Overview
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is a manufacturing process used to reduce the porosity of metals and improve their mechanical properties and workability. This process involves applying high temperature and high pressure uniformly around the metal, typically using an inert gas such as argon. HIP is widely used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical, and energy, due to its ability to produce components with enhanced strength, density, and fatigue resistance.
Table of Metal Powders Used in HIP
| Metal Powder | Composition | Properties | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V | Titanium alloy with 6% Al and 4% V | High strength, lightweight, corrosion-resistant, excellent biocompatibility | Commonly used in aerospace and medical implants, known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio |
| Inconel 718 | Nickel-chromium alloy | High strength, excellent oxidation and corrosion resistance at high temperatures | Widely used in gas turbines, aerospace, and nuclear reactors due to its superior high-temperature properties |
| 17-4 PH Stainless Steel | Martensitic precipitation-hardened stainless steel | High strength, good corrosion resistance, easy to machine | Used in aerospace, chemical, and petrochemical industries |
| AlSi10Mg | Aluminum alloy with 10% Si and 0.5% Mg | Lightweight, good thermal conductivity, corrosion-resistant | Ideal for automotive and aerospace applications requiring lightweight and strong components |
| CoCrMo | Cobalt-chrome-molybdenum alloy | High wear resistance, good biocompatibility | Commonly used in medical implants and dental applications |
| H13 Tool Steel | Chromium-molybdenum hot work steel | High toughness, good thermal fatigue resistance | Used in die-casting, extrusion, and forging applications |
| 316L Stainless Steel | Austenitic stainless steel | Excellent corrosion resistance, good weldability | Commonly used in marine, medical, and food processing applications |
| Ti-5553 | Titanium alloy with 5% Al, 5% V, 5% Mo, 3% Cr | High strength, good creep resistance, lightweight | Used in aerospace and high-performance automotive applications |
| Maraging Steel | Low-carbon iron-nickel steel | Ultra-high strength, good toughness, easy to machine | Often used in tooling, aerospace, and high-stress applications |
| MP35N | Nickel-cobalt-chromium-molybdenum alloy | Excellent strength, corrosion resistance, biocompatibility | Utilized in medical, aerospace, and subsea applications where both strength and corrosion resistance are critical |

Composition of Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
The composition of materials used in HIP varies based on the specific application and desired properties of the final product. Commonly used metal powders in HIP include titanium alloys, nickel-based superalloys, stainless steels, and tool steels. Each of these materials offers unique characteristics that make them suitable for different industrial applications.
Properties and Characteristics of Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
Hot Isostatic Pressing offers numerous benefits, including improved mechanical properties, enhanced density, and reduced porosity. These characteristics result in components with superior strength, fatigue resistance, and overall durability. Below is a detailed table summarizing the properties and characteristics of HIP materials.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Density | HIP significantly reduces porosity, leading to higher density components |
| Strength | The process enhances the mechanical strength of the material |
| Fatigue Resistance | Improved resistance to fatigue and cyclic loading |
| Toughness | Enhanced toughness due to uniform pressure application |
| Corrosion Resistance | Certain alloys used in HIP exhibit excellent corrosion resistance |
| Biocompatibility | Materials like Ti-6Al-4V and CoCrMo are biocompatible, making them suitable for medical implants |
| Thermal Conductivity | Some HIP materials, such as AlSi10Mg, offer good thermal conductivity |
| Wear Resistance | Alloys like CoCrMo and H13 Tool Steel provide high wear resistance, essential for tooling and medical applications |
Applications of Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
HIP is utilized in a variety of applications across different industries. Its ability to produce components with superior mechanical properties makes it an invaluable process in critical sectors. The table below outlines some common applications of HIP.
