Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Electrode Induction Melting Inert Gas (EIMIG), a sophisticated technique used in the production of high-quality metal powders. Whether you’re a materials engineer, a researcher, or simply curious about advanced metallurgical processes, this article is designed to provide you with a detailed understanding of EIMIG. We’ll dive into its mechanics, explore specific metal powder models, and highlight its various applications. So, let’s get started!
Overview of Electrode Induction Melting Inert Gas
Electrode Induction Melting Inert Gas (EIMIG) is a cutting-edge metallurgical process that involves the melting of metals using an electric arc generated between electrodes in an inert gas environment. This method is particularly advantageous for producing high-purity metal powders, which are essential in industries ranging from aerospace to biomedical engineering.
What Makes EIMIG Special?
EIMIG stands out due to its ability to produce metal powders with superior purity and controlled particle sizes. By using an inert gas atmosphere, typically argon or helium, oxidation and contamination are minimized, ensuring the production of high-quality metal powders. The process is also highly versatile, allowing for the melting of a wide range of metals and alloys.
Core Components of EIMIG
- Electrodes: Usually made of graphite or tungsten, these generate the electric arc necessary for melting.
- Inert Gas Environment: Argon or helium is commonly used to prevent oxidation.
- Induction Heating System: Provides the necessary energy to sustain the melting process.
- Crucible: Holds the metal as it melts and cools into powder form.

Types of Metal Powders Produced by EIMIG
EIMIG can produce a variety of metal powders, each with unique properties suitable for different applications. Here are ten specific models:
1. Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V)
Composition: Titanium, Aluminum, Vanadium
Properties: High strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance
Applications: Aerospace components, medical implants
2. Nickel Superalloy (Inconel 718)
Composition: Nickel, Chromium, Iron, Niobium
Properties: High temperature resistance, excellent mechanical properties
Applications: Turbine blades, jet engines
3. Stainless Steel (316L)
Composition: Iron, Chromium, Nickel, Molybdenum
Properties: High corrosion resistance, good formability
Applications: Biomedical devices, food processing equipment
4. Cobalt-Chromium Alloy (Co-Cr-Mo)
Composition: Cobalt, Chromium, Molybdenum
Properties: High wear resistance, biocompatibility
Applications: Dental implants, orthopedic implants
5. Aluminum Alloy (AlSi10Mg)
Composition: Aluminum, Silicon, Magnesium
Properties: Lightweight, good thermal conductivity
Applications: Automotive parts, aerospace structures
6. Copper Alloy (CuNi2SiCr)
Composition: Copper, Nickel, Silicon, Chromium
Properties: High electrical conductivity, good mechanical strength
Applications: Electrical connectors, heat exchangers
7. Tool Steel (H13)
Composition: Iron, Chromium, Molybdenum, Vanadium
Properties: High toughness, excellent heat resistance
Applications: Molds for die casting, extrusion tools
8. Maraging Steel (18Ni300)
Composition: Iron, Nickel, Cobalt, Molybdenum
Properties: High strength, good toughness
Applications: Aerospace components, tooling
9. Tungsten Carbide (WC-Co)
Composition: Tungsten, Cobalt
Properties: Extremely hard, high wear resistance
Applications: Cutting tools, mining equipment
10. Zirconium Alloy (Zr702)
Composition: Zirconium, Hafnium, Iron
Properties: Excellent corrosion resistance, good mechanical properties
Applications: Nuclear reactors, chemical processing equipment
Characteristics of Electrode Induction Melting Inert Gas
EIMIG is known for several key characteristics that make it an attractive option for producing metal powders.
Purity
The inert gas environment significantly reduces contamination, resulting in metal powders with high purity levels.
Particle Size Control
EIMIG allows for precise control over particle size distribution, which is crucial for applications requiring specific powder characteristics.
Versatility
The process is adaptable to a wide range of metals and alloys, making it suitable for diverse industrial applications.
Efficiency
EIMIG is an energy-efficient process, capable of producing high yields of metal powder with minimal waste.
Applications of Electrode Induction Melting Inert Gas
EIMIG-produced metal powders find use in various high-tech industries due to their superior properties.
