Overview of Inert Gas Atomisation
Inert gas atomisation is a fascinating method used to produce metal powders with uniform size, shape, and excellent properties. This technique, widely adopted in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and additive manufacturing, ensures high-quality powders that meet stringent specifications. But what exactly is inert gas atomisation, and why is it so crucial in today’s manufacturing landscape? Let’s dive deep into the intricacies of this process, explore various metal powder models, and understand their applications, specifications, and much more.
What is Inert Gas Atomisation?
Inert gas atomisation is a process where molten metal is transformed into fine powder using high-pressure inert gas, typically argon or nitrogen. The metal is melted in a crucible, and the molten stream is then disintegrated into droplets by a high-velocity gas stream. These droplets solidify into fine, spherical powder particles as they cool down. The use of inert gas prevents oxidation and contamination, ensuring the production of high-purity metal powders.

Process Overview
The inert gas atomisation process can be broken down into several key steps:
- Melting: The metal is melted in a crucible, often using induction heating.
- Atomisation: The molten metal is poured through a nozzle and disintegrated by a high-velocity inert gas stream.
- Solidification: The metal droplets cool and solidify into powder particles.
- Collection: The powder is collected, sieved, and classified based on size.
Types and Characteristics of Metal Powders Produced by Inert Gas Atomisation
The types of metal powders produced using inert gas atomisation vary widely, each with unique compositions and properties tailored for specific applications. Here are ten notable metal powder models:
| Metal Powder Model | Composition | Properties | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| 316L Stainless Steel | Fe-Cr-Ni-Mo | High corrosion resistance, good ductility | Fine, spherical particles, uniform size distribution |
| Inconel 625 | Ni-Cr-Mo-Nb | High strength, oxidation resistance | Superior high-temperature performance |
| Titanium Ti-6Al-4V | Ti-Al-V | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Biocompatible, ideal for medical implants |
| AlSi10Mg | Al-Si-Mg | Good thermal conductivity, lightweight | High strength-to-weight ratio, good castability |
| Cobalt-Chromium | Co-Cr | High wear and corrosion resistance | Biocompatible, used in dental and orthopedic implants |
| H13 Tool Steel | Fe-Cr-Mo-V | High hardness, excellent wear resistance | Ideal for tool and die making |
| Copper-Cr-Zr | Cu-Cr-Zr | High electrical conductivity | Good strength and thermal conductivity |
| Maraging Steel | Fe-Ni-Co-Mo | Ultra-high strength, good toughness | Used in aerospace and tooling |
| Aluminum 6061 | Al-Mg-Si | Good mechanical properties, weldability | Versatile, used in structural components |
| Nickel 718 | Ni-Cr-Fe-Mo | High strength, corrosion resistance | Suitable for high-temperature applications |
Applications of Inert Gas Atomised Metal Powders
Inert gas atomised metal powders find applications across various industries, each leveraging the unique properties of these materials for optimal performance. Here’s a detailed table showcasing different applications:
| Application | Metal Powder Model | Industry | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Additive Manufacturing | Titanium Ti-6Al-4V | Aerospace, Medical | Lightweight, high strength, biocompatible |
| Thermal Spray Coatings | Inconel 625 | Energy, Marine | High corrosion resistance, excellent adhesion |
| Metal Injection Molding | 316L Stainless Steel | Automotive, Medical | Complex shapes, high precision, excellent corrosion resistance |
| Powder Metallurgy | H13 Tool Steel | Tooling, Automotive | High hardness, wear resistance, extended tool life |
| Electrical Components | Copper-Cr-Zr | Electronics | High electrical conductivity, thermal management |
| Structural Parts | Aluminum 6061 | Aerospace, Automotive | Lightweight, good mechanical properties, ease of machining |
| Orthopedic Implants | Cobalt-Chromium | Medical | Biocompatibility, high wear resistance |
| High-Temperature Parts | Nickel 718 | Aerospace, Power | High strength, oxidation resistance, high-temperature stability |
| Automotive Components | Maraging Steel | Automotive, Aerospace | Ultra-high strength, toughness, fatigue resistance |
| Heat Exchangers | AlSi10Mg | HVAC, Automotive | Good thermal conductivity, lightweight |



