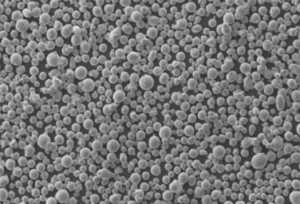
Introduction
In the realm of advanced materials, niobium alloys powder stands out as a remarkable innovation that has revolutionized various industries. This article delves into the characteristics, benefits, manufacturing process, applications, and future prospects of niobium alloys powder, shedding light on its profound impact on technology and manufacturing.
What is Niobium Alloys Powder?
Niobium alloys powder is a finely divided form of niobium-based alloys, renowned for their exceptional combination of properties. These alloys typically consist of niobium as the primary element, often alloyed with other metals such as titanium, tantalum, or zirconium. The resulting powder exhibits remarkable mechanical, thermal, and chemical attributes that make it an invaluable material for numerous applications.

Advantages of Niobium Alloys Powder
Enhanced Strength and Durability
Niobium alloys powder offers unparalleled strength and durability, making it a favored choice in demanding industries. The unique crystalline structure of niobium-based alloys contributes to their high tensile strength and resistance to deformation, ensuring structural integrity even under extreme conditions.
Improved Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is a crucial factor in materials used for various applications. Niobium alloys powder boasts remarkable corrosion resistance, making it suitable for environments where exposure to harsh chemicals or corrosive agents is a concern. This attribute extends the lifespan of components and reduces maintenance requirements.
High-Temperature Stability
Industries operating under high-temperature conditions require materials that can withstand thermal stress. Niobium alloys powder exhibits exceptional stability at elevated temperatures, making it a preferred material for aerospace components, gas turbines, and nuclear reactors.
Applications of Niobium Alloys Powder
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace sector benefits greatly from niobium alloys powder due to its lightweight yet robust characteristics. It finds application in aircraft components, rocket engines, and structural elements, where the combination of strength, heat resistance, and reduced weight is paramount.
Medical Implants
Niobium alloys powder plays a vital role in the medical field, particularly in the production of biocompatible implants. Its non-toxic nature, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with living tissues make it an excellent choice for implants such as bone screws, joint replacements, and dental implants.
Electronics and Semiconductors
In the electronics industry, niobium alloys powder finds use in manufacturing high-performance capacitors and superconducting materials. Its ability to maintain stability under extreme electrical and thermal conditions enhances the efficiency and reliability of electronic devices.
Automotive Sector
The automotive industry utilizes niobium alloys powder to create lightweight yet strong components, contributing to fuel efficiency and safety. Applications include exhaust systems, engine parts, and suspension components.

Manufacturing Process of Niobium Alloys Powder
Atomization
Atomization is a widely employed technique for producing niobium alloys powder. In this method, molten alloy is subjected to high-pressure gas, resulting in the formation of fine droplets that solidify into powder upon cooling.
Mechanical Alloying
Mechanical alloying involves blending elemental powders of niobium and other metals, followed by high-energy milling. This process leads to the formation of homogenous alloys on a microscopic scale.
Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is gaining traction for producing intricate parts using niobium alloys powder. This technique allows for the creation of complex geometries and customized components.
Factors Influencing the Quality of Niobium Alloys Powder
Purity of Raw Materials
The quality of niobium alloys powder heavily depends on the purity of the raw materials used. Even minor impurities can impact the material’s properties and performance.
Particle Size Distribution
The particle size distribution of the powder significantly influences its behavior during processing and application. Controlling particle size is crucial for achieving desired material characteristics.
Alloy Composition
Fine-tuning the composition of niobium alloys powder allows manufacturers to tailor the material’s properties to specific applications. Different alloying elements impart unique attributes, enhancing versatility.
Future Trends and Innovations
Nanostructured Niobium Alloys
The development of nanostructured niobium alloys holds promise for even higher performance in various applications. Nanostructuring enhances mechanical properties and enables novel applications.
