Iron nickel powder, also known as nickel-iron powder or Ni-Fe powder, refers to powder metallurgy forms of an alloy containing iron and nickel. This versatile material offers unique properties and is used across many industries and applications.
This comprehensive guide provides key details about iron nickel powder in an easy-to-use tabular format. We will explore the composition, characteristics, production methods, applications, suppliers, and other technical specifications of iron nickel powder. Whether you are a manufacturer, purchaser, engineer, or researcher, this is your go-to resource for everything you need to know about this multipurpose alloy powder.
Overview of Iron Nickel Powder
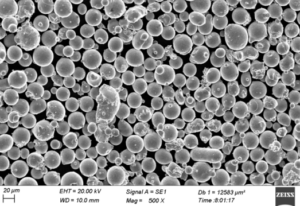
Iron nickel powder is composed primarily of iron and nickel, with small amounts of other alloying elements. It is metallic in nature and magnetic. The powder particles are fine and spherical in shape.
Some of the outstanding properties of this material include high permeability, low coercivity, good machinability, and excellent corrosion resistance. These characteristics make the powder ideal for use in electromagnetic shielding, soft magnetic applications, brazing, welding, and more.
This section provided a brief introduction to iron nickel powder. The tables below cover the composition, properties, applications, specifications, and other details in a convenient format.
Iron Nickel Powder Composition
The typical composition of iron nickel powder is:
| Element | Composition Range |
|---|---|
| Iron (Fe) | 35% – 80% |
| Nickel (Ni) | 20% – 65% |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 0% – 5% |
| Copper (Cu) | 0% – 2% |
The ratio of iron to nickel can be adjusted based on the desired material properties and performance requirements. Specific alloy grades have standardized compositions defined by various societies and standards organizations.
The powder may also contain small amounts of impurities and trace elements picked up during the production process. The composition can be precisely controlled through atomizer design and adjustments to the melting, mixing, and blending parameters.
Iron Nickel Powder Characteristics and Properties
Iron nickel powder possesses a unique combination of chemical, electrical, magnetic, mechanical, and physical properties. The table below summarizes the key characteristics:
| Properties | Details |
|---|---|
| Physical state | Solid powder |
| Color | Metallic gray |
| Crystal structure | Cubic |
| Density | 8.0-9.2 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 1400-1455°C |
| Curie temperature | 280-350°C |
| Resistivity | 94-160 μΩ.cm |
| Permeability | 600-20,000 μ |
| Saturation flux density | 0.6-1.1 T |
| Remanence | 0.7-0.95 T |
| Coercivity | 2.5-64 A/m |
| Thermal conductivity | 21-80 W/m.K |
| Oxidation resistance | Fair to good |
| Corrosion resistance | Excellent |
| Machinability | Good to excellent |
The properties can be tuned by controlling composition, powder size, shape, porosity, processing, and final part parameters. The material offers an unparalleled combination of soft magnetic behavior, modest resistivity, good thermal characteristics, and corrosion resistance.

Production Methods for Iron Nickel Powder
Iron nickel powder can be produced using various methods. The table below outlines the common production techniques:
| Method | Details |
|---|---|
| Gas atomization | Melted alloy poured through nozzle, disintegrated by high-pressure gas jets into fine powder |
| Water atomization | Molten stream broken into droplets by high-velocity water jets |
| Rotating electrode process | Molten material flung off spinning electrode by centrifugal force |
| Carbonyl process | Thermal decomposition of metal carbonyls, followed by comminution |
| Mechanical alloying | Repeated cold welding and fracturing of powder particles in a ball mill |
Gas atomization and water atomization are the most widely used methods. The former allows better control over particle size distribution. Mechanical alloying is used primarily for specialty grades requiring customized compositions.
Applications of Iron Nickel Powder
Iron nickel powder is utilized in a diverse array of applications spanning multiple industries. The major uses are:
| Application | Details |
|---|---|
| Soft magnets | High permeability, low coercivity allows efficient magnetization/demagnetization |
| Electromagnetic shielding | Absorbs EMI/RFI interference across wide frequency range |
| Welding/brazing | Excellent oxidation resistance facilitates joining of materials |
| Metal injection molding | Ideal for complex net-shape part fabrication |
| 3D printing | Print intricate components with magnetic functionality |
| Electromagnetic actuators | Used in solenoids, motors, generators, sensors |
| Microwave devices | Cores, circulators, isolators, filters |
| inductors/transformers | Efficient magnetic flux linkage for electrical components |
| Sintered structural parts | High hardness and strength after compaction and sintering |
The powders can be compacted into various shapes and sintered to obtain soft magnetic composites for induction devices, actuators, electric motors, antennas, and similar equipment. The corrosion resistance allows usage in aggressive environments.
