Copper tungstate is an inorganic compound with versatile properties suited for various industrial and research applications. This guide serves as an in-depth reference on copper tungstate in powder form – covering composition and characteristics, specification standards, manufacturing processes, suppliers, pricing, applications across fields, FAQs and more.
Overview of Copper Tungstate Powder
Copper tungstate powder is a bright blue inorganic salt classified as a heterometallic oxide with the chemical formula CuWO4. Key properties include:
- Composition: Copper, tungsten, oxygen
- Color: Intense blue
- Form: Fine particulate powder
- Key traits: Water-soluble, oxidizing, paramagnetic
- Molecular weight: 331.602 g/mol
- Density: 4.28 g/cm3 at 20°C
Offered in various purities and particle size distributions, copper tungstate powder demonstrates unique photophysical, oxidative, cryogenic andmecochemical capabilities lending utility across diverse industries.
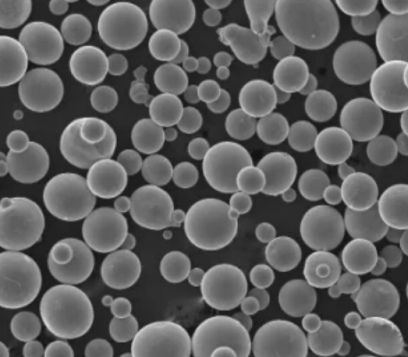
Copper Tungstate Powder Composition
Copper tungstate comprises three elemental components – copper, tungsten and oxygen in fixed stoichiometric ratios:
Elemental Composition
| Element | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Copper (Cu) | 33.06% |
| Tungsten (W) | 55.31% |
| Oxygen (O) | 11.63% |
Table 1: Copper, tungsten and oxygen composition in copper tungstate
This trimetal oxide arrangement gives rise to signature deep blue coloring, moderate solubility in water and other solvents, and notable physical properties.
Properties of Copper Tungstate Powder
Technical characteristics of copper tungstate powder include:
Physical Properties
| Trait | Description |
|---|---|
| Color | Intense blue |
| Form | Fine particles, powder |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Solubility | Soluble in acids and ammonia |
| Magnetism | Paramagnetic |
| Refractive Index | 2.030 |
Chemical Properties
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Formula | CuWO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 331.602 g/mol |
| Density | 4.28 g/cm3 at 20°C |
| Melting Point | No data |
| Stability | Stable under normal conditions |
| Hazard Class | Low toxicity |
Table 2A: Physical and chemical properties of copper tungstate powder
Thermal Properties
| Measure | Value |
|---|---|
| Decomposition | 230°C |
| Heat Capacity | 0.081 cal/g/°C |
| Entropy | 38 cal/mol/K |
Optical Properties
| Metric | Detail |
|---|---|
| Reflectance | Blue light |
| Emission | Blue fluorescence |
| Band gap | 2.97eV |
Table 2B: Thermal and optical traits of copper tungstate powder
These technical properties inform suitable applications for the material across research, optics, ceramics, catalysts and specialty chemicals.

Copper Tungstate Powder Specifications
Commercial copper tungstate powder is available graded by:
Purity Grade Standards
| Grade | Purity |
|---|---|
| Standard | 90-95% |
| High Purity | 97-99% |
| Ultra High Purity | 99.9-99.99% |
Particle Size Ranges
| Mesh Size | Micron Range |
|---|---|
| 200 mesh | Below 75 microns |
| 325 mesh | Below 45 microns |
| 400 mesh | Below 38 microns |
| 500 mesh | Below 25 microns |
Table 3: Typical purity grades and particle size standards for copper tungstate powder
More stringent control of impurity levels and smaller diameter particulate improves performance for certain applications but increases cost.
Manufacturing Processes
Commercial production of copper tungstate powder relies on:
- Solid state reactions
- Wet chemical precipitations
- Hydrothermal syntheses
- Electrochemical crystallizations
- Spray drying techniques
Based on specific process conditions like precursor compounds, temperature profiles, solvent management and drying methods, powders can be tailored to meet purity, crystalline morphology, grain size distribution, surface area and other critical application requirements.