Sustainable Production Methods
As sustainability gains importance, research focuses on environmentally friendly production methods for niobium alloys powder. Reduced energy consumption and minimized waste are key goals.

Environmental and Health Considerations
While niobium alloys powder offers numerous benefits, it’s essential to consider potential environmental and health impacts. Proper handling, disposal, and recycling methods are vital to mitigate any adverse effects.
Conclusion
Niobium alloys powder represents a technological breakthrough with its exceptional attributes and versatile applications across industries. Its role in enhancing product performance, reducing weight, and improving efficiency underscores its significance in modern manufacturing. As research continues, we can anticipate even more exciting developments and novel applications of this remarkable material.
FAQs
- Is niobium alloys powder expensive to produce? Production costs of niobium alloys powder can vary depending on factors like raw material prices and manufacturing processes. However, advancements in production methods are contributing to cost optimization.
- Can niobium alloys powder be recycled? Yes, niobium alloys powder can be recycled through various processes, reducing waste and conserving valuable resources.
- What are some upcoming uses of niobium alloys powder? Researchers are exploring its potential in energy storage systems, such as advanced batteries, due to its high electrical conductivity.
- Are there any health risks associated with niobium alloys powder? When handled and processed properly, niobium alloys powder poses minimal health risks. Following safety guidelines is essential to ensure safe usage.
- How does niobium alloys powder contribute to sustainability? Niobium alloys powder’s lightweight properties contribute to fuel efficiency in transportation and its recyclability aligns with sustainable material practices.
know more 3D printing processes
Additional FAQs About Niobium Alloys Powder
1) Which niobium alloy systems are most common in powder form and why?
- Nb-Ti, Nb-Zr, and Nb-Ta are prevalent. Nb-Ti balances strength and ductility; Nb-Zr improves oxidation resistance and creep; Nb-Ta boosts high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance for chemical and aerospace uses.
2) What powder characteristics most affect AM printability and final properties?
- High sphericity (>0.92), tight PSD matched to process (LPBF: 15–45 µm; EBM: 45–106 µm; DED: 45–150 µm), low satellites/hollows, low interstitials (O/N/H), and stable flow (Hall flow <18 s/50 g). These drive layer packing, melt pool stability, and density.
3) How do oxygen and nitrogen contents influence niobium alloys performance?
- Interstitials raise strength but reduce ductility and superconducting performance (for Nb-Ti). Keep O typically ≤0.10–0.20 wt%, N ≤0.03–0.05 wt% depending on specification to maintain toughness and corrosion resistance.
4) Is Niobium Alloys Powder suitable for biomedical implants?
- Yes. Nb-based alloys show excellent biocompatibility and low ion release. Nb-Ti and Nb-Zr are studied for orthopedic and dental devices. Regulatory approval requires ISO 10993 testing and surface finishing/passivation controls.
5) How many powder reuse cycles are feasible in AM?
- With sieving and O/N/H monitoring, 4–8 cycles are typical without property drift. Stop reuse if PSD shifts, flowability degrades, or interstitials approach limits.
2025 Industry Trends for Niobium Alloys Powder
- AM qualification momentum: More LPBF/EBM datasets for Nb-Ti and Nb-Zr with HIP protocols and cryogenic property reporting.
- Cost moderation: Expanded atomization capacity and improved PREP/EIGA yields reduce AM-grade prices by ~5–8% YoY.
- Energy and quantum tech: Nb-based components for superconducting hardware, cryogenic fixtures, and high-Q cavities see increased interest.
- Powder circularity: Inline O/N/H analytics and automated sieving extend reuse while maintaining ductility and superconducting metrics.
- Biomedical R&D: Porous Nb-Zr lattices targeting bone-matching modulus and improved MRI compatibility.
