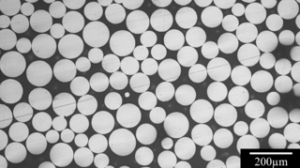
With the rapid advancement of 3D printing technology, 3D printing consumables, especially 3D printing metal powder, are also developing rapidly. This includes the use of titanium powder and titanium alloy powder, titanium aluminum alloy powder, etc., which is particularly notable.
Spherical titanium alloy powder is the most widely used metal powder material in 3D printing. Therefore, this article will focus on several methods of preparing spherical titanium alloy powders and an outlook on future applications of it.
Titanium alloy has low density, high strength, good corrosion resistance, and high melting point, etc. It is one of the most commonly used metals for additive manufacturing technology, and it is widely used as structural parts in the fields of aviation, aerospace, automotive, and biotechnology.
Preparation of Titanium Alloy Powder
We also know that one of the main technologies in 3D printing, Selective Laser Melting (SLM), is suitable for the manufacture of small, precise, and complex parts. This technique needs a narrow particle size of titanium alloy powder and requires a high degree of sphericity, purity, and fluidity of the powder.
We can know that PREP equipment can produce titanium alloy powder with good sphericity, fluidity, and purity to meet the requirements of its usage after comparing several common powder preparation methods, such as Vacuum Inert Gas Atomization (VIGA), Electrode Induction Gas Atomization(EIGA), Plasma Rotating Electrode Process(PREP), Plasma Atomization(PA) and Plasma Spheroidization (PS).
The Plasma Rotating Electrode Process (PREP) is one of the most common methods for the preparation of spherical titanium alloy powders. The principle is to use a titanium alloy bar as a self-consuming electrode and to keep the electrode rotating at high speed while the plasma is used as a heat source to gradually melt the electrode.
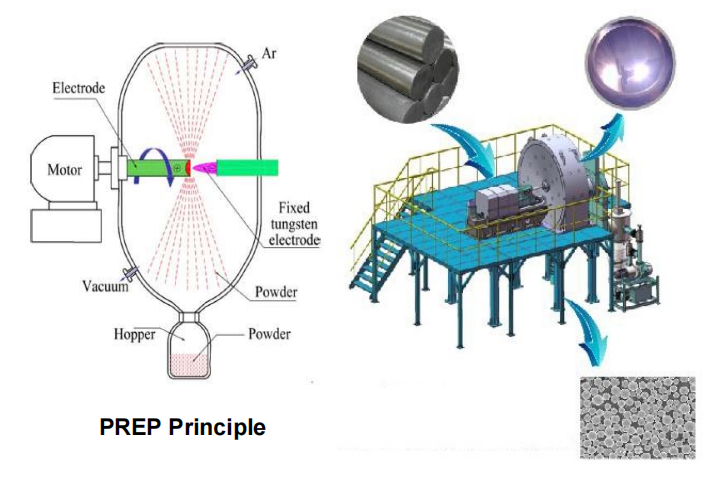
The conventional rotating electrode method (REP) uses a tungsten electrode, which can also be corroded during metal atomization and enter the powder as an impurity component.
In 1985, the Northwest Institute of Non-Ferrous Metals independently designed and developed the first PREP equipment in China.
The preparation process for the PREP they use is that the high-speed rotating electrode (raw material) is melted by the plasma arc under the protection of the high purity inert atmosphere, and the molten metal is thrown out by big centrifugal force to be atomized by the inert atmosphere and condensed into spherical powders when contacting to the internal wall of the cold chamber.
Using this technology and system, we can get high powder sphericity( over 90%), low porosity, and satellite powders. Which is totally meets the requirements of the titanium alloy powder we need.
Application of Titanium Alloy Powder
As mentioned above, titanium alloy powders are used in a wide range of applications, so we will only list some of them here for reference.
Titanium alloy is widely used in the medical field to make joint implants, prostheses, etc. Due to the high machinability of titanium alloys, individual differences can be achieved away from traditional designs, thus improving the adaptability of medical devices. Also the short processing cycle of 3D printed titanium has long-term implications for patients with diseases such as bone tumors.
The high strength, high temperature, and corrosion resistance of titanium and titanium alloys have made them a newcomer to the aerospace sector and have been rapidly adopted in recent years with the development and application of 3D printing technology. In aerospace, titanium and titanium alloys are lighter, stronger, and more ductile than ordinary materials. Its corrosion resistance also makes it increasingly competitive for marine and aircraft applications.
