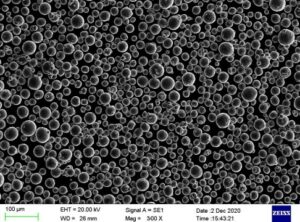
Tungsten powder is a pure elemental powder form of tungsten metal used across industrial applications requiring high density, strength, and heat resistance properties. This guide provides an overview of tungsten powder composition, production methods, applications, tungsten powder supplier, pricing, and comparisons.
Introduction to tungsten powder supplier
Tungsten powder is composed of microscopic particles of relatively pure elemental tungsten metal. Key properties of tungsten making it suitable for powder metallurgy applications are:
- Extremely high density – similar to gold
- Highest melting point of all metals
- Low coefficient of thermal expansion
- High thermal and electrical conductivity
- Resistance to corrosion and acids
- Biocompatibility and non-toxicity
With a density almost 20% higher than lead, tungsten balances performance across strength, conductivity and thermal properties – ideal for use as powder particles.
Tungsten Powder Characteristics
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Composition | 99.9% Pure Tungsten |
| Color | Dark gray with metallic lustre |
| Crystal structure | Cubic |
| Density | 19.3 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 6170°F (3422°C) |
| Mohs hardness | 7-7.5 |
| Thermal conductivity | 163 W/m·K |
| Electrical resistivity | 5.5 μΩ·cm |
These intrinsic material properties enable niche applications for tungsten powder across electronics, alloys, weighting, heating, and more.
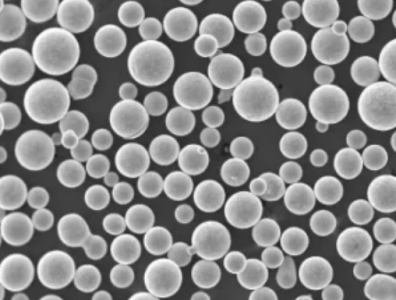
Manufacturing Methods
Tungsten powder is produced from tungsten ore concentrates using advanced metallurgy techniques:
1. Ammonium Paratungstate Processing
- Most common production method
- Involves acid extraction, precipitation, drying, hydrogen reduction
- Creates high purity fine powders
2. Mechanical Milling
- Milling tungsten metal into fine particles
- Tends to produce irregular shapes
- Lower cost but wide size distribution
3. Thermochemical Processing
- Vapor phase conversion of tungsten halides
- Results in very high purity spherical powders
- Small scale specialized production
Manufacturing method determines powder particle size distribution, shape, tap density and surface chemistry – which dictate applicability.
Applications of Tungsten Powder
Unique high density properties of tungsten powder make it suitable for:
Table: Tungsten Powder Applications
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Counterweights | High density balance weights for vibration sensitive equipment |
| Radiation Shielding | Tungsten alloys used as gamma ray shielding material |
| Ballast | Alternative to lead weights in yacht keels for stability |
| Rotating Equipment | Tungsten heavy metal used in gyroscopes and centrifuges |
| Thermal Management | Heat sinks made using tungsten due to high thermal conductivity |
| Carrier Powders | Binder matrix for catalysts requiring chemical resistance |
| Electrical Contacts | Tungsten-silver alloys used in switches and relays |
| 3D Printing Powders | High density tungsten used in additive manufacturing |
Tungsten’s suitability for high temperature thermionic emission also makes it useful for electron emitters in electric welding and vacuum tube equipment as a powder cold-pressed into electrodes.
Specifications
Tungsten powder for industrial and commercial use is categorized by:
Table: Tungsten Powder Specifications
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Purity Grades | 99.9%, 99.95%, 99.99% pure tungsten |
| Particle Size | 0.5 to 150 microns |
| Morphology | Irregular, spherical |
| Tap Density | 2 to 12 g/cm3 |
| Surface Area | 0.5 to 10 m2/g |
| Appearance | Dark gray powder |
| Packaging | 1lb bottles to 55 lb pails |
Other application-specific technical specifications may include thermal expansion coefficients, compressibility, hydrogen content, oxygen analysis, and green strength values.
Where to Buy Tungsten Powder
Tungsten being relatively rare is available from specialized manufacturers and suppliers:
Table: tungsten powder supplier
| Supplier | Location | Product Grades |
|---|---|---|
| Midwest Tungsten Service | USA | Tungsten alloys, pure tungsten |
| Buffalo Tungsten | USA | Powders, rods, wires |
| Tungsten Heavy Powder | China | 99.995% (5N) purity powder |
| Xiamen Tungsten | China | 5N, 5N5, 6N powder |
| Beck Alloys | UK | Elemental and alloyed tungsten |
| HC Starck | Germany | High purity refractory metals |
| Nanjing Tungsten | China | Pure tungsten powder |
| Japan New Metal | Japan | Nano to coarse tungsten powder |
As tungsten mining and refining both require specialized processing, economical availability comes primarily from China followed by Russia, Canada, Bolivia and Portugal. Established manufacturers provide different purity levels suitable for medical, industrial and research applications.
