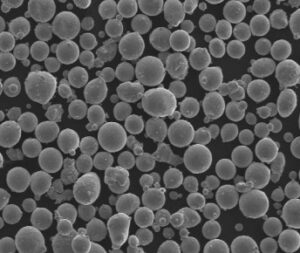
Overview of Tool Steel Powder
Tool steel powder is a specialized material used in various industrial applications, particularly in the manufacturing of tools and components that require exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and toughness. These powders are finely milled forms of tool steel, which is a class of steel known for its ability to retain a sharp cutting edge, resist deformation, and withstand high temperatures.
Tool steel powders are essential in the production of high-performance tools and components through processes like Additive Manufacturing (AM), Metal Injection Molding (MIM), and Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP). The versatility of tool steel powder lies in its ability to be molded into complex shapes while maintaining the inherent properties of the steel, making it an invaluable resource in industries ranging from automotive to aerospace.

Types of Tool Steel Powder
The diversity in tool steel powders comes from their varied compositions and the specific properties each type brings to the table. Here’s a detailed table that categorizes the different types of tool steel powder, their composition, and their unique characteristics.
| Type | Composition | Key Properties | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| M2 High-Speed Steel | Tungsten (6%), Molybdenum (5%), Vanadium (2%), Carbon (0.85%) | High hardness, excellent wear resistance, high temperature stability | Cutting tools, punches, dies |
| D2 Tool Steel | Carbon (1.5%), Chromium (12%), Vanadium (1%), Molybdenum (0.75%) | High wear resistance, excellent toughness, moderate hardness | Dies, knives, industrial blades |
| A2 Tool Steel | Carbon (1%), Chromium (5%), Molybdenum (1%), Vanadium (0.25%) | Good wear resistance, tough, excellent dimensional stability | Punches, dies, cutting tools |
| H13 Tool Steel | Chromium (5%), Molybdenum (1.5%), Vanadium (1%), Silicon (1%) | High toughness, excellent thermal stability, good wear resistance | Extrusion dies, injection molds, hot forging tools |
| O1 Tool Steel | Carbon (0.95%), Chromium (0.6%), Tungsten (0.5%) | High machinability, good wear resistance, oil-hardenable | Knives, bushings, gauges, cutting tools |
| S7 Shock-Resistant Steel | Carbon (0.5%), Chromium (3.25%), Molybdenum (1.4%), Silicon (0.25%) | High impact resistance, good hardness, shock-resistant | Chisels, hammers, heavy-duty dies |
| P20 Tool Steel | Chromium (2%), Molybdenum (0.5%), Nickel (1%) | High polishability, good toughness, moderate wear resistance | Plastic injection molds, die casting dies |
| T15 High-Speed Steel | Tungsten (12.5%), Cobalt (5%), Vanadium (5%), Carbon (1.5%) | Extremely high hardness, excellent wear resistance | Precision cutting tools, taps, dies |
| M42 High-Speed Steel | Cobalt (8%), Tungsten (10%), Molybdenum (1.5%), Vanadium (1.2%) | High red hardness, excellent cutting ability, good wear resistance | Heavy-duty cutting tools, drills, milling cutters |
| H11 Tool Steel | Chromium (5%), Molybdenum (1.25%), Vanadium (0.4%) | High toughness, good thermal shock resistance, moderate wear resistance | Hot work tools, extrusion dies, plastic molds |
Characteristics of Tool Steel Powder
Tool steel powders are not just any ordinary materials. Their distinct characteristics are what make them ideal for high-performance applications. Here’s a closer look at some of the key characteristics:
- Hardness: Tool steel powders, when sintered, exhibit exceptional hardness, making them suitable for applications where wear resistance is critical. For instance, high-speed steel (HSS) powders like M2 and T15 are renowned for their hardness, which allows them to maintain a sharp cutting edge even at high temperatures.
- Toughness: Despite their hardness, tool steel powders like S7 and H13 are engineered to be tough, meaning they can absorb energy without fracturing. This toughness is crucial for tools that undergo significant impact, such as chisels and hammers.
- Wear Resistance: Tool steels such as D2 and M42 are formulated to resist wear, extending the life of the tools made from these powders. This wear resistance is especially important in applications where tools are subjected to abrasive materials or high-stress conditions.
- Thermal Stability: Tool steels like H13 and H11 are designed to withstand high temperatures without losing their hardness, making them ideal for hot-working tools and molds used in processes like extrusion and die-casting.
- Machinability: Some tool steels, like O1 and P20, are easier to machine, which means they can be shaped and finished with greater ease, reducing production costs and time.
Advantages of Tool Steel Powder
Using tool steel powder in manufacturing offers several advantages, which we’ll explore in this section:
- Precision in Manufacturing: Tool steel powders allow for precise control over the composition and distribution of the alloying elements, resulting in uniform properties throughout the final product. This precision is particularly beneficial in additive manufacturing, where complex geometries can be produced with consistent quality.
