gas atomized metal powder has emerged as a preferred production method for spherical alloy powders with controlled attributes ideal for additive manufacturing, powder injection molding, and other leading edge applications. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of compositions, properties, manufacturing processes, key suppliers, and comparative advantages of gas atomized powders versus alternatives like water atomized materials.
Alloy Chemistries for gas atomized metal powder
Gas atomization can process almost any alloy into powder form including:
Nickel superalloys with high strength from solid solution strengthening by refractory metals like tantalum, tungsten, molybdenum etc. Used extensively in aerospace components.
Cobalt superalloys with excellent heat and wear resistance. Biocompatible grades used in dental implants and medical devices.
Tool steel alloys like H13 enhanced with vanadium, molybdenum, and tungsten for hardness retention at high temperatures. Essential for metal forming tools.
Stainless steel powders including 304, 316, and 17-4 precipitation hardening grades for combination of corrosion resistance and mechanical performance.
Copper alloys such as beryllium copper or chromium zirconium copper widely formulated into spheres for thermal management applications exploiting thermal conductivity.
Aluminum alloys like 2024, 6061, and 7075 are economic options for light weight structural components fabricated through powder bed fusion or metal injection molding.
Exotic alloys including tungsten heavy metals, bulk metallic glasses, and precious metals like gold, platinum benefit from gas atomization’s rapid quenching rates to freeze in metastable nonequilibrium phases unique to powder.
Reactive materials like titanium, tantalum with high affinity for oxygen and nitrogen can be gas atomized under vacuum using high purity inert gases preventing contamination.
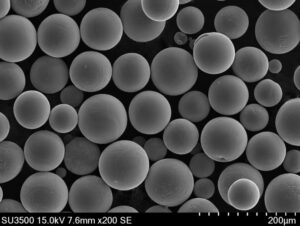
Characteristics of Gas Atomized Metal Powders
| Attribute | Typical Values | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Particle shape | Mostly spherical | Enhances powder flow and packing density |
| Satellite fraction | <5% | Lower is better for powder bed printing |
| Size range | 10 to 150 microns | Tailorable to application method |
| Distribution | Gaussian | Consistent from batch to batch |
| Oxygen ppm | <500 ppm | Prevents oxide inclusions in final part |
| Surface oxides | Thin passivated layer | Maintains powder recyclability |
The combination of cleanliness, spherical morphology and optimized particle size distribution allows gas atomized powders to offer superior performance across most powder metallurgy and additive techniques relative to alternatives.

How Gas Atomization Powder Production Works
Gas atomized powders start from feedstock ingots of wrought alloy compositions. The metal is induction melted under vacuum or inert atmosphere and then ejected as a thin stream into high velocity jets of argon or nitrogen gas. The power of supersonic gas impacting molten metal breaks the stream into fine droplets that solidify rapidly during flight below the melting point. The cooling rate exceeds 106 °C per second quenching the alloy into solid powder particles accumulating at collection hoppers underneath the atomization tower. By adjusting gas pressure, flow parameters and nozzle geometries, particle size distribution can be tuned for different applications. The inert gas prevents oxidation keeping contamination low. After classification to remove any oversize particles, the powder is packaged under vacuum ready for use.
Industry Applications for Gas Atomized Metal Powders
| Industry | Uses and Components | Critical Attributes |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, airfoils | High strength, creep resistance |
| Medical | Orthopedic implants, devices | Biocompatibility, corrosion resistance |
| Automotive | Connecting rods, gears | Wear resistance, fatigue life |
| Additive manufacturing | 3D printed parts for form and fit prototyping, digital inventory, functional testing | Spherical morphology, flowability |
| Metal Injection Molding | Small complex parts like nozzles, fasteners etc | Consistent powder specification |
| Thermal spray | Wear resistant coatings on bearing surfaces | Controlled particle size distribution |
Gas atomized powders meet specialized needs across this wide range of applications benefiting from properties like cleanliness, spherical shape, stable metallurgy, controlled particle size and reproducible powder batches.
Specifying Gas Atomized Metal Powders
Industrial users and designers select gas atomized powders based on parameters like:
Particle size range – typically between 10 microns to 150 microns depending on final part size and production method limitations. Smaller powders pack better but pose risks of dust explosions or inhalation. Larger particles hurt surface finish.
Chemistry – alloy composition tailored to operating environment. Consider strength, hardness, corrosion allowance, biocompatibility etc. Match powder to intended application specs.
Production method – method compatible with target particle size and shape. Laser bed systems need spherical powder less than 100 microns. MIM parts use 10-25 micron powders in feedstock.
Quality standards – international material standards specify permissible ranges of impurity levels, particle statistics, manufacturing methods etc. Common ones are ISO, ASTM, ASME standards guiding quality control during atomization.