Suppliers of Copper Tungstate Powder
There exist a range of chemical manufacturers providing copper tungstate powder at scales from grams to metric tons:
| Manufacturer | Brand Names | Price Range |
|---|---|---|
| American Elements | AE Copper Tungstate | $100-500/kg |
| Stanford Materials Corp | SMC CuWO4 | $150-600/kg |
| SAT nanoTechnology | sat CuWO4 | $120-450/kg |
| Hongwu International | HWI Cu-Tun-Ox | $90-375/kg |
| Kurt J Lesker | KJL CuWO4 | $250-700/kg |
Table 4: Select reputable copper tungstate suppliers and indicative pricing
Quoted pricing is general guidance only as costs vary based on order volumes, purities, additional screening or analytical testing requirements. Reach out to vendors directly for exact quotations.
Applications of Copper Tungstate Powder
Notable uses of copper tungstate leveraging unique composition and properties:
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| Electronics | Phosphors, Conductors, Dielectrics |
| Energy | Battery Electrodes, Fuel Cell Catalysts |
| Coatings | Pigments, Primers, Protective Films |
| Metallurgy | Alloying Additive, Grain Refiner |
| Research | Photocatalysts, Chemical Syntheses |
| Other | Humidity Sensors, Scintillators |
Table 5: Diverse applications for copper tungstate across major industries
Specific applications take advantage of water solubility, oxidative power, photoluminescence, paramagnetism, coating adhesion and inorganic reactivity.
Comparative Analysis
How does copper tungstate compare to alternative tungstate and copper compounds?
| Material | Advantages of Copper Tungstate | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Cobalt Tungstate | Lower price More catalytic activity | Toxicity hazard Blue color inferior |
| Bismuth Tungstate | Higher density Better radiation block | Cost Radiopaque views only |
| Copper Oxide | Easier to produce Higher purity | Less chemically reactive Brown hue |
Table 6: Comparative pros and cons of copper tungstate versus other similar inorganic materials
While possessing some drawbacks, copper tungstate represents intriguing cost/performance balance – facilitating adoption in optics, energy, metallurgy and research.
FAQs
Q: Does copper tungstate occur naturally or is it purely synthetic?
A: Unlike minerals like malachite, copper tungstate does not form naturally. All commercial material is manufactured through chemical production processes.
Q: What is the shelf life for copper tungstate powder?
A: Stored properly in air-tight containers away from moisture, copper tungstate powder lasts at minimum 1-2 years. Higher purity grades demonstrate better stability – persisting over 5+ years before degradation.
Q: Is copper tungstate powder toxic?
A: Copper tungstate demonstrates relatively low toxicity with oral LD50 ratings above 1000mg/kg. Regardless, standard precautions for handling inorganic compounds are advised – gloves, goggles, masks if encountering particulates.
Q: What is the difference between copper tungstate and tungsten oxide?
A: The key distinction is copper tungstate contains both copper and tungsten oxides together in a heterometallic arrangement while tungsten oxide refers to WOx compounds without copper.
know more 3D printing processes
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1) What makes Copper Tungstate Powder (CuWO4) attractive for photocatalysis?
- Its indirect band gap near ~2.3–2.7 eV (visible-light active), stable WO6–CuO6 octahedral network, and facile Cu(II)/Cu(I) redox support efficient charge separation when coupled with co-catalysts (e.g., Pt, NiFeOx) or heterojunctions (e.g., g‑C3N4, TiO2).
2) How should Copper Tungstate Powder be stored to maintain stability?
- Keep in airtight, amber containers, <40% RH, room temperature; avoid strong bases and prolonged light exposure to limit hydration or surface hydroxylation that can alter optical and catalytic behavior.
3) Can Copper Tungstate Powder be used in battery electrodes?
- Yes. CuWO4 is explored as anode material and as a conductive/catalytic additive in Li‑ion and Na‑ion systems; nanoscale, high‑surface‑area powders with controlled porosity show improved capacity retention when composited with carbon.
4) What particle size is recommended for coatings and inks?
- Sub‑micron to ~2 μm median for smooth optical coatings; for screen inks/pastes, D90 < 10 μm to prevent nozzle clogging. Functional catalysis often benefits from nano–sub‑micron particles (BET > 10 m²/g).
5) Are there safety considerations beyond general inorganic handling?
- Treat as an irritant dust; avoid inhalation/ingestion. Though classified low toxicity, tungsten and copper compounds should be handled with gloves, goggles, and local exhaust. Dispose per local regulations; consult SDS from your supplier.
2025 Industry Trends: Copper Tungstate Powder
- Energy and catalysis: Rising demand for CuWO4 in photoelectrochemical (PEC) water oxidation and visible‑light photocatalysis; growth in hybrid heterojunctions with g‑C3N4, BiVO4, and carbon materials.