Iron Nickel Powder Specifications
Iron nickel powder is available in various size ranges, compositions, and other specifications tailored to different production techniques and applications. Typical parameters are provided below:
Iron Nickel Powder Sizes
| Mesh Size | Particle Diameter |
|---|---|
| -140+325 mesh | 44-105 μm |
| -325 mesh | <44 μm |
| -100+400 mesh | 20-149 μm |
| 10-50 μm | 10-50 μm |
Narrower size ranges and custom particle distributions are available. Finer powders provide higher green strength and density while coarser powders improve flowability.
Iron Nickel Powder Compositions
| Grade | % Iron | % Nickel | Other Elements |
|---|---|---|---|
| FN-020 | 35-40% | Balance | Small amounts of Mo, Cu, Mn, Si, C |
| FN-024 | 40-45% | Balance | ” |
| FN-027 | 45-50% | Balance | ” |
| FN-050 | 35-40% | Balance | 1-5% Mo |
| FN-052 | 40-45% | Balance | 1-5% Mo |
| FN-055 | 45-50% | Balance | 1-5% Mo |
| FN-077 | 52-57% | Balance | ” |
| FN-080 | 57-62% | Balance | ” |
Other niche compositions are manufactured for specialty magnetic, brazing, welding, and high-temperature applications.

Iron Nickel Powder Standards
Key iron nickel powder standards:
- ASTM B833 – Standard Specification for Powder Metallurgy (PM) Iron-Nickel-Base Soft Magnetic Alloys
- ISO 4491 Metallic powders – Determination of oxygen content by reduction methods
- ISO 4490 Metallic powders – Determination of hydrogen content — Inert gas fusion thermal conductivity method
- MPIF Standard 56 – Magnetic Materials Producers Properties and Terminology
Iron Nickel Powder Pricing
| Powder Grade | Price Range |
|---|---|
| -325 Mesh | $7 – $11 per kg |
| -140 + 325 Mesh | $8 – $12 per kg |
| 10-50 μm | $15 – $20 per kg |
| Spherical | $25 – $35 per kg |
Prices vary based on composition, shape, size range, quantity, manufacturer, and geographic region. Custom grades are more expensive.
Iron Nickel Powder Handling and Safety
Recommended handling procedures and safety practices for iron nickel powder:
- Use spark-proof tools and explosion-proof equipment
- Avoid dust formation and ignition sources
- Ensure adequate ventilation and respiratory protection
- Keep away from heat, flames, and incompatibles like oxidizers
- Ground containers and powders transfer equipment
- Store sealed containers in a cool, dry area away from moisture
Use appropriate PPE and follow safety data sheet precautions. Proper handling and housekeeping minimizes risks of fires, explosions, and health hazards.
Inspection and Testing of Iron Nickel Powder
Iron nickel powder quality is evaluated through standardized test procedures:
| Test Method | Parameter Measured |
|---|---|
| Sieve analysis | Particle size distribution |
| Apparent density | Powder packing density |
| Tap density | Settled density after tapping |
| Hall flowmeter | Powder flow rate |
| SEM, optical microscopy | Particle morphology |
| XRF, ICP-OES | Chemical composition |
| Inert gas fusion | Oxygen and nitrogen content |
| Mercury porosimetry | Porosity |
| Vibrating sample magnetometer | Magnetic properties |
Meeting specification requirements for composition, powder characteristics, microstructure, and performance is critical for quality control and lot acceptance.

Advantages and Limitations of Iron Nickel Powder
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Tunable magnetic properties | Lower saturation flux density than ferrites or Fe powders |
| High permeabilities possible | Requires care in handling and processing |
| Excellent machinability and formability | Shape complexity limited in powder processing |
| Resistant to oxidation and corrosion | Not suitable for low core loss applications |
| Wide range of compositions available | More expensive than iron powder |
| Good wear resistance | Brittle after sintering if porosity not controlled |
| Custom particle distributions and shapes |
By understanding the capabilities and restrictions of the material, it can be effectively implemented within design constraints. Continued research and development further expands the possibilities and applications of this multifunctional powder.
