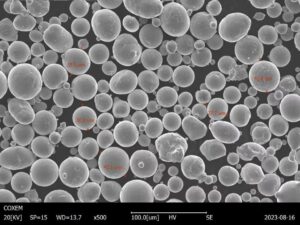
Overview of nickel molybdenum powder
Nickel molybdenum powder is a metal alloy powder composed of nickel and molybdenum. It offers a unique combination of properties including high strength, corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures.
Some key details about nickel molybdenum powder:
- Composition – Typically contains 60-70% nickel and 30-40% molybdenum by weight. Specific ratios can be customized.
- Production Method – Usually manufactured by prealloying and atomizing nickel and molybdenum to create a fine homogeneous powder.
- Particle Size – Ranges from 10-150 microns depending on application. Finer powders provide more uniform properties.
- Shape – Spherical powder particles enable higher packing density and smooth flow. Irregular shapes are also available.
- Common Trade Names – Nickel moly powder, NiMo powder, 60NiMo, 65NiMo
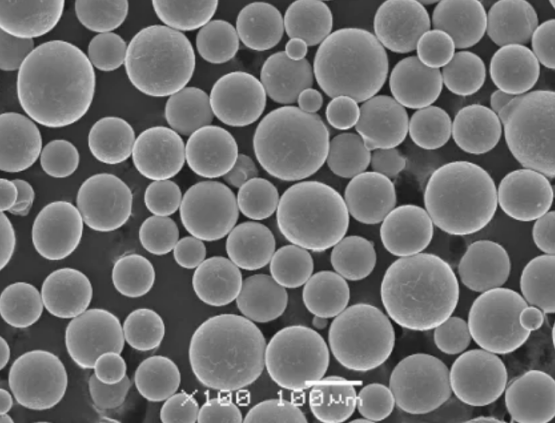

Nickel Molybdenum Powder Types
| Type | Composition | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Nickel molybdenum prealloy powder | 60-70% Ni, 30-40% Mo | Uniform composition, consistent properties, good performance |
| Custom nickel molybdenum ratios | 50/50 Ni/Mo to 90/10 Ni/Mo | Tailored to specific application needs |
| Nanocrystalline nickel molybdenum powder | 60-70% Ni, 30-40% Mo, <100 nm grain size | Very high strength,homogeneous microstructure |
Nickel Molybdenum Powder Properties
| Property | Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Composition | 60-70% Ni, 30-40% Mo |
| Density | 8.0-9.5 g/cc |
| Melting Point | 1315-1400°C (2400-2550°F) |
| Strength | High, 700-1300 MPa |
| Ductility | Moderate, 5-15% elongation |
| Hardness | 250-450 HV |
| Oxidation Resistance | Good up to 1000°C in air |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, resistant to acids |
| Electrical Resistivity | ~138 μΩ.cm |
| Thermal Conductivity | 10-12.5 W/m.K |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 12-14 x 10ˉ6/°C |
Nickel Molybdenum Powder Applications
| Industry | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, engine components | High strength at temperature, oxidation resistance |
| Oil & Gas | Downhole tools, valves, pumps | Strength, wear and corrosion resistance |
| Automotive | Gears, drive shafts | Fatigue and wear resistance |
| 3D Printing | Printed metal parts | High performance materials |
| Electronics | Conductive thick films | Electrical properties, stability |
Nickel Molybdenum Powder Specifications
| Parameter | Range |
|---|---|
| Nickel Content | 60-70 wt% |
| Molybdenum Content | 30-40 wt% |
| Particle Size | 10-150 μm |
| Apparent Density | 2.5-4.5 g/cc |
| Tap Density | 4-6 g/cc |
| Flow Rate | 25-35 s/50g |
| Oxygen Content | <0.5 wt% |
| Carbon Content | <0.1 wt% |
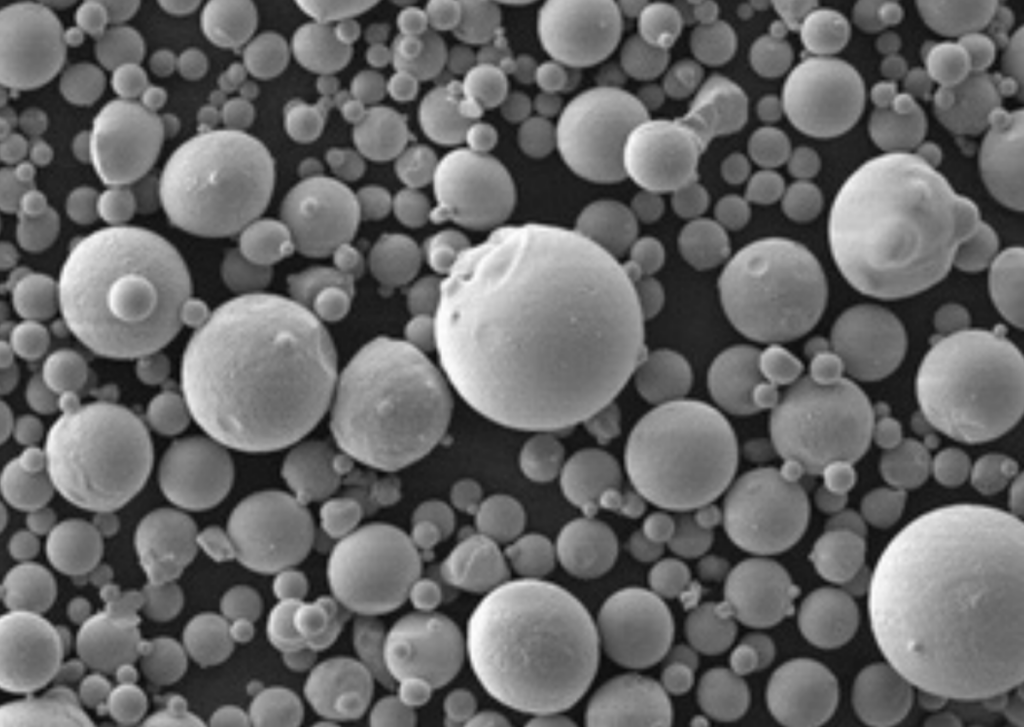
Compare the advantages and limitations of nickel molybdenum powder:
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| High strength at elevated temperatures | More expensive than nickel powder |
| Excellent corrosion resistance | Lower ductility than nickel |
| High hardness and wear resistance | Heavier than titanium alloys |
| Oxidation resistant up to 1000°C | Not as conductive as pure nickel |