- Flexibility in Design: Unlike traditional ingot-based methods, powder metallurgy allows for the creation of complex shapes and sizes with minimal material wastage. This flexibility is ideal for industries that require custom tools and components.
- Improved Material Utilization: With tool steel powder, manufacturers can achieve near-net-shape parts, meaning the parts are very close to the final desired shape, which reduces the need for extensive machining and material waste.
- Enhanced Mechanical Properties: The fine grain structure of tool steel powders often results in superior mechanical properties compared to conventionally produced tool steels. This enhancement translates to better performance in demanding applications.
- Sustainability: Powder metallurgy processes, such as additive manufacturing, often produce less waste and use less energy compared to traditional manufacturing methods, making tool steel powders a more sustainable choice.
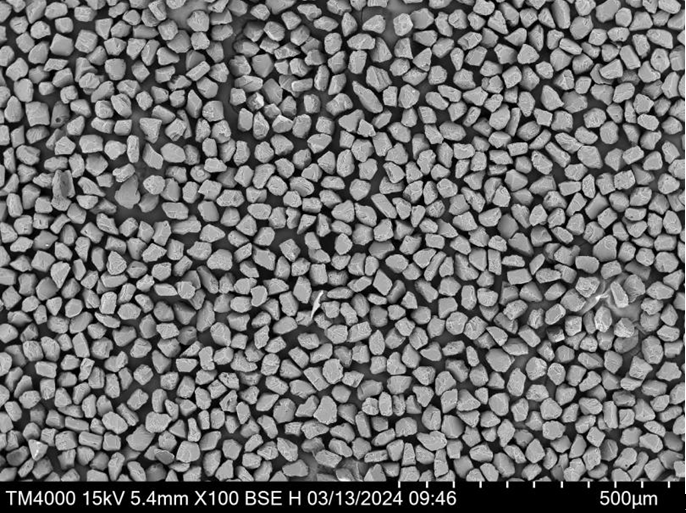
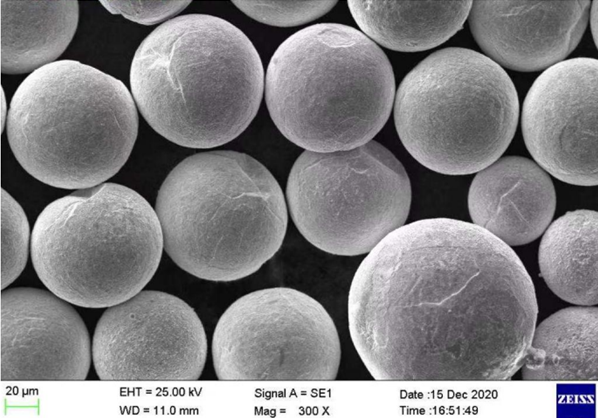

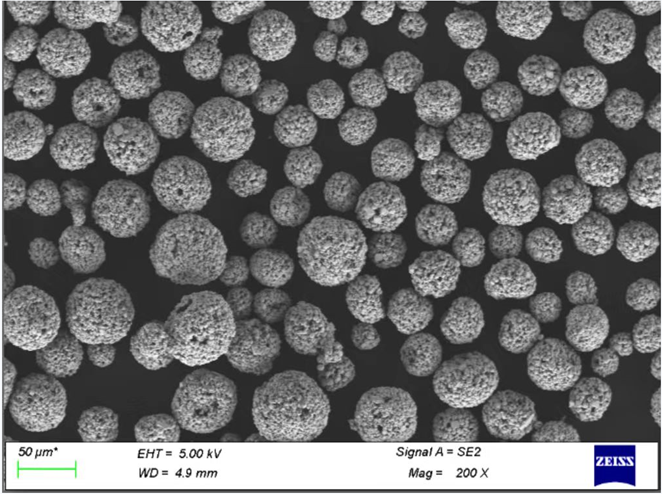




Applications of Tool Steel Powder
Tool steel powder is indispensable in a variety of applications, thanks to its unique properties. Here’s a detailed table showcasing the common applications of different types of tool steel powders.
| Application | Tool Steel Powder Type | Reason for Use |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Tools | M2, M42, T15 | High hardness, wear resistance, heat resistance |
| Injection Molds | H13, P20 | High toughness, thermal stability, good machinability |
| Extrusion Dies | H13, H11 | Thermal shock resistance, toughness |
| Industrial Knives and Blades | D2, A2 | Wear resistance, edge retention |
| Chisels and Hammers | S7, A2 | Impact resistance, toughness |
| Plastic Injection Molds | P20, H13 | Polishability, toughness |
| Die Casting Dies | H13, H11 | Thermal stability, toughness |
| High-Performance Drills and Taps | M42, T15 | Red hardness, wear resistance, cutting ability |
| Punches and Dies | A2, D2 | Toughness, wear resistance, dimensional stability |
| Precision Cutting Tools | T15, M2 | High hardness, wear resistance |
Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards
When selecting tool steel powder for a specific application, it’s crucial to consider the specifications, sizes, grades, and standards that govern its use. Here’s a table outlining these important details.