FAQ
What is iron nickel powder?
Iron nickel powder is a metallic powder composed primarily of iron and nickel that is manufactured through gas atomization, water atomization, or other powder production techniques. It is used for soft magnetic applications, welding, brazing, and other areas.
How is iron nickel powder made?
The common production methods are gas atomization, water atomization, and mechanical alloying. The process generally starts by induction melting an alloy with the target composition, followed by disintegration of the molten stream into fine droplets that solidify into powder particles.
What are the contents of iron nickel powder?
Typical iron nickel powder contains 35-80% iron, 20-65% nickel, and small amounts of molybdenum, copper, and other trace elements. Specific compositions are formulated based on magnetic, mechanical, and other property requirements.
Is iron nickel powder ferromagnetic?
Yes, iron nickel powder exhibits ferromagnetic behavior, meaning it can be magnetized or attracted to magnetic fields. It has high initial permeability and low coercivity. This makes it well-suited for applications like electromagnetic shielding, inductors, transformers, and electric motors.
What is iron nickel powder used for?
Major uses include soft magnets, electromagnetic shielding, welding, brazing, metal injection molding, 3D printing, actuators, microwave components, inductors, and sintered structural parts across the automotive, aerospace, electronics, and other industries.
What are the advantages of iron nickel powder?
Key advantages include tunable magnetic properties, excellent machinability and formability, good corrosion and oxidation resistance, ability to tailor composition and powder characteristics, and capabilities for complex part fabrication through pressing and sintering.
What are the disadvantages of iron nickel powder?
Limitations include lower saturation flux density than ferrite or iron powders, more difficult handling and processing, restricted shape complexity in powder processing, unsuitability for low core loss uses, brittleness after sintering if porosity not controlled properly, and higher cost than pure iron powder.
know more 3D printing processes
Additional FAQs on Iron Nickel Powder
1) Which Fe-Ni ratios are best for soft-magnetic performance?
Permalloy-type grades near 80% Ni/20% Fe deliver ultra-high permeability and very low coercivity, ideal for shielding and sensor cores. Intermediate alloys (45–65% Ni) balance permeability, Bsat (~0.9–1.1 T), and mechanical strength for inductors and actuators.
2) Can iron nickel powder be used in metal additive manufacturing (AM)?
Yes. Gas-atomized spherical Fe-Ni and Ni-Fe-Mo powders are processed by laser/e-beam powder bed fusion and binder jetting. Applications include magnetic motor laminations, RF components, and shielding. Control oxygen/nitrogen (<0.1 wt% O typical) and consider stress relief or HIP to stabilize magnetic properties.
3) How do Mo and Cu additions affect properties?
Mo (1–5%) lowers coercivity and core losses, improves permeability stability vs. stress; Cu (≤2%) can aid sintering and refine grain structure. Both may slightly reduce saturation flux density.
4) What processing steps most influence magnetic performance after sintering?
- Compaction pressure and green density
- Dewaxing atmosphere and sintering temperature/time (often H2 or high vacuum)
- Magnetic anneal (e.g., 1100–1200°C, controlled cool) to relieve stress and align domains
- Final sizing and surface finish for consistent flux paths
5) How do you qualify iron nickel powder for critical applications?
Use a combination of: PSD (laser diffraction/sieve), flow (Hall), apparent/tap density, O/N/H (inert gas fusion), chemistry (XRF/ICP), VSM for B-H curves, and microstructure (SEM/EBSD). Reference ASTM B833, MPIF 35/Standard 56, and ISO 4490/4491.
2025 Industry Trends in Iron Nickel Powder
- AM-ready magnetic alloys: Growth of spherical Ni-Fe(-Mo) powders optimized for LPBF/binder jetting with tighter PSD and low interstitials for repeatable permeability.
- Electrification demand: EV inverters, EMI shielding, and compact inductors drive soft-magnetic component volumes using MIM/press-sinter and AM for complex cooling and flux paths.
- Lower core loss strategies: Stress-relief anneals, nano-oxide insulation for powder cores, and Mo-lean grades tuned for mid-frequency operation (1–50 kHz).
- Traceability and sustainability: Wider adoption of powder material passports, recycled Ni content reporting, and MES-linked batch genealogy.
