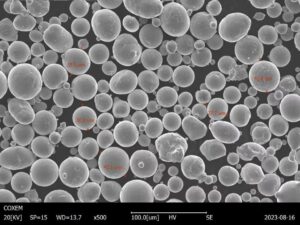
powder atomization have revolutionized various industries, offering unique properties that traditional manufacturing methods cannot replicate.
Aerospace and Aviation
In the aerospace sector, atomized powders are utilized to produce lightweight yet high-strength components for aircraft and spacecraft. The fine particle size and controlled microstructures contribute to improved mechanical properties, making these powders ideal for critical applications like turbine blades and structural components.
Additive Manufacturing
powder atomization have significantly impacted the field of additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing. These powders are specifically engineered for various printing processes, allowing the creation of intricate and complex designs with superior material properties. From aerospace to healthcare, additive manufacturing benefits from atomized powders’ ability to produce customized parts with exceptional precision.
Medical Devices
The medical industry benefits from atomized powders in the production of implants and medical devices. Materials such as titanium alloys and biocompatible ceramics are atomized to create powders that can be shaped into implants matching the patient’s anatomy. This process ensures better integration with surrounding tissues and reduces the risk of rejection.
Automotive Industry
Atomized powders find applications in the automotive sector, where they contribute to lightweighting and enhanced fuel efficiency. These powders are used to manufacture parts like pistons, connecting rods, and gears, providing better performance and durability while reducing overall weight.

Challenges in Powder Atomization
While powder atomization offers numerous advantages, it also comes with its fair share of challenges that researchers and manufacturers must address.
Contamination Concerns
Contaminants from the environment or the atomization process itself can affect the quality of the powders. Ensuring a clean and controlled environment is crucial to prevent unwanted impurities in the final product.
Particle Size Distribution
Achieving a consistent and desired particle size distribution can be challenging. Variations in particle size can lead to inconsistencies in material properties and performance.
Energy Consumption
Atomization processes often require high-energy inputs, primarily due to the need to melt the material and generate the necessary forces for disintegration. Researchers are actively exploring energy-efficient alternatives to reduce the environmental impact.
Innovations in Atomization Technology
In recent years, significant innovations have emerged in the field of atomization technology, aiming to address challenges and push the boundaries of what’s possible.
Custom Alloy Development
Researchers are working on developing new alloys tailored to specific atomization techniques. These alloys are designed to solidify quickly during atomization, resulting in unique microstructures and improved properties.
Nanostructured Powders
Advancements in atomization technology have enabled the production of nanostructured powders with enhanced properties. These powders find applications in fields like electronics and advanced materials.
Sustainable Atomization Methods
Efforts are being made to develop more environmentally friendly atomization methods. This includes utilizing renewable energy sources and optimizing process parameters to reduce energy consumption.

Future Trends in Powder Atomization
The evolution of powder atomization continues to shape the future of materials science and manufacturing.
Industry 4.0 Integration
The integration of Industry 4.0 principles, such as automation, data exchange, and advanced analytics, will lead to more precise control over the atomization process. This will result in even more tailored powders for specific applications.
Eco-Friendly Atomization Techniques
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, researchers are focusing on developing atomization techniques with minimal environmental impact. This includes reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste, and using greener processing methods.
Precision Powder Production
Future trends point toward achieving even greater precision in particle size control and composition. This will open up opportunities for applications requiring ultra-fine powders with precise characteristics.