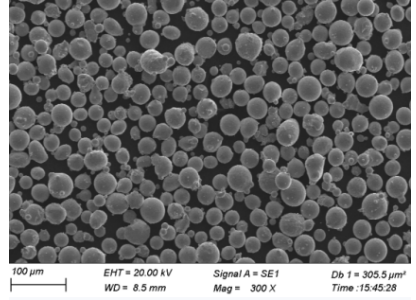


Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards of Inert Gas Atomised Metal Powders
When it comes to metal powders, specifications, sizes, grades, and standards are crucial for ensuring consistent quality and performance. Here’s a detailed table with this information:
| Metal Powder Model | Particle Size Range | Grade | Standards |
|---|---|---|---|
| 316L Stainless Steel | 15-45 µm | ASTM F138 | ISO 5832-1 |
| Inconel 625 | 15-53 µm | AMS 5666 | UNS N06625 |
| Titanium Ti-6Al-4V | 20-45 µm | Grade 5 | ASTM B348, AMS 4928 |
| AlSi10Mg | 10-50 µm | A360 | ISO 3522 |
| Cobalt-Chromium | 15-45 µm | ASTM F75 | ISO 5832-4 |
| H13 Tool Steel | 20-63 µm | AISI H13 | ASTM A681 |
| Copper-Cr-Zr | 10-45 µm | C18150 | ASTM B937 |
| Maraging Steel | 15-53 µm | 18Ni(250) | AMS 6521 |
| Aluminum 6061 | 20-63 µm | 6061-T6 | ASTM B209 |
| Nickel 718 | 15-53 µm | AMS 5662 | UNS N07718 |
Suppliers and Pricing Details for Inert Gas Atomised Metal Powders
Finding the right supplier and understanding the pricing details are essential for sourcing metal powders. Here’s a table with some leading suppliers and approximate pricing:
| Supplier | Metal Powder Model | Price (USD/kg) | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| Höganäs AB | 316L Stainless Steel | 50-70 | Global leader, high-quality metal powders |
| Sandvik Materials | Inconel 625 | 90-110 | Specialized in high-performance alloys |
| GKN Powder Metallurgy | Titanium Ti-6Al-4V | 200-250 | Extensive portfolio, advanced manufacturing techniques |
| LPW Technology | AlSi10Mg | 30-50 | Focused on additive manufacturing powders |
| Carpenter Technology | Cobalt-Chromium | 100-130 | Known for high-performance and specialty alloys |
| Eramet Group | H13 Tool Steel | 25-40 | Offers a range of tool steels and high-performance alloys |
| Vale S.A. | Copper-Cr-Zr | 15-25 | One of the largest producers of nickel and copper alloys |
| Aubert & Duval | Maraging Steel | 70-90 | Expert in high-performance steel and alloys |
| AMETEK Specialty Metal | Aluminum 6061 | 20-30 | Provides a variety of aluminum alloys |
| ATI Metals | Nickel 718 | 80-100 | High-strength and corrosion-resistant alloys |
Advantages and Limitations of Inert Gas Atomisation
Every process has its pros and cons, and inert gas atomisation is no exception. Here’s a comparative table to help you weigh the advantages and limitations:
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | High purity, minimal contamination | Requires inert gas supply |
| Particle Shape | Spherical particles, excellent flowability | May have size distribution limitations |
| Process Control | Precise control over particle size and distribution | High initial setup cost |
| Applications | Suitable for a wide range of applications | Not all metals are suitable for atomisation |
| Scalability | Scalable for large production volumes | Energy-intensive process |
| Consistency | Consistent quality and repeatability | Requires regular maintenance and monitoring |

FAQs
Let’s address some common questions about inert gas atomisation to clear up any doubts you might have:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the main advantage of inert gas atomisation? | The main advantage is the production of high-purity, spherical metal powders with uniform size. |
| Which inert gases are commonly used in this process? | Argon and nitrogen are the most commonly used inert gases. |
| Can all metals be atomised using this method? | Not all metals are suitable; the process is ideal for metals with high melting points. |
| What industries benefit the most from this technology? | Aerospace, automotive, medical, and additive manufacturing industries benefit significantly. |
| How does inert gas atomisation compare to water atomisation? | Inert gas atomisation provides higher purity and spherical particles, whereas water atomisation can lead to oxidation and irregular shapes. |
| Is inert gas atomisation environmentally friendly? | It is relatively environmentally friendly, especially when compared to processes that use water or other reactive media. |
| What are the typical particle sizes produced? | Particle sizes typically range from 10 to 63 µm, depending on the material and process parameters. |
| How is the powder quality controlled? | Quality is controlled through careful monitoring of gas flow, temperature, and particle collection. |
| Are there any special storage requirements for atomised powders? | Yes, they should be stored in a dry, inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation and contamination. |
| What advancements are being made in inert gas atomisation technology? | Advancements include improved process control, new materials, and enhanced scalability. |
Conclusion
Inert gas atomisation is a pivotal technology in the production of high-quality metal powders, meeting the exacting demands of modern manufacturing. Its ability to produce uniform, spherical particles with high purity makes it indispensable in various industries. As we continue to innovate and refine this process, the future of metal powder production looks incredibly promising, opening new avenues for advanced applications and improved material properties.
So, the next time you come across a sleek aerospace component or a robust medical implant, remember the intricate dance of molten metal and inert gas that made it possible. Happy atomising!
