Overview
Vacuum Inert Gas Atomisation (VIGA) is a highly sophisticated process used in the production of metal powders. This technique involves melting metals under a vacuum and then disintegrating the molten metal into fine particles using an inert gas such as argon or nitrogen. The resulting powders are crucial in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and additive manufacturing.
VIGA offers superior control over powder characteristics, such as particle size distribution and purity, making it ideal for applications that demand high-quality materials. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of vacuum inert gas atomisation, explore various metal powder models, and provide detailed insights into their properties, applications, and more.
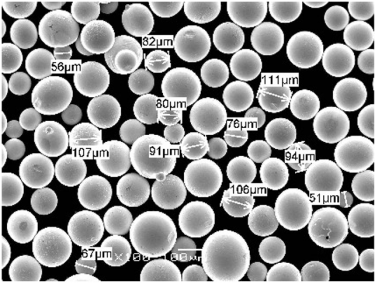
Composition of Vacuum Inert Gas Atomisation
The composition of metal powders produced through VIGA can vary widely depending on the specific metals and alloys used. Here, we list and describe some popular metal powders produced by this method:
| Metal Powder Model | Composition | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| 316L Stainless Steel | Fe-Cr-Ni-Mo | Excellent corrosion resistance, good mechanical properties |
| Inconel 625 | Ni-Cr-Mo-Nb | High strength, oxidation resistance, and weldability |
| Titanium Ti-6Al-4V | Ti-Al-V | High strength-to-weight ratio, excellent biocompatibility |
| Aluminum AlSi10Mg | Al-Si-Mg | Lightweight, good casting properties, high strength |
| Maraging Steel M300 | Fe-Ni-Co-Mo | High strength, toughness, and ductility |
| Copper Cu-CrZr | Cu-Cr-Zr | High electrical and thermal conductivity, good mechanical properties |
| Cobalt-Chromium CoCr | Co-Cr | High wear and corrosion resistance, biocompatibility |
| Nickel 718 | Ni-Cr-Fe | Excellent mechanical properties, resistance to high temperatures |
| Hastelloy X | Ni-Cr-Mo-Fe | High temperature strength, oxidation resistance |
| Tool Steel H13 | Fe-Cr-Mo-Si | High toughness, wear resistance, thermal fatigue resistance |
Characteristics of Vacuum Inert Gas Atomisation
VIGA offers distinct advantages that make it a preferred method for producing metal powders. Let’s examine the key characteristics:
- Particle Size Distribution: VIGA produces powders with a uniform and controlled particle size distribution, essential for high-performance applications.
- Purity: The use of inert gas prevents oxidation and contamination, ensuring high purity of the metal powders.
- Sphericity: Powders produced are highly spherical, improving flowability and packing density, which is crucial for powder-based manufacturing processes.
- Versatility: VIGA can be used to produce a wide range of metal powders, including complex alloys.
Applications of Vacuum Inert Gas Atomisation
Metal powders produced by VIGA find applications in various industries due to their superior properties. Here are some of the primary uses:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Additive Manufacturing | Used in 3D printing for creating complex, high-strength parts |
| Aerospace | Production of lightweight, high-performance components |
| Automotive | Manufacturing of durable and lightweight engine and structural parts |
| Medical Devices | Creating biocompatible implants and prosthetics |
| Tooling | High-strength tools and molds |
| Electronics | High-purity materials for electronic components |






Specifications, Sizes, Grades, Standards
When selecting metal powders for specific applications, it’s crucial to consider their specifications, sizes, grades, and standards:
| Metal Powder Model | Particle Size Range (µm) | Grade | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| 316L Stainless Steel | 15-45, 45-100 | AISI 316L | ASTM A276 |
| Inconel 625 | 15-45, 45-100 | UNS N06625 | ASTM B443 |
| Titanium Ti-6Al-4V | 15-45, 45-100 | Grade 5 | ASTM B348 |
| Aluminum AlSi10Mg | 15-45, 45-100 | – | EN AC-43000 |
| Maraging Steel M300 | 15-45, 45-100 | Grade 300 | ASTM A538 |
| Copper Cu-CrZr | 15-45, 45-100 | – | ASTM B224 |
| Cobalt-Chromium CoCr | 15-45, 45-100 | – | ASTM F75 |
| Nickel 718 | 15-45, 45-100 | UNS N07718 | ASTM B637 |
| Hastelloy X | 15-45, 45-100 | UNS N06002 | ASTM B435 |
| Tool Steel H13 | 15-45, 45-100 | – | ASTM A681 |
Suppliers and Pricing Details
Finding reliable suppliers and understanding the pricing landscape is crucial for sourcing high-quality metal powders. Here are some key suppliers:
| Supplier | Metal Powder Models | Pricing (per kg) | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sandvik | 316L, Ti-6Al-4V, Inconel 625 | $100 – $500 | Sweden |
| Praxair | AlSi10Mg, Maraging Steel M300 | $80 – $450 | USA |
| Höganäs | Copper Cu-CrZr, Cobalt-Chromium | $90 – $400 | Sweden |
| Carpenter Technology | Nickel 718, Hastelloy X | $120 – $550 | USA |
| LPW Technology | Tool Steel H13, 316L, Ti-6Al-4V | $100 – $500 | UK |
Comparing Pros and Cons
Different metal powders offer unique advantages and limitations. Let’s compare some key aspects:
| Metal Powder Model | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| 316L Stainless Steel | Corrosion resistance, mechanical properties | Higher cost compared to other stainless steels |
| Inconel 625 | High strength, oxidation resistance | Expensive, difficult to machine |
| Titanium Ti-6Al-4V | Strength-to-weight ratio, biocompatibility | Costly, reactive with oxygen at high temperatures |
| Aluminum AlSi10Mg | Lightweight, strength | Lower strength than steel |
| Maraging Steel M300 | High strength, ductility | Expensive, requires aging process |
| Copper Cu-CrZr | Conductivity, mechanical properties | Lower strength than some other alloys |
| Cobalt-Chromium CoCr | Wear and corrosion resistance | Costly, difficult to machine |
| Nickel 718 | Mechanical properties, temperature resistance | Expensive, difficult to machine |
| Hastelloy X | High temperature strength, oxidation resistance | Expensive, limited machinability |
| Tool Steel H13 | Toughness, wear resistance | Prone to cracking during heat treatment |
FAQ
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is Vacuum Inert Gas Atomisation? | It’s a process that produces metal powders by melting metals under vacuum and disintegrating them with inert gas. |
| Why use inert gas in atomisation? | Inert gas prevents oxidation and contamination, ensuring high purity of the powders. |
| What are the advantages of VIGA powders? | They offer uniform particle size, high purity, and excellent flowability, among other benefits. |
| Which industries benefit from VIGA powders? | Aerospace, automotive, medical devices, tooling, and electronics industries benefit significantly. |
| How does VIGA compare to other powder production methods? | VIGA provides better control over particle size and purity compared to many other methods. |
| What are common materials used in VIGA? | Stainless steels, superalloys, titanium alloys, aluminum alloys, and more. |
| Can VIGA powders be used in additive manufacturing? | Yes, they are highly suitable due to their uniform size and high quality. |
| Are there limitations to using VIGA powders? | They can be more expensive and difficult to machine, depending on the material. |
| How do I choose the right metal powder for my application? | Consider the specific properties required, such as strength, corrosion resistance, and conductivity. |
| Where can I purchase high-quality VIGA powders? | Reputable suppliers include Sandvik, Praxair, Höganäs, Carpenter Technology, and LPW Technology. |