Tungsten Powder Price
Being relatively rare, tungsten powder is more expensive than common metals – priced between $50 to $500 per kilogram based on:
Table: Tungsten Powder Pricing
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Purity | 99.9% costs ~$50/kg; 99.999% costs ~$500/kg |
| Particle Size | Nano powder is pricier than micron sizes |
| Quantity | Bulk orders of 25kg+ enables volume discounts |
| Manufacturing Method | Chemical vs mechanical process |
| Grain Shape | Spherical powder carries a premium |
Exact pricing varies across time and geographies – contact trusted suppliers to request latest quote with shipping charges. Consider quantity discounts above 25 kgs for cost savings on high purity powders.
How to Select Tungsten Powder
Factors guiding tungsten powder selection:
Table: Tungsten Powder Selection Criteria
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Application Requirements | Density needs, operating temperatures, loads, expected lifetime, approvals required |
| Specification Match | Particle size, purity level, tap density, surface area etc |
| Supplier Qualifications | Experience, quality systems and control practices |
| Sampling | Get powder samples to test suitability |
| Total Cost | Compare pricing from shortlisted suppliers including logistics |
| Technical Support | Evaluate supplier design support vs just sales |
| Certifications | Review material test reports (MTRs) for peace of mind |
Work with qualified suppliers to procure your optimal tungsten powder grade cost-effectively based on intended production method and performance criteria.
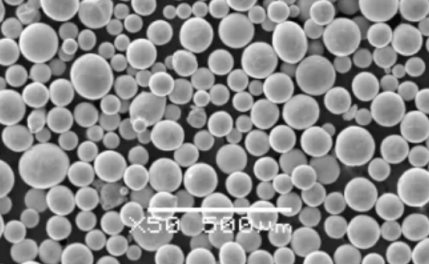
Pros and Cons of Using Tungsten Powder
Table: Advantages and Disadvantages of Tungsten Powder
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Extremely high density | Expensive compared to common metals |
| Highest melting point of metals | Limited global supply and availability |
| Thermal/electrical conductivity | Requires careful handling given high density |
| Alloy flexibility | Considered hazardous shipping material |
| Biocompatible for medical uses | Need for experienced suppliers |
| Enables performance enhancements | Potential for counterfeit products |
For specialty applications needing high density or thermal conductivity, tungsten powder provides significant benefits. Cost and availability concerns require careful management.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is tungsten powder safely handled and stored?
Follow safety datasheets – wear personal protective equipment, avoid inhalation using respirators, handle packages carefully given heavy weight. Store sealed containers properly labeled away from moisture and extremes of temperature in cool, inert environments.
What industries use tungsten powder the most?
Industries taking advantage of tungsten’s special properties include aerospace, radiation shielding, automotive, batteries, and medical plus emerging areas like additive manufacturing/3D printing.
Does tungsten powder require special shipping or export controls?
As tungsten qualifies as a dual-use product, exporting may require licenses. Classified as dangerous goods during shipping, it needs competent handlers aware of density and combustion hazards following applicable regulations.
What substitutes exist for tungsten powder?
Few alternative materials match tungsten’s thermal stability and density. Depleted uranium approaches density but introduces radioactivity concerns. Lead is cheaper for some weighing applications but toxic while lacking strength and temperature performance.
What typical size is tungsten powder used for 3D printing?
Particle size distribution averaging 20 microns works well for powder bed fusion 3D printing processes enabling complex, high density metal part production – used alone or blended with other powders.
Conclusion
Offering extraordinary density paired with temperature resistance, tungsten powder suits special performance requirements despite higher costs. Carefully selecting specifications like particle size and purity along with reputable suppliers enables tapping benefits across electronics, radiation shielding and modern metal additive manufacturing. As an impactful pure element, tungsten powder facilitates pushing application boundaries when engineered creatively.
know more 3D printing processes
Additional FAQs: tungsten powder supplier
1) What certifications should a tungsten powder supplier provide?
- Look for ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environment), and where applicable IATF 16949 (automotive) or ISO 13485 (medical). Material Test Reports (MTRs) with ICP‑OES chemistry, oxygen/hydrogen/nitrogen (LECO) and particle size (laser diffraction) should be standard. Conflict minerals and REACH/RoHS declarations are often required.
2) How do I compare powders from different tungsten powder suppliers?
- Normalize by PSD (D10/D50/D90), morphology (SEM with sphericity/satellites), purity (ppm O, C, N, H), tap/apparent density, flow (Hall/Carney), and lot‑to‑lot Cpk. Request identical sieve cuts and test methods per ASTM B214/B212/B527.
3) What impacts tungsten powder pricing most in 2025?
- APT (ammonium paratungstate) index, energy costs for hydrogen reduction, purity grade (5N vs 3N), PSD fineness (<10 µm premium), and morphology (spherical carries a premium over irregular). Regional logistics and export controls can add surcharges.
