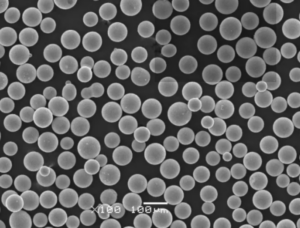
Titanium Hydride (TiH₂) powder is a versatile and vital material used in a range of industries, including aerospace, automotive, metallurgy, and even electronics. This article explores every nuance of TiH₂ powder, from its composition to applications, and everything in between. Whether you’re a professional in the field or just curious, let’s dive into the fascinating world of TiH₂ powder.
Overview of TiH₂ Powder
TiH₂ powder, also known as titanium hydride powder, is formed by combining titanium with hydrogen. The material offers unique properties like high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and excellent reactivity, making it a favorite in advanced manufacturing processes like powder metallurgy and 3D printing.
Key Properties of TiH₂ Powder
- Chemical Formula: TiH₂
- Appearance: Grey or black powder
- Density: ~3.91 g/cm³
- Hydrogen Content: Typically around 4% by weight
- Thermal Stability: Decomposes to titanium and hydrogen at elevated temperatures.

Composition of TiH₂ Powder
Understanding the composition of TiH₂ powder is essential for selecting the right grade for your needs. The powder’s purity and particle size significantly influence its behavior in various applications.
| Component | Typical Content (%) |
|---|---|
| Titanium (Ti) | ≥ 96.0 |
| Hydrogen (H) | 3.8 – 4.5 |
| Oxygen (O) | ≤ 0.3 |
| Nitrogen (N) | ≤ 0.2 |
| Carbon (C) | ≤ 0.05 |
| Iron (Fe) | ≤ 0.1 |
Characteristics of TiH₂ Powder
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Titanium hydride retains titanium’s hallmark feature—superior strength while remaining lightweight. This is invaluable for aerospace and automotive applications where weight savings are critical.
Decomposition Potential
At elevated temperatures, TiH₂ releases hydrogen, making it a unique precursor for titanium powders in sintering and additive manufacturing.
Corrosion Resistance
TiH₂ is naturally resistant to many corrosive environments, ensuring durability in demanding conditions.
Applications of TiH₂ Powder
TiH₂ powder finds its way into various industries thanks to its exceptional properties.
| Application | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Powder Metallurgy | Enhances sintering efficiency and reduces production costs. |
| 3D Printing | Offers precision in additive manufacturing with excellent material properties. |
| Aerospace Components | Used in lightweight, high-strength parts such as airframes and engine parts. |
| Hydrogen Storage Systems | Acts as a hydrogen storage medium in advanced energy applications. |
| Metal Matrix Composites | Improves wear resistance and mechanical strength. |
| Welding and Soldering | Serves as a source of titanium in filler materials. |
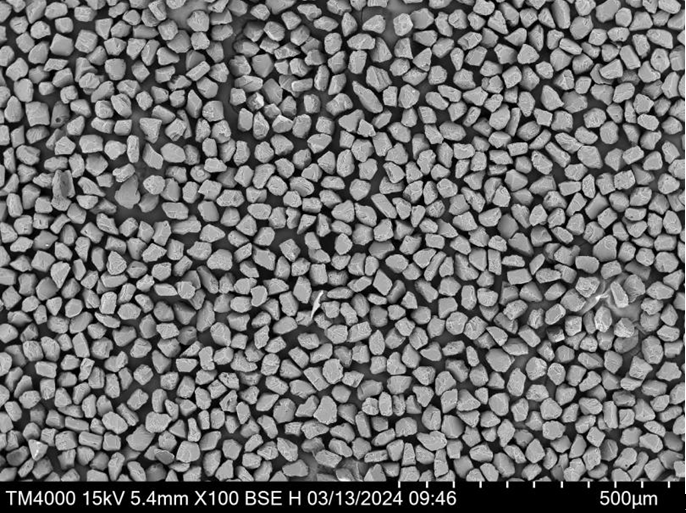
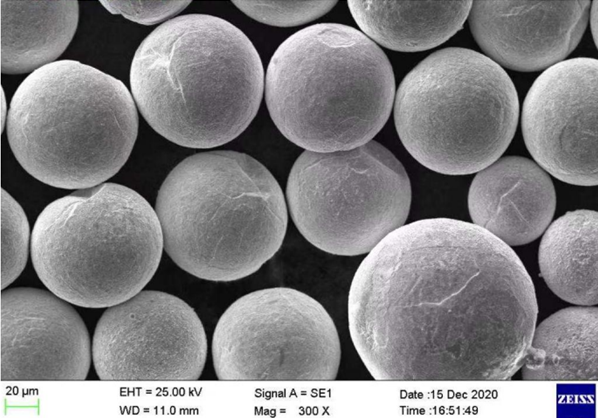
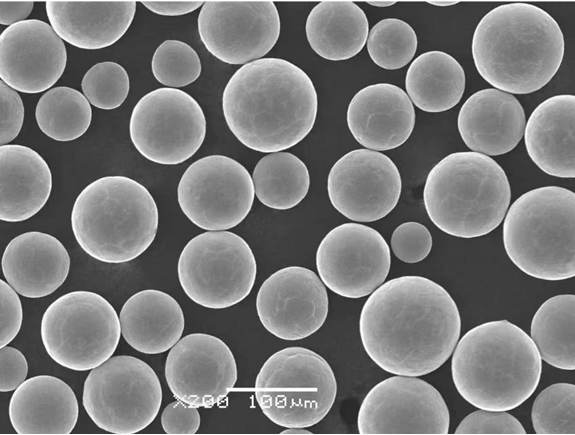



