Overview of CuSnTi Powder
CuSnTi Powder is a unique copper-tin-titanium alloy powder commonly used in advanced manufacturing industries. Its exceptional properties—like corrosion resistance, durability, and thermal stability—make it ideal for industries from aerospace to electronics. In this article, we’ll break down the specific qualities, applications, and top product models of CuSnTi Powder in detail.
Whether you’re a buyer, an engineer, or just curious about CuSnTi Powder, this guide covers everything you need.
Key Topics Covered
- What is CuSnTi Powder?
- Detailed compositions and properties
- Applications across industries
- Specifications, sizes, and grades
- Pros and cons of various CuSnTi Powder models
- FAQs and expert insights

Composition of CuSnTi Powder
CuSnTi Powder typically contains copper (Cu), tin (Sn), and titanium (Ti) as primary elements. The exact composition varies by model, influencing characteristics like melting point, corrosion resistance, and compatibility in different manufacturing processes. Here, we break down the composition specifics to help you understand what sets each model apart.
| Powder Model | Copper (%) | Tin (%) | Titanium (%) | Additional Elements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | 75 | 20 | 5 | None |
| Model B | 70 | 25 | 5 | Trace amounts of iron |
| Model C | 68 | 30 | 2 | Boron for enhanced strength |
| Model D | 80 | 15 | 5 | Molybdenum for toughness |
| Model E | 65 | 25 | 10 | Nickel for added corrosion resistance |
| Model F | 60 | 30 | 10 | Zinc for increased hardness |
| Model G | 72 | 18 | 10 | None |
| Model H | 78 | 12 | 10 | Chromium for thermal stability |
| Model I | 62 | 28 | 10 | Phosphorus for casting ease |
| Model J | 64 | 26 | 10 | Aluminum for lightweighting |
Characteristics of CuSnTi Powder
The properties of CuSnTi Powder depend heavily on the composition ratios of copper, tin, and titanium, each adding unique qualities. Here’s a breakdown of the core characteristics that make CuSnTi Powder a popular choice for high-demand applications:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| High Corrosion Resistance | CuSnTi Powder resists rust and corrosion, making it perfect for parts exposed to moisture or chemicals. |
| Thermal Conductivity | Excellent thermal conductivity makes CuSnTi ideal for heat-exchanging applications, from cooling electronics to high-heat manufacturing. |
| Strength and Durability | Adding titanium enhances tensile strength and durability, allowing parts to withstand heavy use in tough conditions. |
| Malleability | Offers moderate malleability, allowing it to be shaped or molded, but with better hardness than pure copper powders. |
| Wear Resistance | The alloy’s structure contributes to wear resistance, making it suitable for components that endure friction. |
| Lightweight Composition | Despite its strength, CuSnTi is relatively lightweight compared to other metallic powders with similar durability, improving efficiency in aerospace parts. |
| Oxidation Resistance | Highly resistant to oxidation, maintaining structural integrity even when exposed to air or water for long periods. |
Applications of CuSnTi Powder
CuSnTi Powder finds applications across various industries due to its robust qualities. Here’s a look at where it’s commonly used and why:
| Industry | Application | Why CuSnTi Powder is Ideal |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Jet engine components, structural supports | Lightweight and durable, able to withstand high temperatures and stress. |
| Automotive | Gears, pistons, and bearings | Resists wear and tear, great for moving parts exposed to friction and heat. |
| Electronics | Heat sinks, printed circuit boards | High thermal conductivity aids in heat management, crucial for electronic stability and longevity. |
| Medical Devices | Surgical instruments, implantable components | Biocompatible and corrosion-resistant, making it safe for use in the human body. |
| Marine | Propeller blades, underwater fittings | Exceptional corrosion resistance, essential for parts exposed to saltwater and marine environments. |
| Manufacturing | Mold inserts, cutting tools | High strength and resistance to deformation, ideal for molds and tooling that experience high stress and wear. |
| Construction | Structural reinforcements, fittings | Durable, corrosion-resistant, and cost-effective for structural integrity. |
| Jewelry | Decorative components, high-end watches | Unique coloration and resistance to tarnish, ideal for aesthetic and functional longevity. |
| 3D Printing | Metal additive manufacturing for prototypes | Fine powder grain allows precise layering, perfect for high-definition prototypes and customized parts. |


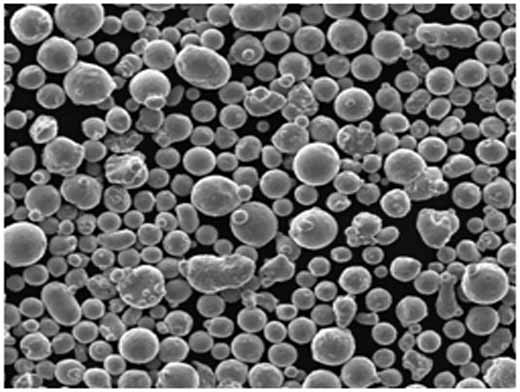



Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards for CuSnTi Powder
Choosing the right CuSnTi Powder often depends on your project specifications, which may require specific grades, particle sizes, or compliance standards.
| Grade | Particle Size Range (µm) | Standard Compliance | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 100 | 10-20 | ASTM B213 | Suitable for fine-detail applications like 3D printing and precision casting. |
| Grade 200 | 20-50 | ISO 3923-1 | Ideal for mid-detail, high-strength needs in automotive parts. |
| Grade 300 | 50-100 | ASTM B962 | Coarser grain, suitable for structural reinforcements and heavy-duty applications. |
| Grade 400 | 10-45 | AMS 4990 | Aerospace-grade powder meeting high durability and thermal resistance requirements. |
| Grade 500 | 30-70 | JIS Z2505 | Versatile grade for general industrial use, offering good balance between strength and malleability. |
| Grade 600 | 70-150 | EN 13942 | Best for larger structural components that don’t require fine precision, such as mold inserts and tooling. |
| Grade 700 | 15-35 | ASTM B329 | Designed for heat sinks and thermal management parts due to superior conductivity. |
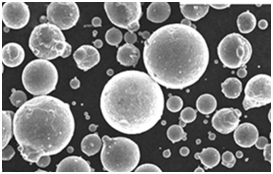
Comparing Pros and Cons of CuSnTi Powder Models
Different models have specific pros and cons based on composition and intended applications. Here’s a comparison:
| Powder Model | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Model A | Cost-effective, good for general use | Lower corrosion resistance compared to others |
| Model B | Excellent strength and wear resistance | Slightly higher cost due to added elements |
| Model C | Great for heat management, balanced durability | Less malleable for intricate designs |
| Model D | Tough and long-lasting, ideal for structural use | Heavier than other powders |
| Model E | High corrosion resistance, lightweight | Higher cost due to nickel addition |
| Model F | High hardness, good for machinery | Lower thermal conductivity |
| Model G | Versatile, suitable for both automotive and aerospace | Less effective in saltwater environments |
FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is CuSnTi Powder primarily used for? | CuSnTi Powder is commonly used in aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical devices for its strength and resistance. |
| How do I choose the right grade of CuSnTi Powder? | Consider the application requirements, such as particle size, durability, and specific industry standards. |
| Is CuSnTi Powder suitable for 3D printing? | Yes, especially in fine grades; it provides good precision and durability for additive manufacturing. |
| How does CuSnTi Powder compare to pure copper? | It offers better corrosion resistance, durability, and thermal stability, though it’s slightly less conductive. |
| What is the cost of CuSnTi Powder? | Prices vary depending on composition and grade, typically from $50 to $150 per |