4) Can I reuse tungsten powder in AM?
- Yes, with strict controls. Implement sieving, oxygen tracking, moisture control, and blend caps (e.g., ≤30–50% reused with virgin) based on property drift. Characterize O/N/H, PSD tails, and flow each cycle. Follow ISO/ASTM 52907 guidance.
5) What shipping and compliance issues should I expect?
- Tungsten powder may fall under dangerous goods depending on particle size and form; ensure SDS alignment and proper UN classification if applicable. Some jurisdictions require export licenses for high‑purity W powders due to dual‑use controls.
2025 Industry Trends: atomized and reduced tungsten powders
- Supply diversification: More APT‑to‑powder capacity outside China (EU/NA) to improve resilience.
- Spherical W powders for AM: Growth in plasma/thermochemical routes to support collimators, heat sinks, and radiation shielding via LPBF/DED.
- Sustainability: Suppliers issuing Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) and offering take‑back/recycling of off‑spec powder and used builds.
- Digital powder passports: Lot genealogy tying APT source, reduction parameters, O/N/H, PSD, and flow to downstream part quality.
- Cost control: Hydrogen recovery and furnace heat‑recirculation reduce kWh/kg by 5–12% at leading plants.
2025 Snapshot: Tungsten Powder Supplier Benchmarks (Indicative)
| Metric | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 YTD (Aug) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global W powder demand (kt) | ~17.5 | ~18.2 | ~19.0–19.5 | Aerospace, medical, AM lift |
| Avg. irregular W powder price (USD/kg, 99.9%, 10–45 µm) | 70–110 | 72–115 | 75–120 | Tracks APT, energy |
| Avg. spherical W powder price (USD/kg, 99.95%, 15–45 µm) | 180–280 | 190–300 | 200–320 | AM‑grade premium |
| Typical oxygen (ppm) after reduction | 300–800 | 250–700 | 200–600 | Better inert handling |
| Energy intensity (kWh/kg, reduction + classification) | 10–14 | 9–13 | 8–12 | Heat/H2 recovery |
| Lots with digital passports (%) | ~30 | ~45 | ~65 | Driven by aerospace/medical |
Sources:
- ITIA (International Tungsten Industry Association): https://www.itia.info
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (metal powder feedstock), ASTM B777/B214/B212/B527: https://www.astm.org
- ISO 9001/14001 registries; OEM/application notes from major suppliers
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Spherical Tungsten Powder Improves LPBF Shielding Parts (2025)
Background: A medical device firm printing radiation collimators had poor flow and high porosity using irregular W powder.
Solution: Qualified a tungsten powder supplier offering plasma‑spheroidized W (15–45 µm), implemented inert closed transfer, and added digital powder passports with O/N/H and SEM morphology.
Results: Flowability improved 22% (Hall flow), relative density +1.1% (to 99.1%), CT‑flagged porosity −38%, first‑pass yield +14%; material cost +18% but total cost of quality −9%.
Case Study 2: Hydrogen Recovery Cuts Cost for Reduced Tungsten Powders (2024)
Background: An industrial supplier faced margin pressure from energy spikes.
Solution: Installed hydrogen recirculation and furnace heat recovery; optimized reduction dwell and cooling under inert to limit re‑oxidation.
Results: Energy/kilogram −11%; oxygen ppm median 520→370; stable PSD; enabled 3–5% list price reduction on select grades without margin loss.
Expert Opinions
- Dr. Dirk Dubbers, Technical Director, International Tungsten Industry Association (ITIA)
- “Secure APT sourcing and hydrogen efficiency are the two biggest levers tungsten powder suppliers have for price stability in 2025.”
- Dr. Brandon A. Lane, Additive Manufacturing Metrologist, NIST
- “For AM, the morphology and PSD tails of tungsten powder are decisive. When paired with digital passports, porosity hot‑spots become predictable and avoidable.”
- Maria Kovacs, Head of Powder Metallurgy R&D, Sandvik (refractory metals)
- “Spherical tungsten grades are expanding beyond shielding into thermal management, where consistent flow and low oxygen enable reliable LPBF process windows.”
Practical Tools/Resources
- International Tungsten Industry Association (market stats, HSE): https://www.itia.info
- ASTM standards for tungsten and powders: B777 (heavy alloys), B214/B212/B527 (powder tests): https://www.astm.org
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (AM feedstock quality) and 52904 (LPBF metals): https://www.iso.org
- Senvol Database for AM material–machine mapping: https://senvol.com
- LME/Minor Metals trade data for price tracking: https://www.lme.com
- NFPA 484 combustible metal standards for safe handling
Last updated: 2025-08-25
Changelog: Added 5 buyer-focused FAQs; included a 2025 benchmark table with market/pricing metrics; provided two case studies (AM collimators, energy reduction); added expert viewpoints; compiled standards and industry resources
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if APT prices move >15% QoQ, major export controls change, or new AM spherical tungsten grades shift pricing/yield benchmarks