| Type | Grades Available | Particle Sizes | Standards (e.g., ASTM, DIN) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M2 High-Speed Steel | M2, PM M2 | -325 mesh, -400 mesh | ASTM A600, DIN 1.3343 |
| D2 Tool Steel | D2, PM D2 | -325 mesh, -400 mesh | ASTM A681, DIN 1.2379 |
| A2 Tool Steel | A2, PM A2 | -325 mesh, -400 mesh | ASTM A681, DIN 1.2363 |
| H13 Tool Steel | H13, PM H13 | -325 mesh, -400 mesh | ASTM A681, DIN 1.2344 |
| O1 Tool Steel | O1, PM O1 | -325 mesh, -400 mesh | ASTM A681, DIN 1.2510 |
| S7 Shock-Resistant Steel | S7, PM S7 | -325 mesh, -400 mesh | ASTM A681, DIN 1.2357 |
| P20 Tool Steel | P20, PM P20 | -325 mesh, -400 mesh | ASTM A681, DIN 1.2311 |
| T15 High-Speed Steel | T15, PM T15 | -325 mesh, -400 mesh | ASTM A600, DIN 1.3247 |
| M42 High-Speed Steel | M42, PM M42 | -325 mesh, -400 mesh | ASTM A600, DIN 1.3247 |
| H11 Tool Steel | H11, PM H11 | -325 mesh, -400 mesh | ASTM A681, DIN 1.2343 |
Suppliers and Pricing Details
Here’s a table listing some prominent suppliers of tool steel powder, along with indicative pricing details. Note that prices can vary based on order quantity, location, and specific requirements.
| Supplier | Location | Type of Powder | Indicative Price (per kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy Tool Steel | USA | M2, D2, A2, H13 | $25 – $45 |
| Metal Powder Co. | Germany | D2, O1, S7 | €20 – €40 |
| Powder Metals Inc. | USA | M42, T15, H11 | $30 – $60 |
| Precision Powders | UK | A2, P20, H13 | £22 – £48 |
| Techno Steel Ltd. | Japan | M2, T15, D2 | ¥3000 – ¥6000 |
| Steel Supply Co. | Australia | S7, H11, P20 | AUD 30 – AUD 55 |
| Global Metals | China | M42, H13, P20 | CNY 150 – CNY 300 |
| Advanced Tooling | USA | M2, D2, T15 | $28 – $50 |
| Ultimate Metals | India | A2, D2, M42 | INR 2000 – INR 4000 |
| Metallurgy Pro | South Korea | M2, S7, H13 | KRW 25000 – KRW 50000 |
Pros and Cons of Tool Steel Powder
Here’s a balanced view of the pros and cons associated with tool steel powders.
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| High Performance | Cost |
| Tool steel powders deliver exceptional performance in terms of hardness, toughness, and wear resistance, making them ideal for demanding applications. | Tool steel powders can be more expensive compared to traditional bulk materials, which may impact budget considerations. |
| Precision and Flexibility | Processing Complexity |
| The ability to produce complex shapes and sizes with high precision reduces material waste and allows for custom designs. | The manufacturing process for tool steel powders can be complex, requiring specialized equipment and expertise. |
| Enhanced Mechanical Properties | Limited Availability |
| The fine grain structure often results in improved mechanical properties, providing better overall performance. | Some specific types of tool steel powders may have limited availability or longer lead times. |
| Reduced Material Waste | Environmental Considerations |
| Near-net-shape production reduces material wastage and is more environmentally friendly. | The production and disposal of metal powders can have environmental impacts, which need to be managed responsibly. |

FAQ
Here’s a handy FAQ section to address some common questions about tool steel powder.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is tool steel powder? | Tool steel powder is a finely milled form of tool steel used in various manufacturing processes like additive manufacturing and metal injection molding. |
| How is tool steel powder produced? | It is produced by pulverizing tool steel into fine particles, which are then used in powder metallurgy processes to create high-performance components. |
| What are the benefits of using tool steel powder? | Benefits include high precision, reduced material waste, enhanced mechanical properties, and the ability to produce complex shapes. |
| What are some common applications of tool steel powder? | Common applications include cutting tools, molds, dies, and high-performance industrial components. |
| How do I choose the right tool steel powder? | Consider the specific requirements of your application, including hardness, toughness, wear resistance, and thermal stability. |
| Where can I purchase tool steel powder? | Tool steel powder can be purchased from specialized metal suppliers, industrial distributors, and manufacturers of powder metallurgy products. |
Conclusion
Tool steel powder is a versatile and high-performance material that plays a crucial role in modern manufacturing processes. Its unique properties, such as exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and flexibility in design, make it a preferred choice for a wide range of industrial applications. Understanding the different types of tool steel powders, their characteristics, and their applications can help in selecting the right material for specific needs. As industries continue to evolve and demand more from their tools and components, the use of tool steel powder will likely expand, offering new possibilities and innovations in manufacturing.
If you have more questions or need further information about tool steel powders, feel free to reach out to suppliers or industry experts who can provide additional insights and assistance.