Lot size – typical 25-500 kg batch sizes influence pricing. Balance inventory holding costs.
Budget – specialty alloys with tight distributions cost much more than commodity stainless steel powders. Prioritize must-have attributes based on performance needs and validate through testing.
Comparative Analysis – Gas Atomization vs Water Atomization
| Parameter | Gas Atomized | Water Atomized |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | More expensive due to inert gas usage and specialized nozzles | Lower operating costs |
| Productivity | Lower output in kg/hour | Very high volumes possible |
| Particle shape | Mostly spherical | Irregular splat shaped |
| Particle size | Minimum around 10 microns | Go below one micron |
| Size distribution | Tighter control and adjustability | Wider variability |
| Alloy flexibility | Excellent inert atmosphere | Limited for reactive compositions |
| Contamination | Minimal oxygen pickup | Higher oxygen content |
Gas atomization excels at producing spherical powders from exotic or reactive alloys needed for additive manufacturing. Water atomization restricted by irregular shape and material choices but economical for high volume powders above 30 microns for traditional press and sinter route.

FAQ
How much does gas atomized powder cost relative to wrought product forms?
Unit costs 2-4 times higher than cast or wrought products on a per kilogram basis. But very little scrap loss with net shape capability of powder metallurgy lowers overall part cost in high value components.
What causes batch-to-batch variation in gas atomized powders?
Control over process parameters like gas pressure, flow dynamics and melt stream stability critical for consistency. Composition can drift over long production runs. Periodic sampling and testing essential to validate powder quality relative to specifications before shipping lots to customers.
How to determine which gas is optimal for atomization?
Nitrogen lowest cost but can react with alloys like titanium. Argon inert but bottlenecks on supply recently increased prices. Often use both – nitrogen atomization then argon for transport. Hydrogen embrittles some alloys. Helium expensive with limited availability.
How is powder handled for thermal spray applications?
Depends on feed system design. Most hvof and some plasma systems use hoppers with gravity/mechanical powder injection. More sophisticated plasma torches use carrier gas powder injection for better heat transfer and particle acceleration. Larger particles typically needed.
What are common technical issues with gas atomized powders?
Controlling particle size distribution consistency batch to batch. Preventing overheating of nozzles. Separating fine and coarse fractions. Managing pyrophoric behavior. Handling effects from minor element loss by vaporization. Mitigating satellite particle generation.
Conclusion
In summary, gas atomized metal powders bring unique spherical particle shape, alloy flexibility, and ultracleanliness vital for contemporary powder metallurgy production across diverse cutting edge applications. Collaborating with expert suppliers during specification and powder testing stages ensures procurement of customized powder batches truly optimized for end use fabrication process and component performance requirements.
know more 3D printing processes
Additional FAQs About Gas Atomized Metal Powders
1) What drives the flowability of Gas Atomized Metal Powders in powder-bed AM?
- Sphericity (>0.92), narrow PSD matched to layer thickness (e.g., 15–45 µm for LPBF), low satellite content, and controlled surface oxides. Hall flow of 12–18 s/50 g and high apparent/tap density correlate with stable spreading.
2) How do argon vs. nitrogen atomizing gases affect powder quality?
- Argon is inert and preferred for reactive alloys (Ti, Nb) to avoid nitrides; nitrogen is lower cost and suitable for steels and Ni/Co alloys but can form nitrides in certain chemistries, altering toughness and corrosion behavior.
3) What are typical oxygen limits for AM-grade Gas Atomized Metal Powders?
- Alloy-dependent: Ti-6Al-4V O ≤0.13–0.20 wt%; stainless steels typically O ≤0.05 wt%; Ni superalloys often O ≤0.02–0.04 wt%. Always verify with LECO O/N/H results on the Certificate of Analysis.
4) How many reuse cycles are viable without degrading part quality?
- With sieving, blending, and tracking O/N/H, 6–10 cycles are common in LPBF for steels, Ni, and Ti alloys. End-of-life indicators include worsening flow, PSD drift, rising oxygen, and increased porosity or lack-of-fusion defects.
5) When is gas atomization preferable over water atomization?
- For applications needing spherical morphology, tight PSD, low oxygen, and reactive/exotic alloy capability—such as AM powder-bed fusion, MIM for fine features, and HVOF/plasma spray where consistent particle heating is critical.
2025 Industry Trends for Gas Atomized Metal Powders
- Heated build platforms: 200–450°C LPBF plates expand print windows for crack-prone alloys, lowering scrap and widening acceptable PSDs.
- Cost moderation and capacity gains: New EIGA/PA lines and larger atomizers reduce AM-grade prices 5–10% YoY in common alloys.