- Cost stabilization: Diversified Ni supply and improved powder reuse in AM reduce cost volatility for Fe-Ni applications.
| 2025 Metric | Typical Range/Value | Relevance/Notes | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| LPBF relative density (spherical Fe-Ni) | 98.0–99.8% | With optimized power/speed/hatch; contour scans for surface | Peer-reviewed AM studies; OEM app notes |
| Coercivity (pressed/sintered Fe-45–65Ni) | 5–40 A/m | Depends on Mo, density, and anneal | MPIF/ASTM B833 data ranges |
| Initial permeability μi (80Ni-20Fe, annealed) | 20,000–100,000 | Shielding and sensor cores | Materials datasheets, VSM tests |
| Resistivity (μΩ·cm) | 94–160 | Impacts eddy-current losses | ASM data; measured ranges |
| AM powder O content | ≤0.05–0.12 wt% | Target to maintain ductility and magnetic performance | ISO/ASTM 52907 practices |
| Binder-jetted Fe-Ni final density (sinter/HIP) | 95–99% | Near-net for complex magnetic parts | Vendor case data; journals |
Authoritative references:
- ASTM B833; MPIF Standard 56 and MPIF 35: https://mpif.org
- ISO 4490/4491; ISO/ASTM AM standards: https://www.iso.org and https://www.astm.org
- ASM Handbook, Magnetic Materials: https://www.asminternational.org
- NIST materials/EMI resources: https://www.nist.gov
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: LPBF Ni-Fe-Mo Soft-Magnetic Core with Integrated Cooling (2025)
Background: An e-mobility supplier needed compact inductors with reduced core losses and improved thermal management.
Solution: Printed a Ni-Fe-2%Mo alloy core with conformal cooling channels via LPBF (spherical 15–45 μm powder, O ≤0.08 wt%); stress-relief + HIP; magnetic anneal in H2.
Results: 23% lower temperature rise at 20 kHz/0.2 T, coercivity reduced from 28 to 12 A/m after anneal, and 16% volume reduction vs. laminated baseline while meeting inductance stability spec.
Case Study 2: Binder-Jetted Fe-50Ni EMI Shield for Avionics (2024)
Background: Aerospace OEM sought weight and lead-time reductions for complex EMI housings.
Solution: Binder jetting of Fe-50Ni powder, debind/sinter under H2, optional HIP; nickel flash plating for corrosion resistance.
Results: 35% weight reduction and 40% machining time saved vs. wrought machining; shielding effectiveness improved by 8–12 dB in 10 MHz–1 GHz tests; passed thermal cycling and salt fog.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. David Jiles, Distinguished Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Iowa State University
Key viewpoint: “Proper thermal treatments are pivotal—magnetic annealing of Fe-Ni reduces internal stresses, lowers coercivity, and yields predictable B–H behavior essential for precision inductive devices.” - Dr. Tatiana Sikanen, Senior Research Scientist, VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland
Key viewpoint: “For AM iron nickel powder, interstitial control and powder reuse governance directly affect ductility and permeability. Inline O/N/H analytics with MES traceability is now best practice.” - Dr. Eric Fessler, Director of Powder Metallurgy, MPIF (personal capacity)
Key viewpoint: “Mo additions remain a practical lever to stabilize permeability over stress and temperature, especially where mid-frequency loss must be limited without costly laminations.”
Citations for expert profiles:
- Iowa State University: https://www.iastate.edu
- VTT: https://www.vttresearch.com
- MPIF: https://mpif.org
Practical Tools and Resources
- Standards and qualification
- ASTM B833; MPIF 35/56: https://mpif.org
- ISO 4490/4491 gas analysis methods: https://www.iso.org
- Design and simulation for magnetic parts
- Ansys Maxwell and Motor-CAD for electromagnetic design: https://www.ansys.com
- COMSOL Multiphysics (AC/DC Module): https://www.comsol.com
- AM process and materials databases
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (feedstock) and 52910 (DFAM): https://www.astm.org
- Senvol Database (machines/materials): https://senvol.com/database
- Powder QC and metallurgy
- LECO O/N/H analyzers: https://www.leco.com
- EBSD/SEM service providers for grain/texture analysis (university cores; vendor labs)
- EMI/EMC best practices
- NIST EMI/EMC resources and measurement guides: https://www.nist.gov
Last updated: 2025-08-21
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs, 2025 trend table with metrics and sources, two recent Fe-Ni application case studies, expert viewpoints with credible affiliations, and a curated tools/resources list.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ASTM/MPIF/ISO standards update, AM powder O/N/H limits change, or major OEMs release new Fe-Ni AM parameter sets or EMI shielding specifications.