Aerospace Industry
High-strength, lightweight alloys like Ti-6Al-4V are crucial for aircraft components, where performance and reliability are paramount.
Biomedical Engineering
Biocompatible materials such as Co-Cr-Mo are used in medical implants and devices, ensuring safety and effectiveness for patients.
Automotive Sector
Aluminum alloys like AlSi10Mg are used in automotive parts to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency.
Electronics
Copper alloys with high electrical conductivity are essential for connectors and other electronic components.
Tooling and Manufacturing
Tool steels and tungsten carbide powders are used to create durable molds and cutting tools for various manufacturing processes.



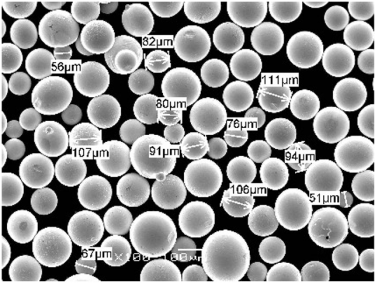
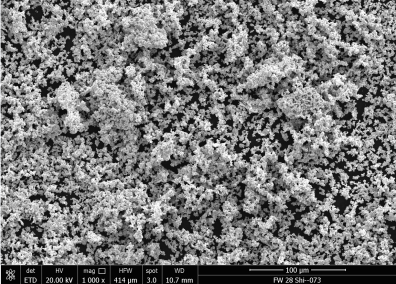

Detailed Specifications of EIMIG Metal Powders
Properties and Characteristics
| Metal Powder | Density (g/cm³) | Melting Point (°C) | Hardness (HV) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V | 4.43 | 1660 | 349 | 895 | 10 |
| Inconel 718 | 8.19 | 1350 | 330 | 1240 | 12 |
| 316L Stainless Steel | 7.99 | 1375 | 217 | 620 | 40 |
| Co-Cr-Mo | 8.29 | 1330 | 450 | 900 | 8 |
| AlSi10Mg | 2.68 | 570 | 85 | 310 | 7 |
| CuNi2SiCr | 8.78 | 1083 | 100 | 450 | 20 |
| H13 Tool Steel | 7.80 | 1427 | 750 | 1450 | 12 |
| 18Ni300 Maraging Steel | 8.00 | 1413 | 340 | 2000 | 10 |
| WC-Co | 15.60 | 2870 | 1600 | – | – |
| Zr702 | 6.50 | 1855 | 250 | 550 | 30 |
Applications and Uses
| Metal Powder | Primary Applications | Additional Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V | Aerospace components, medical implants | Sporting goods, marine applications |
| Inconel 718 | Turbine blades, jet engines | Nuclear reactors, space vehicles |
| 316L Stainless Steel | Biomedical devices, food processing | Chemical processing, marine applications |
| Co-Cr-Mo | Dental implants, orthopedic implants | Watch components, industrial bearings |
| AlSi10Mg | Automotive parts, aerospace structures | Consumer electronics, bicycles |
| CuNi2SiCr | Electrical connectors, heat exchangers | Marine applications, coinage |
| H13 Tool Steel | Molds for die casting, extrusion tools | Injection molds, forging dies |
| 18Ni300 Maraging Steel | Aerospace components, tooling | High-performance gears, shafts |
| WC-Co | Cutting tools, mining equipment | Wear-resistant parts, drilling tools |
| Zr702 | Nuclear reactors, chemical processing | Medical devices, aerospace components |
Specifications, Sizes, Grades, Standards
| Metal Powder | Grade | Size Range (µm) | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V | Grade 5 | 15-45 | ASTM B348 |
| Inconel 718 | UNS N07718 | 15-53 | AMS 5662 |
| 316L Stainless Steel | 316L | 10-45 | ASTM F138 |
| Co-Cr-Mo | ASTM F75 | 20-63 | ISO 5832-4 |
| AlSi10Mg | – | 15-45 | DIN EN 1706 |
| CuNi2SiCr | – | 20-50 | ASTM B422 |
| H13 Tool Steel | H13 | 20-63 | ASTM A681 |
| 18Ni300 Maraging Steel | 18Ni300 | 10-45 | AMS 6514 |
| WC-Co | 1-20 | ISO 4499-1 | |
| Zr702 | R60702 | 15-45 | ASTM B551 |
Suppliers and Pricing Details
| Supplier | Metal Powder | Price (per kg) | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Powders Inc. | Ti-6Al-4V | $150 | In stock |
| Specialty Metals Co. | Inconel 718 | $200 | Limited stock |
| Medical Materials LLC | 316L Stainless Steel | $120 | In stock |
| BioMetals Corp. | Co-Cr-Mo | $180 | Pre-order required |
| Light Metals Inc. | AlSi10Mg | $100 | In stock |
| Electrical Alloys Ltd. | CuNi2SiCr | $160 | In stock |
| Tool Steel Supply Co. | H13 Tool Steel | $140 | Limited stock |
| High Strength Metals | 18Ni300 Maraging Steel | $220 | In stock |
