When we talk about high-performance materials, Pure Molybdenum (Mo) powder often steals the spotlight. Known for its remarkable properties such as high melting point, excellent thermal conductivity, and outstanding corrosion resistance, this metal powder is a cornerstone in various industries. But what makes it so special? Let’s dive deep into the world of Pure Mo powder, exploring its types, characteristics, uses, and more.
Overview of Pure Mo Powder
Pure Mo powder is a refined form of molybdenum, an essential transition metal. It is widely recognized for its durability and resistance to extreme conditions. Engineers and manufacturers value it for its ability to maintain structural integrity under intense heat, making it a prime choice in aerospace, electronics, and energy industries.
Key Features of Pure Mo Powder:
- High melting point: Over 2,600°C (4,700°F), making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
- Thermal and electrical conductivity: Ensures efficient energy transfer.
- Corrosion resistance: Protects against chemical reactions in harsh environments.
- Low thermal expansion: Reduces deformation risks in precision machinery.
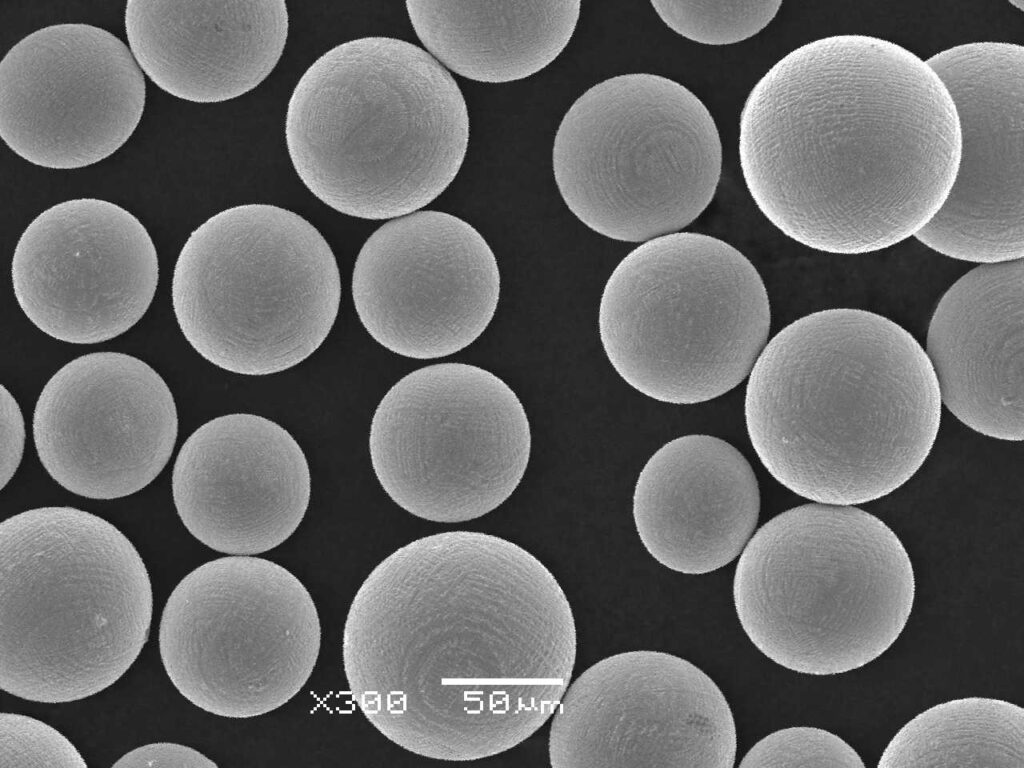

