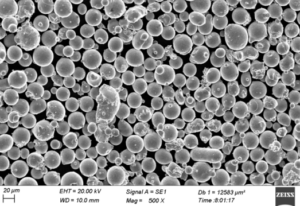
What are aluminium alloys powder and how are they made?
Aluminium alloys powder consists of metallic aluminium mixed with other elements to enhance certain properties. The creation of this powder involves several steps:
- Alloying: Aluminium is combined with elements like magnesium, silicon, copper, and zinc to form an alloy. The exact proportions vary depending on the desired properties.
- Melting: The alloy is melted in a furnace.
- Atomization: The molten alloy is sprayed through a nozzle where it’s broken up into small droplets. These droplets solidify into powder as they cool.
- Collection: The resulting powder is collected and sorted by particle size.
- Heat Treatment: To achieve desired characteristics, the powder may undergo heat treatment.
- Final Processing: The powder is further refined to achieve specific granular properties.
Table: Steps in producing aluminium alloys powder
| Step | Process | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alloying | Combining aluminium with other elements. |
| 2 | Melting | Melting the formed alloy. |
| 3 | Atomization | Spraying and solidifying the alloy into powder form. |
| 4 | Collection | Sorting by particle size. |
| 5 | Heat Treatment | Modifying properties through heating. |
| 6 | Final Processing | Further refining granular properties. |

Why are aluminium alloy powders preferred in the industry?
Aluminium alloy powders are sought after in many industries due to their unique properties:
- Lightweight: Aluminium alloys are lighter than many other metals. This makes products made from them ideal for aerospace and automobile applications.
- Strength: Despite being lightweight, they are remarkably strong.
- Corrosion Resistance: Aluminium forms a protective oxide layer, preventing rust and corrosion.
- Thermal Conductivity: They’re excellent conductors of heat, useful for electronic devices.
- Recyclability: Aluminium can be recycled multiple times without losing its properties.
- Cost-effective: In many applications, using aluminium alloy powders is more cost-effective than solid or other forms of aluminium.
- Versatility: With various alloys available, there’s flexibility in selecting the right one for specific needs.
- Ease of Fabrication: Aluminium alloy powders can be easily shaped, joined, and finished.
- Electrical Conductivity: Aluminium is a good conductor of electricity.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Products made of aluminium have a modern and clean appearance.
The preferred use in sectors like aerospace, automotive, electronics, and construction is due to these advantageous properties.
What are the most common applications of aluminium alloy powders?
Aluminium alloy powders find applications in a range of sectors due to their versatility:
- Aerospace: Used in making lightweight and strong aircraft parts.
- Automotive: Essential for manufacturing parts in cars to reduce weight.
- Electronics: Incorporated in devices for heat dissipation.
- 3D Printing: Aluminium alloy powders are widely used in additive manufacturing.
- Paints and Coatings: Provides a metallic finish to paints.
- Energy: Used in making solar panels and other energy devices.
- Pharmaceuticals: Act as catalysts in certain reactions.
- Pyrotechnics: Used in fireworks and other explosive materials.
- Construction: For rust-proof and lightweight structures.
- Marine: In manufacturing parts for ships and underwater equipment.
These applications take advantage of the powder’s physical and chemical properties.

How do the properties of aluminium alloy powders compare to other metallic powders?
Aluminium alloy powders have distinct characteristics:
- Density: Aluminium is significantly lighter than metals like steel or copper. This results in a lower density powder which is advantageous for specific applications.
- Melting Point: Aluminium has a lower melting point compared to many other metals, making it easier to process.
- Oxidation: Aluminium can oxidize rapidly, forming a protective layer.
- Reactivity: Pure aluminium is reactive; however, alloying it can adjust its reactivity.
- Thermal Conductivity: It is one of the best conductors of heat.
- Electrical Conductivity: It conducts electricity efficiently, second only to copper.
- Malleability: Aluminium is highly malleable, making it suitable for various applications.
- Corrosion Resistance: Its corrosion resistance is superior to many metals.
- Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Aluminium alloy powders offer an excellent strength-to-weight ratio.
- Economical: Often, aluminium alloy powders can be more economical than other metal powders.
What challenges arise in handling and storing aluminium alloy powders?
Handling and storing aluminium alloy powders can pose unique challenges:
- Flammability: Aluminium powders can be flammable, posing a risk of explosions.
- Oxidation: Prolonged exposure to air can lead to oxidation, affecting the powder’s quality.
- Moisture Sensitivity: Aluminium powders can react with moisture, potentially causing degradation.
- Particle Agglomeration: Particles can clump together, affecting the consistency.
- Contamination: The powder can easily get contaminated if not stored correctly.
