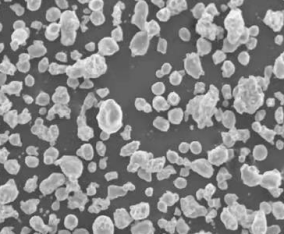
Overview of 6061 Aluminium Alloy Powder
6061 aluminium alloy powder is one of the most widely used aluminium alloys for powder metallurgy applications. Some key features of 6061 aluminium alloy powder include:
- Excellent corrosion resistance and weldability
- Good mechanical properties and strength-to-weight ratio
- Versatile alloy that can be strengthened through heat treatment
- Widely available and cost-effective
6061 alloy powder can be used to manufacture high-performance components through powder metallurgy techniques such as metal injection molding (MIM), cold isostatic pressing (CIP), additive manufacturing, and conventional press and sinter methods. Parts made from 6061 powder exhibit properties comparable to or better than wrought 6061 alloy.
Types of 6061 Aluminium Alloy Powder
There are several types of 6061 aluminium alloy powder available depending on particle size, shape, and production method:
| Type | Description | Typical Particle Size | Shape | Production Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomized | Irregular spheroidal particles produced by gas or water atomization | 10 – 150 μm | Rounded | Gas atomization or water atomization |
| Spherical | Highly spherical powder produced through plasma atomization | 5 – 45 μm | Highly spherical | Plasma atomization |
| Flattened | Flattened particle morphology with high flowability | 5 – 150 μm | Flattened, angular | Mechanical comminution |
| Blended | Mixture of particle sizes and shapes | 5 – 150 μm | Mixed | Blending of atomized and comminuted powders |
Atomized powders with spherical particles typically have better flow and packing properties. Spherical and flattened powders improve powder injection molding behavior. Blended powders provide a balance of properties and cost.
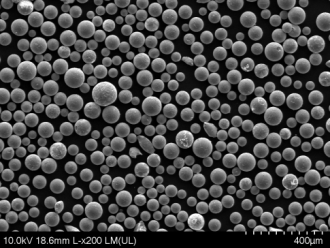
Characteristics and Properties of 6061 Aluminium Powder
6061 aluminium alloy powder offers a versatile mix of properties that make it suitable for a wide range of applications.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Composition | Al-Mg-Si alloy with Cu and Cr additions |
| Density | 2.7 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 582°C |
| Strength | 190 – 310 MPa |
| Hardness | 55 – 100 HB |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent resistance in various environments |
| Thermal Conductivity | 167 W/m-K |
| Electrical Conductivity | 41% IACS |
| Fatigue Strength | 100 – 155 MPa |
| Elongation | 8 – 15% |
| Workability | Excellent formability in softened condition |
| Heat Treatability | Can be heat treated to high strength – T4 and T6 tempers |
| Weldability | Excellent weldability using most techniques |
| Machinability | Fair machinability but high speeds and feeds required |
The properties of sintered parts can be tailored by 6061 powder characteristics, process parameters, and heat treatment. Proper control ensures high strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance.
Applications and Uses of 6061 Aluminium Alloy Powder
The versatile properties of 6061 alloy powder make it suitable for manufacturing lightweight, high-performance components across many industries:
Transportation: Engine brackets, steering knuckles, suspension arms, wheels
Aerospace: Aircraft fittings, helicopter rotors and transmission parts
Military: Grenades, shell casings, gun components
Marine: Gears, shafts, fittings, fasteners, pumps
Electronics: Heat sinks, packaging, enclosures, shields
Industrial: Flanges, couplings, valves, tooling fixtures, gears
Consumer: Power tools, sporting goods, hardware, appliances
Medical: Orthopedic implants, dental implants, medical instruments
6061 is commonly used instead of 2014 and 7075 alloys when very high strength is not required. It offers the best balance of cost, corrosion resistance, and mechanical properties.
Specifications for 6061 Aluminium Powder
6061 aluminium alloy powder must conform to certain specifications for chemistry, particle size distribution, flow rate, and other properties based on the intended application:
| Parameter | Specification | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminium Content | Balance | ASTM E539 |
| Magnesium | 0.8-1.2 wt% | ASTM E539 |
| Silicon | 0.4-0.8 wt% | ASTM E539 |
| Iron | Max 0.7 wt% | ASTM E539 |
| Copper | 0.15-0.4 wt% | ASTM E539 |
| Manganese | Max 0.15 wt% | ASTM E539 |
| Chromium | 0.04-0.35 wt% | ASTM E539 |
| Zinc | Max 0.25 wt% | ASTM E539 |
| Titanium | Max 0.15 wt% | ASTM E539 |
| Particle Size | 10 – 150 μm | ASTM B822 |
| Flow Rate | Min 25 s/50 g | ASTM B213 |
| Apparent Density | Min 2.5 g/cm3 | ASTM B212 |
| Tap Density | Min 75% of alloy density | ASTM B527 |
The particle shape, size ranges, flow, and chemistry must be optimized to the specific component requirements and manufacturing process.
