides the knowledge and insights needed to navigate the complexities of EIGA powders and make informed decisions for your specific needs.

