Silicon Carbide (SiC) powder is an innovative material that’s been making waves in industries ranging from automotive to electronics and even aerospace. Known for its exceptional hardness, high thermal conductivity, and resistance to chemical corrosion, SiC powder has become a go-to material for numerous cutting-edge applications. But what exactly makes it so special, and how can you make the best use of it? Let’s dive in!
Composition of SiC Powder
SiC powder is a compound of silicon and carbon. Its crystalline structure is typically hexagonal (alpha-SiC) or cubic (beta-SiC), each offering unique properties tailored to specific applications. The exact composition of SiC powder determines its strength, thermal properties, and chemical resistance, making it an ideal choice for a variety of industrial processes.
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | SiC (Silicon Carbide) |
| Purity Levels | 90% – 99.999% |
| Crystalline Structure | Alpha (Hexagonal), Beta (Cubic) |
| Density | 3.21 g/cm³ (approx.) |
| Particle Size Range | Nano (20-200 nm) to Micron Scale (1-500 μm) |
| Additives (Optional) | Boron, Aluminum, or Nitrogen (for enhanced properties) |
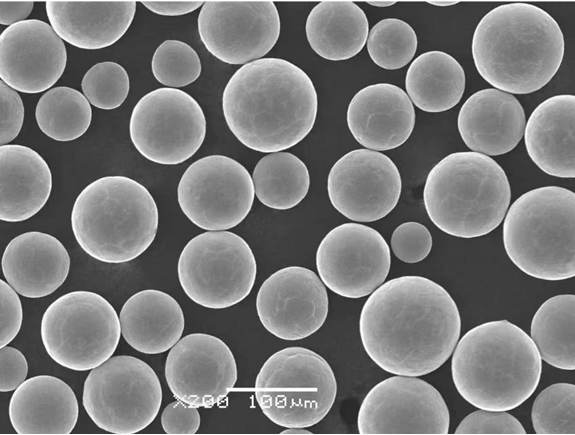
Characteristics of SiC Powder
What sets SiC powder apart from other materials? Let’s explore some of its standout features:
- Extreme Hardness: SiC ranks just below diamond on the Mohs scale, making it an excellent abrasive material.
- High Thermal Conductivity: Perfect for heat dissipation in electronics and high-temperature environments.
- Chemical Stability: Resistant to oxidation, acids, and alkalis.
- Lightweight: Despite its hardness, SiC is significantly lighter than metals like steel or aluminum.
- High Melting Point: Withstands temperatures exceeding 2,700°C.
| Characteristic | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 9.2 |
| Thermal Conductivity | 120-200 W/mK (depending on purity and type) |
| Melting Point | ~2,730°C |
| Electrical Conductivity | Can vary from semiconductor-like to insulating |
| Density | Lower than many metals, enhancing its use in lightweight applications |
Types and Models of SiC Powder
When it comes to SiC powder, one size definitely doesn’t fit all. Here are 10 specific models tailored to different industries and applications:
| Model | Description |
|---|---|
| SiC F240 | Ultra-fine abrasive powder for precision grinding and polishing tasks |
| SiC 99.9% Pure Nano | High-purity nano-sized powder for advanced electronics and coatings |
| SiC Beta-45 | Beta-phase powder optimized for chemical resistance applications |
| SiC Alpha-100 | Alpha-phase powder ideal for structural ceramics |
| SiC Metallurgical | Coarser powder for steelmaking and foundry applications |
| SiC Green Powder | High-purity green SiC for refractory applications |
| SiC Black Powder | Lower purity, cost-effective option for industrial abrasives |
| SiC Coated | Surface-treated SiC powder for enhanced bonding in composites |
| SiC Reinforcement | Used in fiber-reinforced polymers for improved strength and durability |
| SiC Thermal-Grade | Specifically designed for heat sinks and thermal management systems |
Applications of SiC Powder
SiC powder’s versatility means it’s found in a range of applications. Here’s where you’re likely to encounter this remarkable material:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Abrasives | Grinding wheels, sandpaper, and cutting tools |
| Electronics | Semiconductors, power devices, and LED manufacturing |
| Aerospace | High-strength components in jet engines and spacecraft |
| Automotive | Brake pads, clutches, and lightweight structural parts |
| Metallurgy | Enhancing steel hardness and chemical resistance |
| Refractories | Linings for kilns, furnaces, and reactors |
| Thermal Management | Heat sinks and electronic cooling solutions |




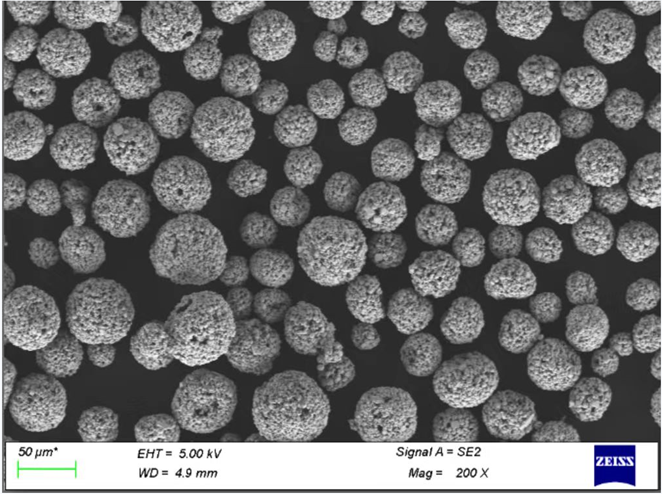

Specifications and Standards of SiC Powder
Understanding the specifications of SiC powder is key to choosing the right type for your application:
| Specification | Range/Detail |
|---|---|
| Particle Size | Nano-scale (20 nm) to coarse (500 μm) |
| Purity | Industrial-grade (90%) to ultra-high-purity (99.999%) |
| Packaging | 1 kg, 5 kg, 25 kg, bulk options |
| Standards | ISO 9001, ASTM E-11 |
| Thermal Conductivity | 120-200 W/mK |
Suppliers and Pricing Details
Looking to purchase SiC powder? Here’s a comparison of leading suppliers and their offerings:
| Supplier | Product | Price Range (per kg) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| GreenTech Materials | SiC 99.5% Pure Green | $25 – $50 | High-grade powder for refractories |
| NanoFab Innovations | SiC Nano-Particle Powder | $200 – $400 | Ultra-high-purity nano-particles |
| Abrasive World | SiC F240 | $10 – $25 | Affordable option for industrial abrasives |
| Thermal Solutions | SiC Thermal-Grade Powder | $150 – $300 | Designed for heat sinks |
| Metallurgy Pro | SiC Metallurgical | $5 – $15 | Cost-effective for foundry applications |
Advantages and Limitations of SiC Powder
Every material has its pros and cons, and SiC powder is no exception. Let’s weigh them up:
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| High hardness and thermal stability | Can be expensive, especially high-purity grades |
| Versatile across multiple industries | Requires specific handling and safety measures |
| Lightweight but strong | Limited electrical conductivity for some uses |
| Chemically inert | Can be brittle under certain stresses |

FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is SiC powder commonly used for? | Abrasives, electronics, metallurgy, and thermal management systems. |
| How does SiC powder compare to diamond abrasives? | SiC is less hard but much more cost-effective, making it widely usable. |
| Is SiC powder environmentally friendly? | Yes, it’s reusable in many applications and has a minimal environmental footprint. |
| Can SiC powder be 3D printed? | Yes, in some advanced manufacturing setups, SiC powder is used in 3D printing for ceramics. |