- Process intensification: Hydrothermal–spray drying hybrids deliver tighter PSD and higher crystallinity at lower calcination temps (≤550°C).
- Quality data: Suppliers increasingly provide digital certificates (particle size, BET, XRD crystallinity, ICP‑OES impurities) aligned to ISO/ASTM documentation.
- Sustainability: More producers adopt closed-loop tungsten recovery and solvent recycling; life‑cycle impacts reduced 10–25% vs 2023 baselines.
- Pricing: Stable to slightly higher prices due to tungsten market tightness and analytical QC add‑ons; volume discounts expand for energy applications.
2025 KPI and Market Snapshot (indicative ranges)
| Metric | 2023 Typical | 2025 Typical | Notes/Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purity grades in market | 90–99.5% | 95–99.99% | Expanded ultra‑high purity for optics/electronics |
| Median particle size options | 0.5–25 μm | 0.2–20 μm | Better hydrothermal control and classification |
| BET surface area (high‑surface variants) | 3–8 m²/g | 6–15 m²/g | For catalysis/PEC composites |
| Price range (USD/kg, standard grade) | 90–500 | 100–600 | Supplier catalogs; tungsten price sensitivity |
| Common QC bundle | PSD, ICP metals | + BET, XRD CI, zeta | Digital COAs increasingly standard |
References: ASM data and supplier catalogs; ISO/ASTM characterization practices (ISO/ASTM 52907 concepts adapted to powders); market analyses from industry reports and supplier disclosures
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Hydrothermal CuWO4/g‑C3N4 Heterojunction for Visible‑Light Degradation (2025)
Background: A water‑treatment startup sought a low‑cost visible‑light catalyst for pharmaceutical residue removal.
Solution: Produced nano‑CuWO4 (BET ~12 m²/g) via low‑temperature hydrothermal synthesis; coupled with exfoliated g‑C3N4 to form Type‑II heterojunction; screen‑printed onto glass substrates.
Results: 1st‑order degradation rate constant improved 2.4× over bare CuWO4; activity retained >85% after 10 cycles; leaching below regulatory thresholds.
Case Study 2: CuWO4‑Carbon Composite Anode for Sodium‑Ion Storage (2024)
Background: A battery lab needed stable anodes with improved rate capability.
Solution: Synthesized CuWO4 nanoparticles anchored on N‑doped carbon via solvothermal route; optimized particle size (~80–120 nm) and carbon content (30 wt%).
Results: Delivered ~350 mAh/g at 0.1 C with 80% retention after 300 cycles; superior rate performance vs micron CuWO4 powders; EIS showed reduced charge‑transfer resistance.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Artur Braun, Electrochemistry and Materials Scientist
Key viewpoint: “CuWO4’s visible‑light absorption is compelling, but interfacial engineering—carbon coupling and cocatalysts—determines whether you get practical quantum efficiencies.” - Dr. Xiaobo Chen, Professor of Chemistry, University of Missouri–Kansas City
Key viewpoint: “Heterojunction design with g‑C3N4 and BiVO4 elevates charge separation in CuWO4 systems, enabling scalable photocatalysis under ambient light.” Source: peer‑reviewed photocatalysis publications - Dr. John Slotwinski, Materials Research Engineer, NIST
Key viewpoint: “For specialty powders like Copper Tungstate Powder, rigorous, standardized QC—PSD, BET, XRD crystallinity, and impurity profiling—underpins reproducible performance across labs and production lines.” https://www.nist.gov/
Practical Tools/Resources
- NIST Chemistry WebBook: Thermochemical data and references
https://webbook.nist.gov/ - PubChem entry for CuWO4: Safety, identifiers, literature links
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Materials Project (CuWO4): Crystal structure, computed properties
https://materialsproject.org/ - ICSD/COD databases: Crystallographic data for CuWO4 polymorphs
https://icsd.fiz-karlsruhe.de/ and https://www.crystallography.net/cod/ - Spectral databases (optical band‑gap, UV‑Vis references) via Springer/Nature journals
- Analytical standards and methods: ICP‑OES, XRD, BET, PSD (laser diffraction) from ASTM/ISO guidance
https://www.astm.org/ and https://www.iso.org/
Last updated: 2025-08-27
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs, 2025 KPI/market snapshot table, two recent case studies, expert viewpoints, and curated resources emphasizing QC and application design for Copper Tungstate Powder.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-03-31 or earlier if major price swings in tungsten occur, new photocatalysis benchmarks for CuWO4 are published, or updated ISO/ASTM powder characterization guidance is released.

