Overview of TZM Powder
TZM powder is a specialized material composed of a blend of titanium (Ti), zirconium (Zr), and molybdenum (Mo), designed for use in high-performance industrial and scientific applications. Known for its exceptional strength, thermal stability, and resistance to wear and oxidation, TZM powder is a go-to material in industries like aerospace, energy, electronics, and manufacturing.
What makes TZM stand out? It’s all about its unique blend of metals that synergistically combine to deliver enhanced performance. This article explores everything about TZM powder, from its composition and properties to its applications and specific models. We’ll also discuss suppliers, pricing, and tips for choosing the right model.
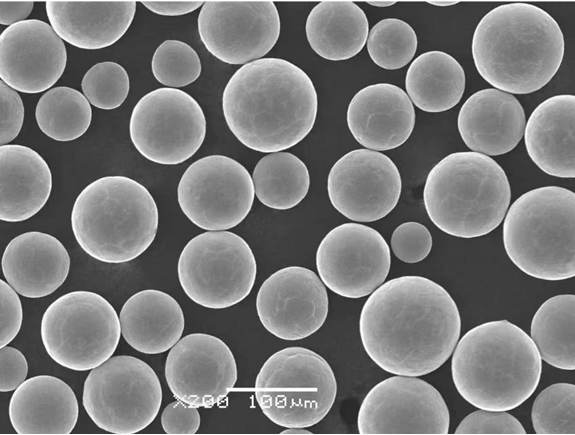
What is TZM Powder?
TZM stands for Titanium-Zirconium-Molybdenum, a molybdenum-based alloy that has been reinforced with small amounts of titanium and zirconium. This alloy exhibits impressive mechanical and thermal properties, making it ideal for demanding applications.
Key Features of TZM Powder
- High melting point (~2617°C for molybdenum).
- Excellent thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion.
- Resistance to corrosion, oxidation, and creep at high temperatures.
- Superior strength and toughness compared to pure molybdenum.
Composition of TZM Powder
Key Elements in TZM Powder
| Element | Percentage | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Molybdenum | ~97-98% | Provides the base material with high melting point and strength. |
| Titanium | ~0.5% | Enhances grain structure and strength. |
| Zirconium | ~0.08-0.12% | Improves ductility and oxidation resistance. |
| Carbon | ~0.01-0.04% | Adds strength by preventing grain growth. |
Properties of TZM Powder
Mechanical and Thermal Characteristics
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 10.22 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | ~2617°C |
| Tensile Strength | 700–800 MPa |
| Thermal Conductivity | 138 W/m·K at 20°C |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 5.4 × 10⁻⁶/K at 20–100°C |
| Hardness | 250–270 HV |




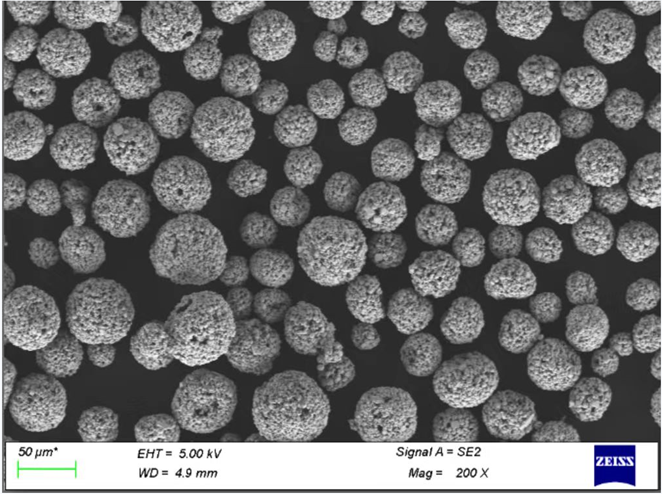

Specific Models of TZM Powder
Top Models and Variants
Here are ten widely used TZM powder models, along with their descriptions:
- TZM-101: Standard grade, suitable for general high-temperature applications like furnace components.
- TZM-102: Enhanced purity for use in nuclear and aerospace industries.
- TZM-103: Ultra-fine particle size, ideal for additive manufacturing and 3D printing.
- TZM-104: High-density grade for extrusion dies and heavy-duty equipment.
- TZM-105: Corrosion-resistant variant used in chemical processing environments.
- TZM-106: Optimized for high creep resistance in vacuum environments.
- TZM-107: Alloyed with extra titanium for increased mechanical strength.
- TZM-108: Radiation-resistant grade used in nuclear reactors.
- TZM-109: High-thermal-conductivity model for heat sinks and cooling systems.
- TZM-110: Lightweight variant, used in aerospace to reduce component weight.
Applications of TZM Powder
Industrial Uses of TZM Powder
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Rocket nozzles, heat shields, and structural components. |
| Energy | Components in nuclear reactors and power generation systems. |
| Manufacturing | Extrusion dies, molds, and high-temperature furnace parts. |
| Electronics | Heat sinks, thermoelectric coolers, and semiconductor components. |
| Medical | High-strength implants and surgical tools in experimental applications. |
Specifications, Sizes, and Grades
TZM Powder Specifications
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Particle Size | Ranges from 1 µm to 100 µm, depending on the application. |
| Purity | >99.9% for high-grade models, >98% for standard grades. |
| Standards | ASTM B386 for TZM sheet and plate, ASTM F2899 for additive manufacturing powders. |
Suppliers and Pricing of TZM Powder
| Supplier | Pricing (Per Kg) | Specialty |
|---|---|---|
| H.C. Starck Solutions | $500–$800 | High-grade TZM for aerospace and energy. |
| Plansee Group | $450–$750 | Fine powders for additive manufacturing. |
| Ed Fagan Inc. | $480–$700 | Industrial-grade TZM powders. |
| Global Tungsten & Powders | $460–$730 | Purity-optimized TZM powders. |
| Advanced Materials Inc. | $490–$770 | Custom particle sizes and applications. |
Advantages of TZM Powder
Why Choose TZM Powder?
- High-Temperature Performance: Works seamlessly under extreme conditions.
- Durability: Withstands mechanical stress without losing integrity.
- Corrosion Resistance: Outlasts other materials in harsh environments.
- Versatility: Suitable for diverse applications, from aerospace to medical fields.
Drawbacks and Limitations
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Excellent mechanical strength | Higher cost compared to standard molybdenum. |
| High thermal stability | Challenging to machine due to hardness. |
| Wide range of applications | Limited availability in ultra-pure grades. |

FAQ
Common Questions About TZM Powder
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is TZM powder used for? | TZM powder is used in high-temperature and high-stress environments like aerospace and energy sectors. |
| How is TZM powder produced? | TZM is typically made using powder metallurgy, combining molybdenum with titanium and zirconium. |
| Is TZM powder expensive? | Yes, it is pricier than pure molybdenum due to its specialized properties. |
| Can TZM powder be 3D printed? | Absolutely! TZM is a popular material for additive manufacturing. |
| What are the alternatives to TZM powder? | Alternatives include pure molybdenum, tungsten alloys, and titanium alloys. |