- Health Hazards: Inhalation of fine particles can pose health risks.
- Disposal Issues: Proper disposal methods need to be followed to ensure environmental safety.
- Transportation: Special precautions are required during transport to prevent accidents.
- Storage Temperature: Certain aluminium alloy powders need specific storage temperatures.
- Hygiene: Regular cleaning of storage spaces is essential to prevent contamination.
Storage facilities and handlers need specialized training and equipment to deal with these challenges.
How is the quality of aluminium alloy powders determined?
Quality determination is crucial for aluminium alloy powders:
- Particle Size Analysis: Determines the range of particle sizes in a sample.
- Chemical Composition: Identifies the elements present and their percentages.
- Flow Rate: Measures how easily the powder flows, affecting its usability.
- Bulk Density: Indicates the mass of the powder in a given volume.
- Tap Density: Measures the powder’s density when it’s been compacted.
- Moisture Content: It’s essential to know the amount of moisture present.
- Oxidation State: Determines how much the powder has oxidized.
- Microscopy: Viewing the powder under a microscope can provide insights into its quality.
- Thermal Analysis: Understanding how the powder reacts to heat.
- Mechanical Properties: Testing the strength and malleability of the powder.
Each test provides crucial data about the powder’s quality.

Are there safety concerns related to aluminium alloy powders?
Safety is a paramount concern when dealing with any metallic powder:
- Explosivity: Fine aluminium powders can be explosive when exposed to a flame or spark.
- Inhalation Risk: Breathing in the powder can cause respiratory issues.
- Eye Irritation: Thepowder, if it comes in contact with the eyes, can cause irritation or damage. 4. Skin Contact: Prolonged skin contact might lead to irritations or allergic reactions.
- Environmental Impact: If not disposed of correctly, it can be harmful to the environment.
- Reactivity: Certain conditions can make aluminium alloy powders react vigorously.
- Storage Concerns: Incorrect storage can lead to contamination or degradation of the powder.
- Transportation Risks: If not transported under the right conditions, it can pose risks.
- Electrical Hazards: Due to its high electrical conductivity, any electrical faults can be dangerous.
- Hygiene: Proper hygiene is essential when handling powders to prevent contamination and health risks.
It’s crucial to adhere to safety protocols when handling and storing aluminium alloy powders.
How are aluminium alloy powders used in additive manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, has seen increased use of aluminium alloy powders:
- Layering: Aluminium alloy powders can be layered thinly, allowing for precise printing.
- Sintering: The powder can be fused together using a laser or electron beam in selective laser sintering (SLS) or electron beam melting (EBM) techniques.
- Complex Structures: The versatility of the powder allows for the creation of intricate and geometrically complex structures.
- Rapid Prototyping: Using aluminium alloy powders in 3D printing can expedite the prototyping process.
- Cost-effective: It can be more economical to print certain parts than to manufacture them traditionally.
- Customization: Each item can be tailored to specific requirements.
- Reduced Waste: Additive manufacturing typically produces less waste than subtractive methods.
- Strength and Durability: Parts made from aluminium alloy powders tend to be robust and durable.
- Lightweight Components: Ideal for industries like aerospace where weight is a concern.
- Post-processing: After printing, parts can undergo various treatments to enhance their properties.
The adoption of aluminium alloy powders in 3D printing is transforming the manufacturing landscape.
How do aluminium alloy powders contribute to sustainability?
Sustainability benefits from the use of aluminium alloy powders:
- Recyclability: Aluminium is one of the most recyclable metals, with little to no degradation in its properties after recycling.
- Energy Efficiency: The production of aluminium powder is often more energy-efficient than producing solid aluminium.
- Waste Reduction: The powder form can lead to reduced waste in manufacturing processes like additive manufacturing.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Lightweight aluminium components in vehicles can lead to fuel efficiency, reducing carbon emissions.
- Longevity: Aluminium products tend to last longer, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Economic: Using aluminium can sometimes be more cost-effective, leading to economical sustainability.
- Solar Panels: Aluminium powders are used in some solar panels, promoting renewable energy sources.
- Local Production: Localized production using 3D printing reduces transportation needs.
- Safe Disposal: Though safety precautions are needed, disposal doesn’t produce toxic waste.
- Research: Ongoing research into more sustainable methods of producing and using aluminium is promising.
These contributions make aluminium alloy powders a sustainable choice in various industries.

How is research advancing the potential uses of aluminium alloy powders?
Research is constantly pushing the boundaries for aluminium alloy powders:
- New Alloys: Researchers are developing new aluminium alloys to cater to specific industrial needs.
- Enhanced Properties: Through alloying and treatment, powders with superior properties are being developed.