Design Considerations for 6061 Aluminium Powder Parts
Proper design is key to achieving optimal properties in sintered 6061 alloy parts:
- Wall thickness: Minimum 2-3 mm. Thinner walls risk lower strength.
- Fillets and corners: Add fillets to minimize stress concentrations. Avoid sharp corners.
- Draft angles: Incorporate draft angles ≥ 1-2° to ease part ejection.
- Surface finish: Finer powder and sizing can improve surface finish. Secondary operations may be required.
- Dimensional tolerances: ±0.5% is achievable but ±0.2% for high precision components.
- Density: Aim for ≥ 97% of theoretical density for highest mechanical properties.
- Heat treatment: T4 and T6 heat treatment significantly increases part strength.
- Secondary operations: Machining, drilling, milling or grinding may be needed for critical features.
Careful control of these aspects during design allows optimal performance of the final part.
Standards for 6061 Aluminium Alloy Powder
6061 aluminium alloy powder must meet the chemical composition limits in national and international standards:
| Standard | Region |
|---|---|
| ASTM B295 | USA |
| EN AC-AlSi0,7Mg0,6 | Europe |
| GB/T 3190-2008 | China |
| IS 733 | India |
| JIS H2080 | Japan |
These standards also specify requirements for powder production method, particle shape and size, sampling, testing, inspection, packaging, and labeling to ensure quality.
Compliance to standards is essential for applications in aerospace, defense, transportation, medical devices and other regulated industries. Customers usually request test reports showing conformance.
Suppliers of 6061 Aluminium Alloy Powder
Some leading global suppliers of 6061 aluminium alloy powder include:
| Supplier | Powder Types | Particle Size | Production Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hoeganaes Corporation | Atomized, AncorMax® spherical | 10-150 μm | High tonnage |
| Kymera International | Blended, spherical | 10-150 μm | High tonnage |
| Sandvik | Osprey® atomized | 5-150 μm | High tonnage |
| AMC Powders | Atomized, spherical | 10-60 μm | Medium tonnage |
| TLS Technik GmbH | Gas atomized | 10-100 μm | Low tonnage |
Key factors to consider when selecting a powder supplier are production capacity, powder quality, particle characteristics, lot-to-lot consistency, and pricing. Some additional customization such as sieving or blending may be required to achieve the desired powder properties.

Pricing for 6061 Aluminium Alloy Powder
The price of 6061 aluminium alloy powder can vary significantly depending on:
- Powder type: Spherical is more expensive than blended or irregular powder
- Particle size: Finer powders below 20 μm cost more
- Order quantity: Prices are highest for low volumes and reduce for bulk orders
- Production method: Plasma atomized powder costs more than gas atomized
- Quality: Aircraft or medical grade powder certified to tight tolerances is costlier
- Supplier: Premium powders from leading suppliers demand higher prices
Typical price ranges are:
| Powder Grade | Particle Size | Price Range |
|---|---|---|
| Irregular | -150 +10 μm | $15-25 per kg |
| Spherical | 15-45 μm | $25-60 per kg |
| Plasma Spherical | 15-45 μm | $45-120 per kg |
Reduced prices can be negotiated for bulk orders exceeding 1 ton. There may also be fluctuating surcharges for raw material, energy, and transportation costs.
Installation, Operation, and Maintenance of 6061 Powder Systems
Proper practices for storage, handling, and processing must be followed when working with 6061 powder:
| Activity | Instructions |
|---|---|
| Storage | Store sealed powder containers in a cool, dry area away from moisture First in, first out inventory management Avoid temperature extremes and humidity |
| Handling | Use PPE – respirators, gloves, eye protection Carefully pour powder to avoid spills and dust Ground all equipment to dissipate static charge |
| Processing | Do not overmix powder or use excess lubricant Ensure uniform powder feed into press or printer Follow recommended thermal debinding and sintering cycles |
| Maintenance | Check powder handling and processing equipment regularly for issues Clean dies, tooling, and accessories after production runs Calibrate critical dimensional checks and scales |
Proper PPE, equipment checks, and process control minimize powder contamination and sustain consistent output quality over long production runs.
How to Select a 6061 Aluminium Powder Supplier
Choosing the right aluminium powder supplier is crucial for manufacturing high quality components economically. Here are key considerations when selecting a supplier:
- Powder types: Supplier should offer a range of powder types – spherical, blended, atomized etc.