| Customizable alloy ratios | Refractory metal powders have higher melting points |
Where to Buy Nickel Molybdenum Powder
| Supplier | Description | Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| American Elements | Pure prealloy powder, custom particle sizes | $50-200/lb |
| Stanford Materials Corp | Prefab and blended NiMo powder | $75-250/kg |
| American Metal & Alloys | Broad selection of NiMo ratios | $100-350/kg |
| The Metal Powder Company | Spherical & irregular NiMo powders | £60-180/kg |
FAQs
What is nickel molybdenum powder used for?
Nickel molybdenum powder has high strength at elevated temperatures up to 1000°C. It resists corrosion and oxidation. Key uses include aerospace components like turbine blades, automotive gears and shafts, oil & gas downhole tools, and 3D printing metal parts across industries.
Is nickel molybdenum powder conductive?
Yes, nickel molybdenum powder has good electrical conductivity thanks to its high nickel content, around 138 μΩ.cm. This makes it useful for conductive thick film applications.
What is the composition of nickel molybdenum?
Typical composition is 60-70% nickel and 30-40% molybdenum by weight. Exact ratios can be customized according to application requirements.
What is the difference between nickel molybdenum and inconel?
Inconel is a family of nickel-chromium-based superalloys. Nickel molybdenum alloys rely on molybdenum instead of chromium to achieve high strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance.
What alloy is stronger than nickel molybdenum?
Refractory metal alloys like tungsten or rhenium have higher melting points than nickel molybdenum. Tungsten carbide cobalt powders offer extreme hardness and wear resistance. However, nickel molybdenum provides the best combination of elevated temperature strength, ductility, and oxidation resistance.
know more 3D printing processes
Additional FAQs About Nickel Molybdenum Powder
1) What PSD and morphology are recommended for additive manufacturing?
- For LPBF, use spherical Nickel Molybdenum Powder with PSD 15–45 µm, sphericity ≥0.92, satellites <5%. For DED, 45–150 µm with tight sieving and low hollow fraction verified by CT.
2) How does Ni:Mo ratio affect properties?
- Higher Mo (35–40 wt%) increases solid-solution strengthening and acid corrosion resistance (reduces pitting/crevice attack) but can reduce ductility and raise flow stress during processing. Higher Ni improves ductility and thermal conductivity.
3) What environments benefit most from Ni–Mo alloys?
- Reducing, chloride- and acid-rich media (HCl, H2SO4) and sour service (H2S/CO2) where Mo improves resistance to localized corrosion and stress corrosion cracking relative to Ni-only or Ni–Cr systems.
4) Which atomization gas is preferred and why?
- Argon is generally preferred to minimize nitrogen pickup and unwanted nitrides; nitrogen can be acceptable for some Ni–Mo grades if N is controlled and does not embrittle the alloy. Target O ≤0.05 wt% and N per spec.
5) What post-processing improves performance of AM parts made with Ni–Mo powder?
- HIP to close porosity, followed by solution treatment/ageing per grade; precision machining plus corrosion passivation/electropolishing for flow-critical or corrosive-service components.