Conclusion
Powder atomization is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling the production of advanced materials with tailored properties. From aerospace to healthcare, the applications of atomized powders are diverse and continually expanding. As technology advances, challenges are being met with innovative solutions, paving the way for a more sustainable and precise atomization process that will shape the industries of tomorrow.
FAQs on Powder Atomization
- What is powder atomization? Powder atomization is the process of breaking down molten materials into fine particles or powders, often used in manufacturing various products.
- What are the benefits of atomized powders in additive manufacturing? Atomized powders provide precise control over material properties, allowing additive manufacturing to create intricate designs with superior performance.
- What industries benefit most from atomization technology? Industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and additive manufacturing benefit significantly from atomized powders.
- What challenges does powder atomization face? Challenges include maintaining consistent particle size distribution, addressing contamination concerns, and reducing energy consumption.
- How is the atomization process evolving for the future? The future of atomization involves Industry 4.0 integration, eco-friendly techniques, and enhanced precision in powder production to meet specific requirements.
know more 3D printing processes
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1) What atomization methods are most common and how do they compare?
- Gas atomization (GA) for highly spherical powders and low oxygen; water atomization (WA) for cost-effective, irregular powders; plasma/centrifugal and PREP/EIGA for ultra-clean, aerospace-grade powders; ultrasonic and electrode induction melting gas atomization (EIGA) for reactive alloys like Ti.
2) How does powder atomization influence additive manufacturing quality?
- Sphericity, tight PSD (e.g., 15–45 μm for LPBF; 20–80 μm for binder jet), low O/N/H, and minimal satellites drive spreadability, density, and mechanical properties. Poor PSD or contamination increases porosity and lack-of-fusion defects.
3) Which alloys benefit most from gas atomization for AM and MIM?
- Ti‑6Al‑4V, nickel superalloys (IN718/625), maraging/tool steels, CoCr, AlSi10Mg, and stainless 316L/17‑4PH. For MIM/binder jet, some WA powders can be post-processed (spheroidized, deoxidized) to lower cost.
4) What are key KPIs to request on a certificate of analysis (COA)?
- PSD (D10/D50/D90), sphericity, apparent/tap density, Hall/Carney flow, O/N/H (ASTM E1019/E1409/E1447), residual elements, morphology (SEM), and moisture. Include reuse counts for AM.
5) How can manufacturers reduce contamination during powder atomization?
- Use inert gas with low dew point, ceramic-lined tundish/nozzle systems, closed-loop gas recirculation with filtration, HEPA-controlled packaging, and inline O2 monitoring from melt to canning.
2025 Industry Trends: Powder Atomization
- Digital material passports: Lot-level traceability (PSD, O/N/H, morphology) embedded in QR-coded COAs adopted across aerospace and medtech supply chains.
- Energy optimization: Heat-recovery melters and argon recirculation cut energy and gas consumption 15–35% vs 2023 baselines.
- Cost-tiered AM feedstocks: Blended WA+GA routes for binder jet and MIM widen access while meeting sinter density targets.
- Micro/ultrafine cuts: Tighter classification enables sub‑25 μm feeds for micro‑LPBF and fine feature BJ, with enhanced anti-agglomeration treatments.
- Sustainability reporting: Suppliers publish CO2e/kg powder and recycled content; OEMs factor ESG into vendor scorecards.
2025 KPI and Market Snapshot (indicative ranges)
| Metric | 2023 Typical | 2025 Typical | Notes/Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sphericity (GA, 15–45 μm) | 0.92–0.95 | 0.94–0.97 | Improved nozzle design/classification |
| Oxygen, Ti‑6Al‑4V GA (wt%) | 0.12–0.18 | 0.08–0.14 | Lower O2 handling in melt path |
| Hall flow (s/50 g), 15–45 μm 316L | 22–30 | 20–26 | ASTM B213 |
| Tap density (g/cm³), 316L GA | 4.0–4.4 | 4.2–4.6 | PSD tuning |
| Argon consumption reduction | — | 20–35% | Recirculation systems |
| Adoption of digital COAs (%) | 25–35 | 50–65 | Aerospace/medtech RFQs |
References: ISO/ASTM 52907; ASTM B212/B213/B703; ASTM E1019/E1409/E1447; NIST AM‑Bench; OEM technical notes (e.g., Carpenter Additive, Höganäs, Sandvik)
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Hybrid WA→Spheroidized 17‑4PH for Binder Jet Production Gears (2025)
Background: An automotive supplier sought lower-cost powders without sacrificing density or fatigue life.
Solution: Qualified water-atomized 17‑4PH with post-spheroidization and deoxidation; narrow PSD 20–60 μm; catalytic debind and vacuum sinter with aging.
Results: Powder cost −22% vs GA; sintered density 98.0–98.8%; rotating bending fatigue +9% vs prior baseline; scrap rate −18% through tighter classification.
Case Study 2: Ultra‑Low Oxygen Ti‑6Al‑4V via EIGA for Orthopedic Implants (2024)
Background: A medtech OEM required consistent low oxygen and high sphericity to reduce HIP time and improve ductility.
Solution: Adopted EIGA atomization with argon recirculation and low-dew-point controls; PSD 15–45 μm; powder passport with lot-level O/N/H and reuse limits.
Results: Oxygen 0.10 wt% average; LPBF density 99.8% as-built; elongation +2.1% post-HIP; HIP time reduced 20%; qualification cycle shortened by 30% with digital COAs.
Expert Opinions
- Dr. John Slotwinski, Materials Research Engineer, NIST
Key viewpoint: “Correlating powder metrics—PSD and O/N/H—to CT porosity and fatigue performance is essential for performance-based sourcing of atomized powders.” https://www.nist.gov/ - Prof. Ian Gibson, Professor of Additive Manufacturing, University of Twente
Key viewpoint: “Cost-tiered feedstocks, including engineered WA powders, are expanding binder jet and MIM adoption without compromising quality when sintering is optimized.” - Dr. Anushree Chatterjee, Director, ASTM International AM Center of Excellence
Key viewpoint: “Standardized reporting per ISO/ASTM 52907 and process data packages (F3301-style) are accelerating regulatory acceptance in aerospace and medical.” https://amcoe.astm.org/
Practical Tools/Resources
- ISO/ASTM 52907: Metal powder feedstock characterization (flow, PSD, O/N/H)
https://www.iso.org/standard/78974.html - ASTM B212/B213/B703, E1019/E1409/E1447: Density/flow and O/N/H methods
https://www.astm.org/ - NIST AM‑Bench: Open datasets linking atomized powder properties to build outcomes
https://www.nist.gov/ambench - Senvol Database: Compare AM materials and machines
https://senvol.com/database - OEM knowledge hubs (Höganäs, Carpenter Additive, Sandvik): Powder datasheets and application notes
https://www.hoganas.com/ | https://www.carpentertechnology.com/additive-manufacturing | https://www.additive.sandvik/ - HSE ATEX/DSEAR: Safe handling of combustible metal powders
https://www.hse.gov.uk/fireandexplosion/atex.htm
Last updated: 2025-08-27
Changelog: Added five FAQs, a 2025 KPI/market table, two atomization-focused case studies, expert viewpoints, and practical tools/resources related to powder atomization.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-03-31 or earlier if ISO/ASTM standards update, major suppliers introduce new low‑O2 atomization lines, or significant changes in AM binder jet/MIM powder requirements occur.