Types of Pure Mo Powder Models
Here’s a breakdown of specific models of Pure Mo powder, each designed for unique applications:
| Model | Composition | Key Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mo-100 | Pure Molybdenum | High purity, low impurity levels | Electronics, thermal spray coatings |
| Mo-110 | Mo + 0.5% Titanium | Improved grain refinement, better ductility | Aerospace components, missile nozzles |
| Mo-Spray | High Purity Mo | Fine particles, excellent flowability | Thermal spray, coatings for turbine blades |
| Mo-Cu50 | Mo + 50% Copper | Enhanced thermal conductivity, machinability | Heat sinks, electronic packaging |
| Mo-TZM | Mo + Ti + Zr + Carbon | Superior strength, creep resistance | Furnace parts, nuclear reactors |
| Mo-L | Low Oxygen Molybdenum | Reduced oxidation risk | Semiconductor manufacturing |
| Nano-Mo | Nano-particle Mo powder | Extremely high surface area | Catalysts, energy storage |
| Mo-HighFlow | Mo with optimized grain | Superior flow properties for additive manufacturing | 3D printing, high-precision components |
| Mo-AG | Mo alloy with Ag traces | Anti-galling properties | Lubrication-free mechanical systems |
| SuperMo-HT | High-Temperature Mo | Enhanced heat resistance, minimal deformation | High-temperature furnaces, crucibles |
Composition of Pure Mo Powder
Pure Mo powder is primarily composed of molybdenum, with varying levels of additives depending on the specific model. Here’s a closer look at its typical composition:
| Element | Typical Range (%) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 99.9%+ | Primary structural element |
| Oxygen (O) | < 0.02% | Controlled for improved corrosion resistance |
| Carbon (C) | < 0.01% | Maintains purity, reduces brittleness |
| Titanium (Ti) | 0-0.5% (in alloys) | Grain refinement, added ductility |
| Zirconium (Zr) | 0-0.2% (in TZM) | Strengthens the grain structure |
| Copper (Cu) | Up to 50% (in Mo-Cu alloys) | Enhances machinability and conductivity |
Characteristics of Pure Mo Powder
The unique characteristics of Pure Mo powder make it stand out in the world of advanced materials:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | One of the highest among metals, over 2,600°C, allowing usage in extreme heat applications. |
| Density | Approximately 10.28 g/cm³, offering robust structural integrity in compact spaces. |
| Thermal Conductivity | High (138 W/m·K), facilitating efficient heat dissipation in electronic components. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Resistant to oxidation and chemical reactions, even in harsh acidic or basic environments. |
| Low Thermal Expansion | Ensures dimensional stability under temperature fluctuations, ideal for precision engineering. |
| Machinability | When alloyed, becomes easier to machine, offering versatility for intricate designs. |
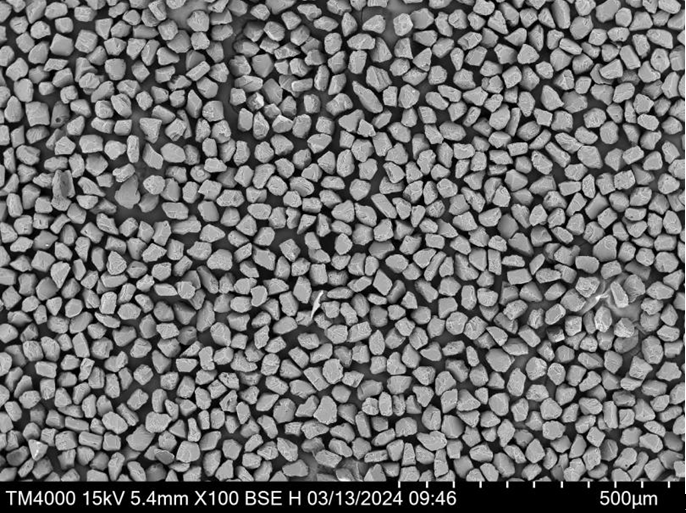
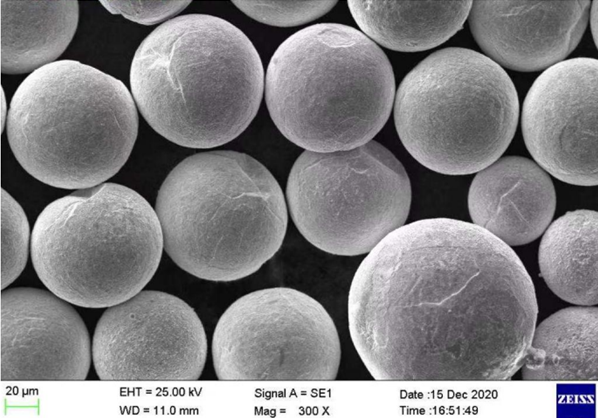




Applications of Pure Mo Powder
Pure Mo powder finds its way into numerous applications, ranging from high-tech to industrial:
| Application | Role of Pure Mo Powder |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Components like turbine blades and rocket nozzles, thanks to high heat resistance. |
| Electronics | Heat sinks and semiconductors for efficient thermal management. |
| Energy | Used in nuclear reactors and as a material in solar panels. |
| Medical | Radiation shielding in X-ray and cancer treatment equipment. |
| Industrial | High-temperature furnaces, cutting tools, and coatings for wear resistance. |
| Automotive | Diesel engine parts and electric vehicle components. |
| Catalysis | Nano-Mo powder for chemical reactions and hydrogen production. |
| Additive Manufacturing | 3D printing high-strength and temperature-resistant parts. |
Specifications, Sizes, and Standards
Here’s a summary of the common specifications for Pure Mo powder:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Purity | 99.9% to 99.99% |
| Particle Size | Nano (10-50 nm), Micro (1-100 µm), Macro (>100 µm) |
| Standards | ASTM B387, ISO 9001 |
| Packaging Options | 1kg, 5kg, 10kg, bulk containers |
| Grade Variants | Mo, TZM, Mo-Cu, Nano-Mo |
Comparison: Advantages and Limitations
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Handles extreme temperatures effortlessly. | Expensive compared to base metals. |
| Conductivity | Excellent thermal and electrical performance. | Requires expertise for proper alloy integration. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Withstands harsh chemical environments. | Not ideal for reducing environments. |
| Machinability | Easy to machine when alloyed. | Pure Mo can be brittle, requiring careful handling. |

Suppliers and Pricing Details
| Supplier | Region | Price Range (per kg) | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global Tungsten & Powders | USA | $200 – $350 | High-purity molybdenum powders. |
| Plansee Group | Europe | $250 – $400 | Specializes in TZM and Mo-Cu alloys. |
| H.C. Starck Tungsten | Germany | $300 – $450 | Offers nano-Mo powders for advanced applications. |
| Luoyang Combat | China | $150 – $300 | Competitive pricing for large quantities. |
FAQ
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is Pure Mo powder made of? | Primarily molybdenum with minimal impurities or alloying elements. |
| Can Pure Mo powder be 3D printed? | Yes, especially with models like Mo-HighFlow for additive manufacturing. |
| What industries use Mo powder? | Aerospace, electronics, medical, automotive, and energy sectors, among others. |
| How do you store Mo powder? | Store in a cool, dry place with minimal exposure to air and moisture to prevent oxidation. |