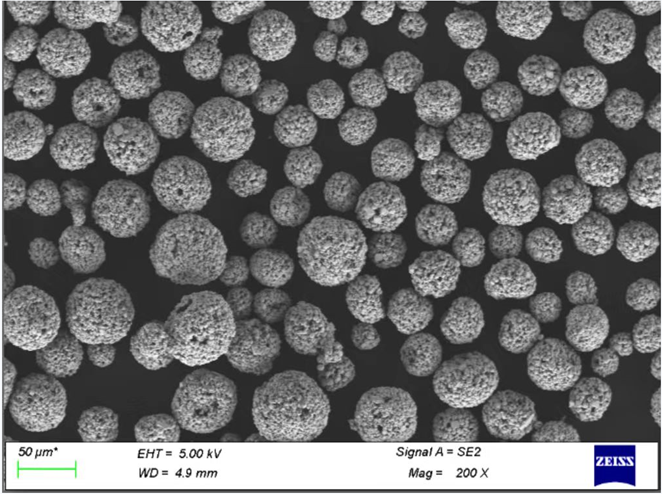

Specifications, Grades, and Standards
Choosing the right TiH₂ powder requires understanding the specifications and grades that align with your project.
| Grade | Particle Size (µm) | Hydrogen Content (%) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiH₂-10 | ≤ 10 | 4.0 | 3D printing, microelectronics |
| TiH₂-20 | ≤ 20 | 3.8 | Powder metallurgy |
| TiH₂-45 | ≤ 45 | 4.2 | General-purpose applications |
| TiH₂-UltraPure | ≤ 10 | 4.5 | High-purity requirements |
Top Models of TiH₂ Powder
Here’s a closer look at some of the popular TiH₂ powder models, tailored for different applications:
- TiH₂-Microfine
- Description: Ultra-fine powder with particle sizes below 5 microns.
- Applications: Ideal for additive manufacturing and high-precision parts.
- TiH₂-Industrial
- Description: Cost-effective, standard-grade powder.
- Applications: General use in welding, soldering, and metal composites.
- TiH₂-HighPurity
- Description: High-purity powder with stringent quality controls.
- Applications: Aerospace and medical devices.
- TiH₂-3DP
- Description: Designed specifically for 3D printing with optimized flowability.
- Applications: Additive manufacturing and prototyping.
- TiH₂-Standard
- Description: Versatile powder for multiple industries.
- Applications: Powder metallurgy and composite materials.
- TiH₂-Energy
- Description: Hydrogen-rich formulation for energy storage.
- Applications: Hydrogen fuel cells and energy systems.
- TiH₂-Plus
- Description: Improved particle size uniformity.
- Applications: Advanced sintering techniques.
- TiH₂-Nano
- Description: Nanoscale powder for cutting-edge research.
- Applications: Nanotechnology and specialized coatings.
- TiH₂-Medical
- Description: Meets biocompatibility standards.
- Applications: Medical implants and surgical tools.
- TiH₂-HighDensity
- Description: Optimized for high-density sintering.
- Applications: Aerospace and defense sectors.
Suppliers and Pricing Details
| Supplier | Price Range ($/kg) | Region | Special Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Materials Inc. | 50 – 100 | USA | Customizable particle sizes and compositions |
| TitanMetals Co. | 45 – 90 | Europe | High-purity grades for aerospace |
| SinoPowder Ltd. | 30 – 70 | Asia | Competitive pricing for bulk orders |
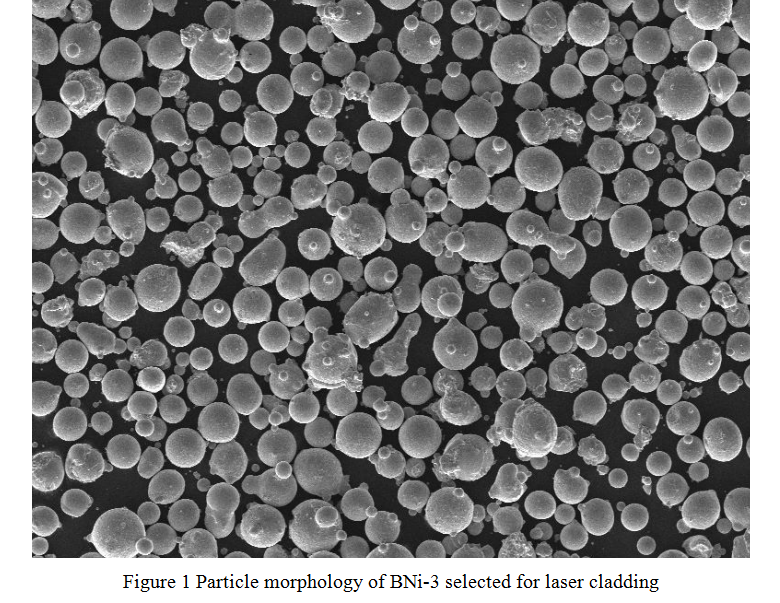
Comparing Advantages and Limitations
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | High strength-to-weight ratio | Brittle in some conditions |
| Hydrogen Storage | Excellent hydrogen carrier | Requires controlled decomposition |
| Cost | Affordable compared to titanium powder | Cost increases for high-purity grades |
FAQ
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is TiH₂ powder used for? | TiH₂ powder is used in powder metallurgy, 3D printing, and hydrogen storage. |
| How is TiH₂ powder produced? | It’s made by reacting titanium with hydrogen under controlled conditions. |
| Can TiH₂ powder be used in aerospace? | Yes, it’s ideal for lightweight, strong aerospace components. |
| What is the typical particle size? | Particle sizes range from nanometers to 45 microns depending on the grade. |