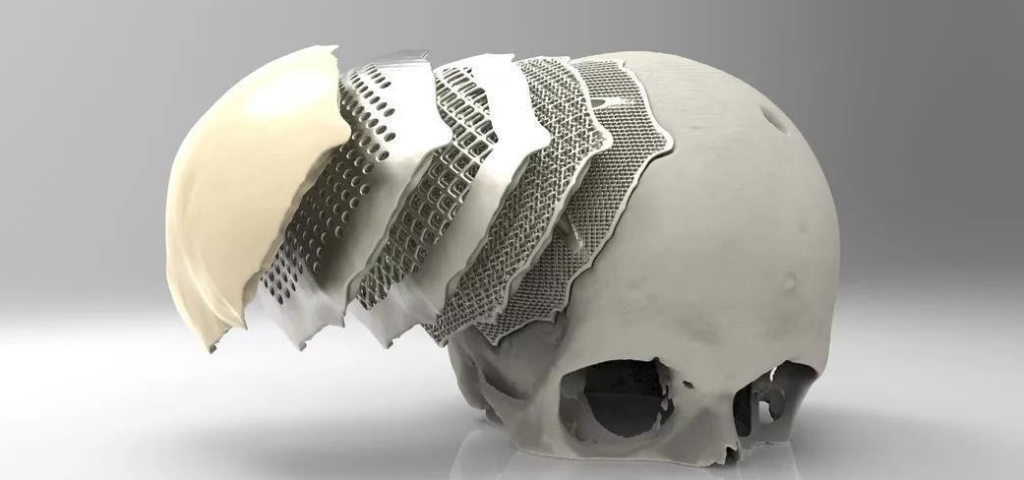
As an important consumable for 3D printing, the application and development of titanium alloys in the aerospace, automotive, and biomedical industries have also driven the development of 3D printing technology.
The Development Prospects of Titanium Alloy Powder
Defined by some as the Fourth Technological Revolution, additive manufacturing is already widely seen by the industry as one of the most cutting-edge and promising technological developments in smart manufacturing, and the development of metallic materials as printing consumables has grown rapidly in response.
According to consultancy SmarTech, the global market for additive manufacturing of metal powders is forecast to reach US$11 billion by 2024.
Titanium and titanium alloys are widely used in aerospace, automotive, biomedical, and other fields due to their excellent strength and toughness, corrosion resistance, low density, and biocompatibility, and the market demand is very promising.
The application and development of plasma technology provide technical support for the preparation of titanium alloy powder.
Although the plasma rotating electrode process is limited by factors such as electrode speed and the coarse particle size of the powder obtained, some research institutes of powder-making equipment are working to solve this problem.
With the development and promotion of plasma rotating equipment, the cost of titanium and titanium alloy powder in the field of 3D printing will be gradually reduced, and will also promote the wide application of metal powder in the field of additive manufacturing.
We have reason to believe that 3D printing will change our lives in many more areas in the future, and the preparation and development of titanium alloy powder will profoundly influence this process.
Additional FAQs: Titanium Alloy Powder and 3D Printing
1) Which titanium alloy powder grades are most used for AM and why?
- Ti6Al4V (Grade 5/23 ELI) dominates due to strength-to-weight, weldability, and biocompatibility. Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-6Mo and Ti-5553 appear in aerospace for higher temperature or strength; CP-Ti (Grade 2) is used for corrosion resistance and formability.
2) What particle size and sphericity are optimal for common AM processes?
- LPBF: 15–45 µm, high sphericity (>90%) for flowability and packing.
- EBM: 45–105 µm to suit elevated preheats and larger melt pools.
- DED: 50–150 µm with consistent flow. PREP/EIGA/PA routes yield excellent sphericity and low satellites.
3) How do oxygen and nitrogen contents affect titanium alloy powder performance?
- Interstitials (O, N) raise strength but reduce ductility and fatigue life. AM-grade Ti6Al4V ELI often targets O ≤ 0.13 wt% and N ≤ 0.05 wt%. Tight humidity control limits O pickup during storage/reuse.
4) PREP vs. VIGA/EIGA/PA: when to choose each for titanium alloy powder?
- PREP: clean, high-sphericity powder with very low inclusions—excellent for medical/aerospace; typically narrower PSD, higher cost.
- VIGA/EIGA: scalable gas atomization; EIGA avoids electrode/contact contamination.
- PA/PS: very spherical, fine PSD; favored for LPBF where low satellites and flow are critical.
5) What post-processing is typical for AM titanium parts?
- Stress relief, HIP for defect closure and isotropy, machining, surface finishing (grit blasting, chemical milling/electropolish), and tailored heat treatments to tune alpha/beta microstructure. For implants: cleaning, passivation, and validation per medical QMS.
2025 Industry Trends: Titanium Alloy Powder
- Medical scale-up: More lattice implants in Grade 23 with validated powder genealogy and in-line O/N/H monitoring.
