Study on laser cladding of nickel-based powder coating
Introduction
Laser cladding is the use of laser technology to coat the surface of the substrate to obtain the required properties. The alloy system of laser cladding mainly includes iron-based alloy, nickel-based alloy, cobalt-based alloy and cermet. Laser cladding of iron-based alloy powder is suitable for parts that require to be partiallyworn andeasy to deform. The substrate of iron-based alloy coating is mostly cast iron and low carbon steel. Nickel-based alloy coatings are suitable for components requiring partial wear resistance, heat corrosion resistance and thermal fatigue resistance, and the required laser power density is slightly higher than that of cladding iron-based alloys. Cobalt-based alloy coatings are suitable for parts that require wear, corrosion and thermal fatigue resistance. Ceramic coating has high strength at high temperature, good thermal stability, high chemical stability, and a wide range of matrix materials. In this paper, the self-fusible alloy powder materials based on nickel used in laser cladding are discussed.

Materials and methods
The nickel-based self-fusion alloy powder used in this experiment was prepared and smelted by gas atomizing. The factors to be considered in powder composition design and smelting raw material formulation design mainly include:both the performance of powder and laser cladding process, the powder should have a low melting point and oxygen content. In order to avoid coating cracking, the cladding layer and the substrate should be matched as much as possible, that is, the thermal expansion coefficient of the coating and the substrate should be as close as possible. The wettability and reaction of the powder should be good.
Based on the above factors, through repeated material composition design and spray welding process performance test, the following nickel based self-fusible alloy powder BNi-3 (AMS 4778) with particle size 45-105um is selected as the laser cladding material (mass fraction %), its chemical composition showed in Table 1. The base material for laser cladding is medium carbon steel. And the thickness of the cladding layer is 0.6mm.
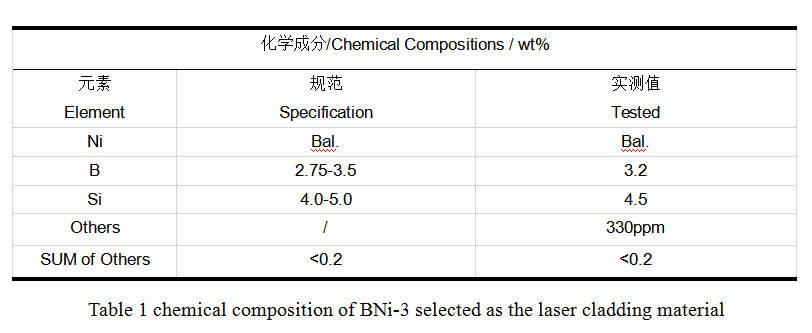
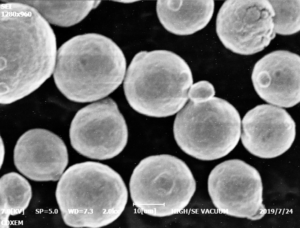
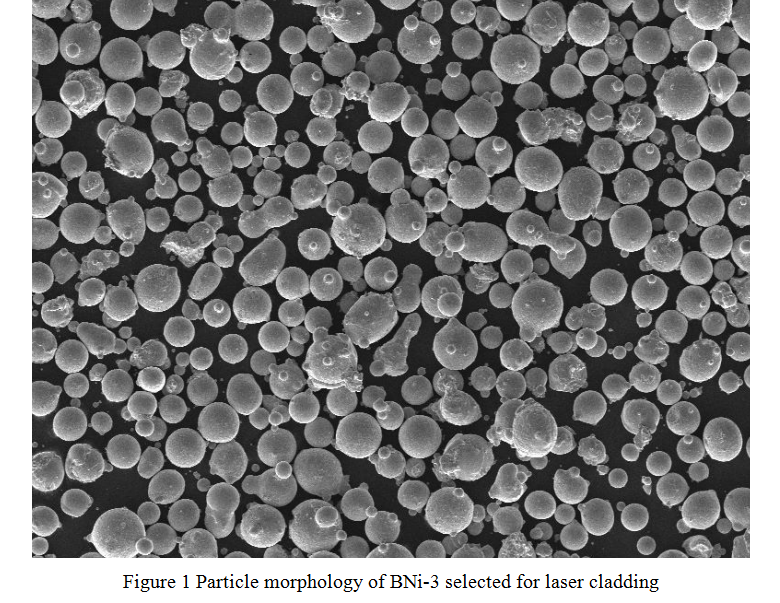
Figure 1 shows the particle morphology of BNi-3 selected as the laser cladding material. It can be seen that the powder particles are spherical. The spherical powder makes the powder have good flowability, so that the powder can reach the surface of the workpiece evenly and smoothly from the powder feeder without blocking the powder nozzle. If the powder shape is complex, the flowability is poor, easy to cause the powder pulsation transport. In addition, if the surface area of the powder increases, the powder will be oxidized when it is heated at high temperature, so the quality of the cladding layer will be affected.
The process test shows that nickel makes the powder have good cladding process performance, and can improve the high temperature performance and crack resistance of the powder. The silicon in the alloy increases the hardness of the coating.Silicon and boron can make the alloy powder self-fusible. In the self-fusible alloy powder, boron and silicon can form slag by themselves, which has self-protection effect. The analysis shows that Ni2B and Ni3B with low melting point are formed from boron and nickel, which reduces the melting point of the alloy and improves the process performance of the powder. However, if the boron content in the alloy is too high, there will be more boron compounds and brittle silicate oxide compounds in the grain boundary, so that the plasticity and toughness of the coating will be reduced, the brittleness will be increased, and the cladding layer will be prone to cracks, so the boron content should be controlled within the appropriate range.
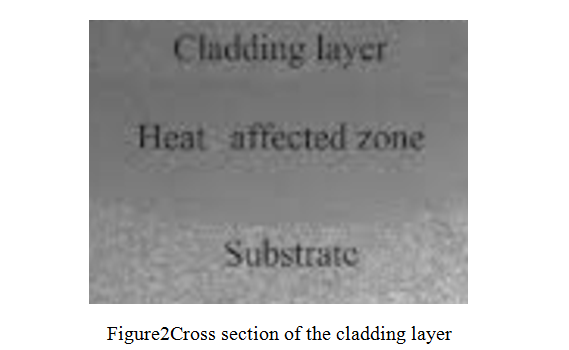
Figure2 shows the cross section of the cladding layer. From the surface layer to the core, the cladding layer zone, heat affected zone and matrix are successively. The cladding layer zone is a very narrow bright zone, which is narrower than the metallurgical bonding zone obtained by thermal spraying, surfacing welding and other methods. The heat affected zone is equivalent to heat treatment due to heat conduction. With the increase of the distance from cladding layer zone, the heating temperature decreases continuously, so from the phase transition zone, part of the phase transition zone, and finally to the original structure of the matrix.
In this project, the wear resistance of the sample coated with this powder was compared with the AISI 52100 standard test block with 62 HRC in the testing conditions of domestic MM-200 wear testing machine, at speed 380 r/min, dry friction, time 1.5 h. The wear resistance is determined by measuring the weight loss of the samples after wear. The results showedthe wear resistance of the laser cladding surface strengthening layer of the nickel-based BNi-3 powder is better than that of AISI 52100, so the service life of the wear-resistant parts will be significantly improved.