- Medical Applications: There’s ongoing research into using aluminium powders in medical implants and devices.
- Nanotechnology: At the nano scale, aluminium powders exhibit unique properties, opening new avenues.
- Efficient Production: Research is optimizing the production process to be more energy-efficient and cost-effective.
- Environmental Impact: Efforts are underway to make the production and use of aluminium more eco-friendly.
- Advanced 3D Printing: New techniques in additive manufacturing using aluminium are under development.
- Improved Safety: Research aims to make the handling and storage of aluminium powders safer.
- Broadened Applications: As more is understood about aluminium alloy powders, they’re finding uses in previously unexplored areas.
- Collaborative Initiatives: Research institutions and industries are collaborating to maximize the potential of aluminium powders.
The future of aluminium alloy powders is bright, with research continuously unveiling new possibilities.
Summary Table
| Key Topic | Highlights |
|---|---|
| Production | Alloying, Melting, Atomization, Collection, Heat Treatment, Final Processing |
| Properties | Lightweight, Strong, Corrosion Resistant, Thermal Conductivity, Recyclability, Versatility |
| Applications | Aerospace, Automotive, Electronics, 3D Printing, Paints, Energy, Pharmaceuticals |
| Comparison with Other Metals | Density, Melting Point, Oxidation, Reactivity, Conductivity, Malleability, Corrosion Resistance |
| Handling Challenges | Flammability, Oxidation, Moisture Sensitivity, Particle Agglomeration, Contamination |
| Quality Determination | Particle Size, Chemical Composition, Flow Rate, Density, Moisture Content, Thermal Analysis |
| Safety Concerns | Explosivity, Inhalation Risk, Eye and Skin Irritation, Environmental Impact |
| Additive Manufacturing | Layering, Sintering, Complex Structures, Rapid Prototyping, Customization |
| Sustainability | Recyclability, Energy Efficiency, Waste Reduction, Carbon Footprint, Longevity |
| Research and Future Advancements | New Alloys, Enhanced Properties, Medical Applications, Nanotechnology, Environmental Impact |
FAQ
Q1. What makes aluminium alloy powders suitable for 3D printing?
The powder’s ability to be layered thinly, sintered efficiently, and produce complex structures makes it ideal for additive manufacturing.
Q2. How does the use of aluminium alloy powders impact the environment?
Aluminium’s high recyclability, energy-efficient production, and contribution to reduced carbon footprints through lightweight components make it environmentally friendly.
Q3. Are there health hazards associated with aluminium alloy powders?
Yes, there are concerns like inhalation risk, eye irritation, and skin contact which necessitate proper safety protocols.
Q4. How do aluminium alloy powders compare to solid aluminium?
While both have their unique advantages, powders are often more versatile in applications like 3D printing, and can sometimes be more economical.
Q5. What industries predominantly use aluminium alloy powders?
Industries such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, construction, and energy frequently use aluminium alloy powders.
know more 3D printing processes
Additional FAQs on Aluminium Alloys Powder
1) Which aluminium alloy powders are most common for additive manufacturing?
- AlSi10Mg and AlSi12 for general LPBF parts; high‑strength Al‑Mg‑Sc (e.g., Scalmalloy‑type) for aerospace; Al‑Cu‑Mg (2xxx) research grades for higher temperature capability; Al‑Zn‑Mg (7xxx) emerging with crack‑resistant chemistries.
2) What powder characteristics most affect print quality in LPBF?
- Spherical morphology, tight PSD (typ. D10–D90 ≈ 15–45 μm), low oxide content, low moisture, minimal satellites, and stable flow (Hall/Carney). These drive layer uniformity, density, and surface finish.
3) How do you minimize oxidation and hydrogen pickup in aluminium alloys powder?
- Use inert gas atomization (Ar preferred), dry gas (<3 ppm H2O), rapid collection, sealed drums with desiccants, low‑humidity handling, and pre‑bake powder at 80–120°C per supplier limits before printing.
4) What post‑processing is typical for LPBF AlSi10Mg?
- Stress relief (e.g., 2–3 h at 300–325°C), optional HIP for critical fatigue parts, solution + aging for certain Al‑Mg‑Sc grades, and surface finishing (shot peen, machining, anodizing).
5) Can recycled aluminium powder be blended back safely?
- Yes, often 20–50% blend‑back with sieving and QC on PSD, moisture, oxide films, and mechanical coupons. Retire lots when oxygen or defect rates trend upward.
2025 Industry Trends for Aluminium Alloys Powder
- Blue/green laser LPBF expands printable Al alloys with higher reflectivity and conductivity.
- Crack‑resistant 2xxx/7xxx chemistries (Zr/Sc inoculation, Si additions) reach pilot production.