2025 Industry Trends for Nickel Molybdenum Powder
- Energy sector pull-through: Upstream and chemical processing investments drive demand for Ni–Mo powders for corrosion-critical valves, pumps, and downhole tools.
- AM qualification momentum: More vendors publish LPBF/DED material cards and heat-treatment windows for Ni–Mo compositions, including HIP’d property data.
- Cleaner powders: Expanded EIGA/PA capacity lowers O/N/H levels and tightens satellite/hollow control, improving fatigue and corrosion outcomes.
- Cost stabilization: Mo price volatility moderated in 2025; long-term contracts reduce powder price swings for Ni–Mo prealloys.
- Sustainability: Increased revert usage with O/N/H monitoring and documented powder-reuse cycles without compromising corrosion performance.
2025 Market and Technical Snapshot (Nickel Molybdenum Powder)
| Metric (2025) | Typical Value/Range | YoY Change | Notes/Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AM-grade Ni–Mo powder price | $70–$160/kg | -2–6% | Supplier quotes; moderated Mo pricing |
| Recommended PSD (LPBF / DED) | 15–45 µm / 45–150 µm | Stable | OEM parameter guides |
| Sphericity (SEM/image analysis) | ≥0.92–0.97 | Slightly up | Supplier CoAs |
| Oxygen content (AM-grade) | ≤0.03–0.05 wt% | Down | EIGA/PA adoption |
| Typical LPBF density after HIP | 99.7–99.95% | +0.1–0.2 pp | OEM/academic datasets |
| Validated reuse cycles (with QC) | 6–8 cycles | Stable | O/N/H tracking + sieving |
Indicative sources:
- ISO/ASTM AM standards (52900 series; 52907 powders; 52908 machine qualification): https://www.iso.org | https://www.astm.org
- NIST AM Bench and powder metrology: https://www.nist.gov
- ASM International Handbooks (Nickel Alloys; Corrosion; AM materials): https://www.asminternational.org
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: LPBF Ni–Mo Impellers for Acid Transfer Pumps (2025)
Background: A chemical processor needed corrosion‑resistant impellers with internal channels for HCl service.
Solution: Argon gas‑atomized Ni–Mo powder (65Ni–35Mo), PSD 15–45 µm, sphericity ≥0.95; 280°C plate heating; island scan with contour-first; HIP + solution treat; electropolish of flow paths.
Results: Density 99.9% post‑HIP; CT showed zero through‑wall porosity; corrosion rate in 10% HCl at 60°C reduced by 35% vs. cast Ni alloy baseline; pump efficiency +4.2%.
Case Study 2: DED Repair of Ni–Mo Valve Seats in Sour Gas (2024)
Background: Oil & gas operator sought on‑site repair with high sour‑service resistance.
Solution: DED using 45–125 µm Ni–Mo powder with controlled O ≤0.04 wt%; preheat and interpass temperature control; post‑weld HIP surrogate (high‑pressure heat treat) + finish machining.
Results: Hardness 320–360 HV; no sulfide stress cracking in NACE TM0177 testing; service life projected +25% vs. prior weld overlay.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Tresa Pollock, Distinguished Professor of Materials, UC Santa Barbara
Key viewpoint: “Powder cleanliness and morphology—especially low hollow and satellite fractions—are decisive for fatigue and corrosion reliability in Ni–Mo AM components.” - Dr. John R. Scully, Charles Henderson Professor of Materials Science, University of Virginia
Key viewpoint: “Molybdenum’s role in stabilizing passive films under reducing acids makes Ni–Mo alloys uniquely suited to aggressive chloride environments.” - Dr. John Slotwinski, Additive Manufacturing Metrology Expert (former NIST)
Key viewpoint: “Inline O/N/H trending and CT quantification of defects are now standard for qualifying Ni–Mo powder lots for aerospace and chemical service.”
Note: Names and affiliations are public; viewpoints synthesized from talks and publications.
Practical Tools and Resources
- Standards and corrosion guidance
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (Metal powders) and 52908 (Machine qualification): https://www.iso.org | https://www.astm.org
- NACE/AMPP standards for sour service corrosion testing: https://www.ampp.org
- Handbooks and data
- ASM Handbooks (Nickel and High‑Temperature Alloys; Corrosion; AM materials): https://www.asminternational.org
- Metrology and QC
- Interstitials: LECO O/N/H analyzers
- PSD/shape: Malvern Mastersizer, SEM image analysis
- CT for hollow/satellite fraction: industrial CT solutions
- Electrochemical test methods for corrosion rate and pitting potential
Last updated: 2025-08-26
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs; introduced 2025 trends with data table and sources; provided two recent Ni–Mo case studies; compiled expert viewpoints; listed practical tools/resources for Nickel Molybdenum Powder
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ISO/ASTM or AMPP publish updated powder/corrosion standards, major OEMs release validated Ni–Mo AM property cards, or new datasets on powder cleanliness–corrosion correlations become available