- Aerospace productivity: Multi-laser LPBF and software-driven scan strategies cut cycle times 10–20% for Ti6Al4V brackets and ducts.
- Feedstock sustainability: Closed-loop recycling of oversize/unused powder with certified impurity limits; EPDs requested by OEMs.
- Process convergence: PREP and EIGA powders increasingly co-qualified as suppliers demonstrate consistent PSD and interstitial control.
- Design maturation: Functionally graded lattices and thin-wall heat exchangers push demand for tighter PSD and low-satellite content.
2025 Titanium Alloy Powder Snapshot (Indicative)
| Metric | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 YTD (Aug) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global titanium AM powder demand (kt) | ~10.4 | ~11.2 | ~12.1 | Driven by aerospace + medical |
| AM-grade Ti6Al4V price (USD/kg) | 180–260 | 170–240 | 160–230 | Scale, reuse, competition |
| Typical O spec (Grade 23, wt%) | ≤0.13 | ≤0.12 | ≤0.11 | Tighter interstitial control |
| LPBF average build-rate gain vs. 2023 | — | +8–12% | +10–20% | Multi-laser and scan tuning |
| Share of PREP/EIGA in medical Ti powders (%) | ~46 | ~50 | ~54 | Inclusion control emphasis |
| Reused powder share in AM builds (%) | 30–40 | 35–45 | 40–50 | With genealogy + O/N/H limits |
Sources:
- ASTM/ISO AM standards: https://www.astm.org, https://www.iso.org
- FDA device databases and AM guidance: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices
- MPIF and industry trackers (Context/Wohlers-type reports)
- Supplier technical notes (AP&C/GE Additive, EOS, Höganäs, Carpenter Additive)
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: High-Fatigue Ti6Al4V ELI Lattice Implants via LPBF (2025)
Background: A medical OEM needed higher fatigue performance and osseointegration for acetabular cups.
Solution: Used ELI powder (D50 ~30 µm, O=0.10 wt%) from EIGA route; gradient lattice (60–80% porosity), contour remelts, HIP, and surface roughening (Ra 20–35 µm) with validated cleaning.
Results: 25–30% increase in high-cycle fatigue life; early osseointegration improved in pilot cohort; powder reuse extended to 10 cycles with O ≤ 0.12 wt%.
Case Study 2: Thin-Wall Ti6Al4V Heat Exchangers with PREP Powder (2024)
Background: An aerospace supplier targeted compact, leak-tight exchangers for bleed-air cooling.
Solution: PREP Ti6Al4V powder (15–45 µm, high sphericity) with adaptive hatch/contour and 200°C plate preheat; selective HIP for core; chemical milling to uniformize walls.
Results: Helium leak ≤1×10^-9 mbar·L/s, density ≥99.7% in HIPed zones; mass reduced 18% vs. brazed assembly; build time -12% using optimized scan order.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Amy J. Clarke, Professor of Metallurgy, Colorado School of Mines
- “Powder PSD stability and interstitial control across reuse cycles are as critical to fatigue scatter as the post-build HIP for Ti6Al4V.”
- Dr. Martin Wegener, Head of Materials and Processes, EOS GmbH
- “For titanium alloy powder, scan strategy and preheat management now rival hardware in achieving density and consistent surface quality on thin walls.”
- Dr. Dirk N. Schwab, Head of R&D, Plansee High Performance Materials
- “PREP and EIGA powders can both meet medical/aerospace needs when oxygen and inclusions are tightly controlled—supplier genealogy is decisive.”
Practical Tools and Resources
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (AM feedstock requirements), ISO/ASTM 52904 (LPBF of metals): https://www.iso.org
- ASTM F3001 (Ti-6Al-4V ELI AM), ASTM F2924 (PBF Ti-6Al-4V), ASTM F3302 (AM material specs): https://www.astm.org
- FDA Technical Considerations for Additive Manufactured Medical Devices: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices
- NIST AM-Bench (datasets for melt pool/porosity studies): https://www.nist.gov/ambench
- Senvol Database for machine–material mapping: https://senvol.com
- OEM application notes: GE Additive/AP&C, EOS, SLM Solutions, Renishaw
- OSHA/NIOSH combustible dust and metal powder handling: https://www.osha.gov, https://www.cdc.gov/niosh
Last updated: 2025-08-25
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs; inserted a 2025 trends snapshot with metrics table and sources; provided two recent case studies; included expert viewpoints; curated standards and resource links
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ASTM/ISO/FDA guidance updates, major OEM qualifications change reuse limits, or market demand shifts >10% in aerospace/medical segments