- Powder passports link PSD, O/N/H, reuse cycles, and in‑situ monitoring to part acceptance.
- Sustainability: higher recycled Al content with documented EPDs; closed‑loop powder handling.
- Binder jetting Al progresses via tailored sinter/HIP cycles and low‑oxide powders.
| 2025 Metric (Aluminium Alloys Powder) | Typical Range/Value | Why it matters | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| LPBF PSD target (Al) | D10–D90 ≈ 15–45 μm | Recoating and density | ISO/ASTM 52907 |
| Oxygen content (AM‑grade Al) | ≤0.10–0.20 wt% O (alloy/process dependent) | Ductility, porosity | OEM specs; ASM |
| Achievable density (LPBF AlSi10Mg) | 99.5–99.9% (with optimized parameters) | Mechanical reliability | Peer‑reviewed AM studies |
| Electrical/thermal conductivity (LPBF pure Al/AlSi) | 58–62% IACS (AlSi10Mg as‑built); higher with HT | Thermal management parts | OEM datasets |
| Typical blend‑back ratio | 20–50% reused powder | Cost, sustainability | Industry benchmarks |
| Indicative price band (AM‑grade Al powders) | ~$25–$120/kg (alloy, PSD, supplier) | Budgeting | Supplier quotes/trackers |
Authoritative references and further reading:
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (AM feedstock): https://www.iso.org
- ASTM F3318 (AM AlSi10Mg) and related AM standards: https://www.astm.org
- ASM Handbook: Powder Metallurgy; Additive Manufacturing: https://www.asminternational.org
- NIST AM Bench datasets: https://www.nist.gov
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Blue‑Laser LPBF of High‑Strength Al‑Mg‑Sc Alloy for UAV Structures (2025)
Background: An aerospace supplier needed higher specific strength than AlSi10Mg while maintaining printability for thin‑wall UAV frames.
Solution: Deployed 450–515 nm lasers with Al‑Mg‑Sc powder (15–45 μm), low‑humidity handling, and solution + aging heat treatment.
Results: Relative density 99.7%; UTS 520–560 MPa, elongation 9–12%; 14% weight reduction vs. AlSi10Mg baseline at equal stiffness; stable properties with 30% powder blend‑back over 6 cycles.
Case Study 2: Binder‑Jetted AlSi‑Based Heat Exchangers with Low‑Oxide Powder (2024)
Background: An EV thermal systems OEM sought low‑cost, intricate heat exchangers not feasible with machining.
Solution: Used fine AlSi powder engineered for low surface oxide, followed by tailored debind, sinter + HIP, and selective impregnation.
Results: Final density 96–98.5%; pressure drop reduced 18% vs. brazed assembly; leak‑tightness >99.9%; unit cost −22% at 3,000 units/year.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Carlos Leal, Materials and AM Researcher, TU Munich
Key viewpoint: “Minor Sc/Zr additions enable grain refinement and hot‑crack resistance, opening 2xxx/7xxx‑like performance windows for LPBF aluminium.” - Dr. Laura Schmidt, Head of Additive Manufacturing, Fraunhofer IAPT
Key viewpoint: “Blue/green lasers and powder handling discipline are the twin enablers for consistent aluminium builds at production scale.” - Dr. John P. Slotwinski, AM Materials Expert and Standards Contributor
Key viewpoint: “Powder genealogy and moisture/oxide control are as critical as laser parameters for aluminium alloys powder to meet serial‑production CQAs.”
Citations for expert profiles:
- Fraunhofer IAPT: https://www.iapt.fraunhofer.de
- TU Munich: https://www.tum.de
- ASTM AM CoE: https://amcoe.org
Practical Tools and Resources
- Standards and safety
- ISO/ASTM 52907; ASTM F3318 (AlSi10Mg); NFPA 484 (combustible metals)
- Powder QC
- LECO O/N/H analyzers: https://www.leco.com
- PSD (ASTM B822), apparent/tap density (ASTM B212/B329), SEM for morphology, moisture analyzers
- Design and simulation
- Ansys Additive, Simufact Additive; nTopology for lattice/heat‑exchanger design
- Market and data
- Senvol Database (machines/materials): https://senvol.com/database
- NIST AM Bench datasets: https://www.nist.gov
Last updated: 2025-08-21
Changelog: Added 5 FAQs, 2025 trends with metrics table and sources, two case studies (blue‑laser Al‑Mg‑Sc LPBF and AlSi binder‑jet), expert viewpoints with citations, and practical tools/resources.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ISO/ASTM standards update, blue/green laser datasets for Al alloys are published, or significant price/spec changes occur in AM‑grade aluminium powders.