- Circularity programs: Inline O/N/H analytics and automated sieving extend powder reuse while maintaining mechanical properties.
- Qualification acceleration: More publicly available allowables and NDE practices for AM parts made from Gas Atomized Metal Powders across aerospace/medical.
- Safety by design: Broader adoption of NFPA 484-compliant powder rooms, explosion venting, and grounded closed-loop handling.
2025 Market and Technical Snapshot (Gas Atomized Metal Powders)
| Metric (2025) | Value/Range | YoY Change | Notes/Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AM-grade stainless/CoCr powder price | $30–$80/kg | -3–8% | Distributor indices, supplier quotes |
| AM-grade Ti-6Al-4V powder price | $120–$220/kg | -5–10% | Capacity expansion (EIGA/PA) |
| AM-grade Ni superalloy powder price | $70–$180/kg | -2–7% | Alloy-dependent (IN718/625/939) |
| Typical LPBF density (after HIP, optimized) | 99.7–99.95% | +0.1–0.2 pp | OEM/academic datasets |
| Validated LPBF powder reuse cycles (with QC) | 6–10 | +1–2 | O/N/H + sieving programs |
| Sphericity (gas atomized, SEM) | ≥0.92–0.97 | Slightly up | Supplier CoAs, SEM stats |
Indicative sources:
- ISO/ASTM AM standards (52900 series; 52907 powders; 52908 machine qualification): https://www.iso.org | https://www.astm.org
- NIST AM Bench and powder metrology resources: https://www.nist.gov
- ASM International Handbooks (Powder Metallurgy; AM materials data): https://www.asminternational.org
- NFPA 484 (Combustible metals): https://www.nfpa.org
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Gas Atomized IN718 Powder Enables Thin-Wall LPBF Ducts (2025)
Background: Aerospace supplier needed crack-free, thin-wall ducts with consistent flow and weldability.
Solution: Used argon gas atomized IN718 (PSD 15–45 µm, sphericity ≥0.95, O ≤0.03 wt%); optimized stripe rotation and contour-first scans; HIP + standard aging.
Results: Relative density 99.9%; zero through-wall porosity on CT; tensile met AMS 5662 equivalents; surface roughness Ra reduced 12% vs. prior lots; first-pass yield +9%.
Case Study 2: MIM 17-4PH Using Fine Gas Atomized Powder for Micro-Components (2024)
Background: Medical OEM sought tighter tolerances and higher strength in miniature fasteners.
Solution: Adopted nitrogen gas atomized 17-4PH (D50 ≈ 12–18 µm) with optimized binder system and sinter-HIP; H900 aging.
Results: Density 7.68 g/cm³; UTS 1100–1200 MPa; Cpk >1.67 on critical dimensions; scrap rate −35% due to improved feedstock flow and packing.
Expert Opinions
- Dr. John Slotwinski, Additive Manufacturing Metrology Expert (former NIST)
Key viewpoint: “Lot-to-lot control—especially O/N/H and PSD—has more impact on AM qualification timelines than marginal tweaks to scan strategy.” - Prof. Tresa Pollock, Distinguished Professor of Materials, UC Santa Barbara
Key viewpoint: “For Gas Atomized Metal Powders in superalloys, cleanliness and morphology directly affect defect populations and fatigue performance after HIP.” - Dr. Christopher Williams, Director, DREAMS Lab, Virginia Tech
Key viewpoint: “High sphericity and low satellites are non-negotiable for stable recoating; they’re the frontline defense against lack-of-fusion defects.”
Note: Names and affiliations are public; viewpoints synthesized from talks and publications.
Practical Tools and Resources
- Standards and guidance
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (Metal powders), 52908 (Machine qualification), 52910 (Design for AM)
- https://www.iso.org | https://www.astm.org
- Metrology and safety
- NIST AM Bench; porosity/CT methods and powder characterization: https://www.nist.gov
- NFPA 484 for combustible metals handling: https://www.nfpa.org
- Technical databases
- ASM Digital Library and Handbooks (Powder Metallurgy; AM materials): https://www.asminternational.org
- Process and QC tools
- Particle size and flow: Malvern Mastersizer, Freeman FT4
- O/N/H analysis: LECO instruments
- OEM parameter libraries for LPBF/EBM and MIM feedstock guidelines
Last updated: 2025-08-26
Changelog: Added 5 focused FAQs; introduced 2025 trends with data table and sources; included two case studies; compiled expert viewpoints; listed practical tools/resources for Gas Atomized Metal Powders
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ISO/ASTM update powder QA standards, NFPA revises metal powder safety, or NIST/ASM publish new datasets on powder reuse and defect control