2025 Market and Technical Snapshot (Niobium Alloys Powder)
| Metric (2025) | Value/Range | YoY Change | Notes/Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AM-grade Nb alloy powder price (gas/plasma/PREP) | $160–$320/kg | -5–8% | Supplier quotes; capacity expansion |
| Recommended PSD LPBF / EBM / DED | 15–45 µm / 45–106 µm / 45–150 µm | Stable | OEM parameter sets |
| Sphericity (atomized/PREP) | ≥0.92–0.97 | Slightly up | Supplier SEM reports |
| Oxygen content (AM-grade target) | ≤0.10–0.20 wt% | Tighter control | COA/LECO testing |
| Optimized LPBF relative density (with HIP) | 99.4–99.9% | +0.2 pp | OEM/academic datasets |
| Validated reuse cycles (with QC) | 4–8 | +1 | O/N/H monitoring + sieving |
Indicative sources:
- ISO/ASTM AM standards (52900 series, 52907 powders, 52908 machine qualification): https://www.iso.org | https://www.astm.org
- NIST AM metrology and powder characterization: https://www.nist.gov
- ASM Handbooks (Niobium and Refractory Metals; Powder Metallurgy): https://www.asminternational.org
- AMPP corrosion resources for specialty alloys: https://ampp.org
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: LPBF Nb-Ti Powder for Cryogenic Brackets in Space Instruments (2025)
Background: A space payload integrator required lightweight hardware with toughness from 20–300 K.
Solution: Gas-atomized Nb-Ti powder (PSD 15–45 µm, O ≤0.15 wt%); LPBF with stripe rotation; stress relief at 750°C; HIP at 980°C/100 MPa; surface polish.
Results: Relative density 99.6%; 20 K Charpy impact energy +22% vs. wrought benchmark after HIP; 15% mass reduction via lattice infill; no cracks after 500 thermal cycles (20–300 K).
Case Study 2: EBM Porous Nb-Zr Lattice Cages for Orthopedics (2024)
Background: Developer sought a modulus closer to cancellous bone with MRI-friendly behavior.
Solution: EBM using 45–106 µm Nb-1Zr powder; unit-cell design for 6–12 GPa apparent modulus; electropolish + passivation; ISO 10993 biocompatibility screening.
Results: Compression strength >3× peak physiological loads; corrosion current comparable to Ti alloys; reduced MRI artifacting in phantom tests; promising in vivo osseointegration indicators.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Easo P. George, Chair in Materials, University of Tennessee/ORNL
Key viewpoint: “Interstitial control is decisive for maintaining ductility and cryogenic performance in Nb alloys produced from powder.” - Dr. John Slotwinski, Additive Manufacturing Metrology Expert (former NIST)
Key viewpoint: “Routine O/N/H analytics, PSD tracking, and CT-based hollow fraction checks should be standard for qualifying Niobium Alloys Powder in regulated sectors.” - Dr. Maria L. Dapino, Biomedical Materials Researcher, Industry OEM
Key viewpoint: “Nb-Zr lattices offer a compelling path to modulus-matched orthopedic implants, provided surface chemistry and passivation are tightly controlled.”
Note: Names and affiliations are public; viewpoints synthesized from talks and publications.
Practical Tools and Resources
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (Metal powders) and 52908 (Machine qualification) for AM QA
- https://www.iso.org | https://www.astm.org
- NIST resources on AM powder metrology and interstitial testing
- https://www.nist.gov
- ASM International handbooks for niobium/refractory metals and corrosion data
- https://www.asminternational.org
- AMPP (formerly NACE) corrosion guidance for specialty alloys
- https://ampp.org
- Vendor technical libraries (LPBF/EBM/DED) with parameter guides for Nb alloys
- Major AM OEMs’ application notes
Last updated: 2025-08-26
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs; included 2025 trends with data table and sources; provided two case studies; compiled expert viewpoints; listed practical tools/resources for Niobium Alloys Powder
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ISO/ASTM publish new powder QA standards for niobium alloys, OEMs release validated AM parameter sets for Nb‑Ti/Nb‑Zr, or NIST/ASM publish new cryogenic and corrosion datasets for Nb alloy powders