| Hard Metals Group | WC-Co | $300 | Pre-order required |
| Nuclear Materials Inc. | Zr702 | $250 | In stock |
Comparing Pros and Cons, Advantages and Limitations
| Metal Powder | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V | High strength, lightweight, corrosion resistant | Expensive, difficult to machine |
| Inconel 718 | Excellent high-temperature properties | High cost, complex processing |
| 316L Stainless Steel | Corrosion resistant, biocompatible | Lower strength compared to other alloys |
| Co-Cr-Mo | High wear resistance, biocompatibility | Brittleness, expensive |
| AlSi10Mg | Lightweight, good thermal properties | Lower strength compared to steel alloys |
| CuNi2SiCr | High electrical conductivity, corrosion resistant | Expensive, limited mechanical strength |
| H13 Tool Steel | High toughness, heat resistance | Susceptible to cracking under stress |
| 18Ni300 Maraging Steel | High strength, good toughness | Expensive, complex heat treatment required |
| WC-Co | Extremely hard, high wear resistance | Brittleness, high cost |
| Zr702 | Excellent corrosion resistance, good mechanical properties | High cost, limited availability |

FAQs
What is Electrode Induction Melting Inert Gas (EIMIG)?
EIMIG is a process where metals are melted using an electric arc between electrodes in an inert gas atmosphere, producing high-purity metal powders.
Why use an inert gas in EIMIG?
Inert gases like argon or helium prevent oxidation and contamination during the melting process, ensuring high-quality metal powders.
What metals can be melted using EIMIG?
EIMIG is versatile and can melt a wide range of metals and alloys, including titanium, nickel, stainless steel, cobalt-chromium, and more.
What are the applications of EIMIG metal powders?
EIMIG metal powders are used in aerospace, biomedical engineering, automotive, electronics, and tooling industries due to their superior properties.
How does EIMIG control particle size?
The process parameters in EIMIG can be finely adjusted to control the particle size distribution, ensuring consistency and precision in the final product.
Are EIMIG metal powders expensive?
The cost of EIMIG metal powders varies based on the metal type and purity but generally tends to be higher due to the advanced nature of the process.
What are the main benefits of EIMIG?
EIMIG offers high purity, precise particle size control, versatility in metal types, and efficient production, making it highly beneficial for producing specialized metal powders.
How is EIMIG different from other melting techniques?
EIMIG uses an inert gas atmosphere and induction heating, which reduces contamination and allows for precise control over the melting process, setting it apart from other techniques like conventional arc melting.
Can EIMIG be used for large-scale production?
Yes, EIMIG can be scaled up for industrial production, making it suitable for both small-scale research and large-scale manufacturing.
Who are the leading suppliers of EIMIG metal powders?
Leading suppliers include Advanced Powders Inc., Specialty Metals Co., Medical Materials LLC, and BioMetals Corp., among others, offering a variety of metal powders for different applications.
Conclusion
Electrode Induction Melting Inert Gas (EIMIG) is a transformative technology in the field of metallurgy, offering unparalleled purity and precision in metal powder production. Its applications span across critical industries, ensuring high performance and reliability in demanding environments. Whether you’re looking into aerospace components, biomedical devices, or high-performance tooling, EIMIG provides the advanced materials needed to push the boundaries of innovation.