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Jet engine components, turbine blades, structural parts |
| Automotive | Engine parts, transmission components, lightweight structures |
| Medical | Implants (hip, knee, dental), surgical instruments |
| Energy | Nuclear reactor components, gas turbines |
| Tooling | Die-casting molds, extrusion dies, forging tools |
| Oil and Gas | Subsea components, drilling tools |
| Defense | Armor plating, weapon components |





Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards of HIP
The specifications and standards for HIP materials vary based on the industry and application. Below is a table that provides an overview of common specifications, sizes, grades, and standards associated with HIP.
| Material | Specifications | Sizes | Grades | Standards |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V | ASTM B348, AMS 4928 | Diameter: 10-500 mm | Grade 5 | ASTM, AMS |
| Inconel 718 | AMS 5662, ASTM B637 | Diameter: 6-400 mm | UNS N07718 | ASTM, AMS |
| 17-4 PH Stainless Steel | ASTM A564, AMS 5643 | Diameter: 8-300 mm | Grade 630 | ASTM, AMS |
| AlSi10Mg | ISO 3522 | Diameter: 5-250 mm | – | ISO |
| CoCrMo | ASTM F75, ISO 5832-12 | Diameter: 4-150 mm | – | ASTM, ISO |
| H13 Tool Steel | ASTM A681, DIN 1.2344 | Diameter: 10-500 mm | H13 | ASTM, DIN |
| 316L Stainless Steel | ASTM A276, AMS 5648 | Diameter: 6-300 mm | 316L | ASTM, AMS |
| Ti-5553 | AMS 4991 | Diameter: 8-200 mm | Grade 5553 | AMS |
| Maraging Steel | AMS 6514 | Diameter: 10-300 mm | Grade 250, 300 | AMS |
| MP35N | ASTM F562, AMS 5844 | Diameter: 5-150 mm | – | ASTM, AMS |
Suppliers and Pricing Details
When considering HIP for your manufacturing needs, it’s essential to know the suppliers and pricing details. The table below lists some reputable suppliers and approximate pricing for various HIP materials.
| Supplier | Material | Price (per kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Carpenter Technology | Ti-6Al-4V | $150 |
| Special Metals | Inconel 718 | $180 |
| Sandvik Materials | 17-4 PH Stainless Steel | $80 |
| ECKA Granules | AlSi10Mg | $50 |
| ATI Metals | CoCrMo | $200 |
| Uddeholm | H13 Tool Steel | $70 |
| Outokumpu | 316L Stainless Steel | $60 |
| TIMET | Ti-5553 | $170 |
| ArcelorMittal | Maraging Steel | $160 |
| Fort Wayne Metals | MP35N | $250 |
Advantages and Limitations of HIP
While HIP offers numerous benefits, it’s essential to understand its advantages and limitations. The table below provides a comparison of the pros and cons of HIP.
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Reduces porosity and improves density | High cost of equipment and operation |
| Enhances mechanical properties | Limited to specific material sizes |
| Increases fatigue and corrosion resistance | Long processing times |
| Uniform pressure application | Requires specialized expertise |
| Improves material homogeneity | Not suitable for all material types |
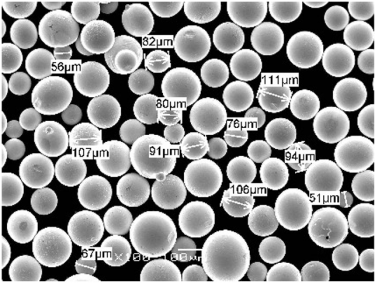
FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)? | HIP is a manufacturing process that applies high pressure and temperature to materials to improve their properties. |
| How does HIP improve material properties? | HIP reduces porosity, increases density, and enhances mechanical properties like strength and fatigue resistance. |
| What materials are commonly used in HIP? | Common materials include titanium alloys, nickel-based superalloys, stainless steels, and tool steels. |
| Are there any limitations to using HIP? | Yes, HIP can be expensive, has long processing times, and is limited to specific material sizes and types. |
| What industries use HIP? | HIP is used in aerospace, automotive, medical, energy, tooling, oil and gas, and defense industries. |
| What are the benefits of HIP? | Benefits include improved density, strength, fatigue resistance, and overall material homogeneity. |
| Is HIP suitable for all materials? | No, HIP is not suitable for all materials. It works best with certain alloys and metals. |
| How does HIP affect the cost of production? | HIP can increase production costs due to the expensive equipment and operational expenses involved. |