- Production capacity: Ensure supplier can provide consistent volumes of powder as per production schedule.
- Quality systems: Supplier must have quality certifications such as ISO 9001 and tightly control processes.
- Technical expertise: Seek suppliers with metallurgy and powder production know-how to collaborate on optimizing powder characteristics.
- Customer service: Responsiveness to inquiries, technical support, and packaging/logistics services are vital.
- Prices: Compare pricing between different suppliers and Powder grades based on quantity. Seek competitive quotes.
- Testing capabilities: Supplier should be able to provide detailed test reports for each powder lot.
- Inventory: Ask about stock levels and lead times for orders. Just-in-time inventory capability is preferred.
- Location: Geographic proximity helps reduce shipping costs and delays especially for frequent small orders.
Selecting a supplier who comprehensively meets these criteria will deliver the most consistent, cost-effective 6061 powder for production.
Pros and Cons of 6061 Aluminium Alloy Powder
6061 aluminium alloy powder offers several benefits but also has some limitations to consider:
Advantages
- Excellent corrosion resistance in various environments
- Higher strength than pure aluminium and many other alloys
- Good weldability using most welding methods
- Versatile alloy that can be heat treated to tune properties
- Better ductility than 2xxx and 7xxx alloys when hardened
- Lower cost than specialty alloys used in aerospace applications
- Readily available from a wide range of powder suppliers
Disadvantages
- Lower strength than 2xxx and 7xxx aluminium alloy powders
- Not recommended for very high temperature applications
- Susceptible to stress corrosion cracking in certain environments
- Powder metallurgy process can be more expensive than wrought processing
- Achieving tensile properties equivalent to wrought 6061 can be challenging
- Surface finish and dimensional precision may be inferior to CNC machined parts
- Powder production requires handling of explosive fine aluminium particles
For many commercial applications where moderate strength, good corrosion resistance, and reasonable cost are required, 6061 alloy powder offers the best trade-offs. Aerospace and defense applications demanding very high strength would need specialty powder alloy grades.
Comparison Between 6061, 6063, 7075 Aluminium Alloy Powders
6061 aluminium alloy powder offers a middle ground between 6063 and 7075 alloys:
| Alloy | Composition | Strength | Corrosion Resistance | Weldability | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6061 | Al-Mg-Si | Medium | Excellent | Excellent | Medium |
| 6063 | Al-Mg-Si | Low | Excellent | Excellent | Low |
| 7075 | Al-Zn-Mg | High | Good | Fair | High |
- 6063 has the lowest strength but best corrosion resistance and weldability. It is commonly used for architectural applications.
- 6061 provides the best combination of medium strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and good weldability. It is widely used in structural applications across industries.
- 7075 offers very high strength but poorer corrosion resistance and weldability. It is predominantly used in high-strength aerospace applications.
For most commercial powder metallurgy applications, 6061 offers the optimal balance of properties and cost-effectiveness.

FAQ
Q: What are the main alloying elements in 6061 aluminium powder?
A: The main alloying elements are magnesium, silicon, copper, and chromium. Magnesium and silicon additions control the precipitation hardening behavior. Copper improves machining characteristics. Chromium contributes to strength and corrosion resistance.
Q: What is the difference between 6061-T4 and T6 tempers?
A: In the T4 condition, 6061 is solution heat treated and naturally aged to a stable condition. T6 is artificially aged after solution heat treatment to achieve peak strength. T6 offers the highest strength in the 6000 series.
Q: Is 6061 aluminium powder weldable?
A: Yes, 6061 powder maintains the excellent weldability of wrought 6061 alloy. Most fusion and solid-state welding processes can be readily used on 6061 components produced from powder. Proper preheating practices should be followed to avoid cracking.
Q: What are common applications of 6061 powder in aerospace?
A: 6061 is used for a variety of non-critical aircraft components like fittings, brackets, landing gear parts, helicopter rotor components, transmission casings, hydraulic manifolds, and other assemblies where medium to high strength and light weight are required.
Q: How does 6061 aluminium powder compare to stainless steel powder?
A: 6061 has lower strength than stainless steel but offers higher strength-to-weight ratio. It provides better corrosion resistance than carbon steel but lower than stainless steel in some environments. 6061 powder can produce components at lower cost than stainless steel in most cases.
Q: What precautions are necessary when handling 6061 aluminium alloy powder?
A: Fine aluminium powder is highly reactive and flammable. Precautions include grounding equipment, avoiding all ignition sources, wearing appropriate PPE, keeping the environment moisture-free, and having fire suppression systems in place. Careful powder handling procedures must be implemented.