When it comes to the world of metallurgy and material science, spherical gas atomized alloy powder holds a place of prominence. This highly versatile and specialized material is crucial in a range of industries from aerospace to additive manufacturing. Let’s dive into the fascinating realm of spherical gas atomized alloy powder, exploring its composition, properties, applications, and more.
Overview of Spherical Gas Atomized Alloy Powder
Spherical gas atomized alloy powder is created through a process known as gas atomization, where molten metal is dispersed into fine droplets using a high-pressure gas stream. This method produces powders with a spherical shape, offering superior flowability and packing density compared to irregularly shaped powders.
Key Features
- Shape: Spherical
- Particle Size: Typically ranges from a few micrometers to hundreds of micrometers
- High Purity: Minimal contamination due to controlled production environment
- Versatility: Suitable for various applications including additive manufacturing, thermal spraying, and metal injection molding
Benefits
- Enhanced Flowability: Easier to handle and process
- Consistent Packing Density: Better performance in applications requiring uniformity
- High Performance: Excellent mechanical and physical properties

Types of Spherical Gas Atomized Alloy Powder
Below are some of the widely used models of spherical gas atomized alloy powders, each with unique compositions and properties.
| Model | Composition | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 316L | Iron, Chromium, Nickel, Molybdenum | Corrosion resistance, excellent mechanical properties | Medical implants, marine applications |
| 17-4PH | Iron, Chromium, Nickel, Copper | High strength, good corrosion resistance | Aerospace components, mechanical parts |
| Inconel 718 | Nickel, Chromium, Iron, Molybdenum | High-temperature strength, oxidation resistance | Turbine blades, aerospace engines |
| Ti6Al4V | Titanium, Aluminum, Vanadium | High strength-to-weight ratio, biocompatibility | Medical implants, aerospace structures |
| AlSi10Mg | Aluminum, Silicon, Magnesium | Good casting properties, high thermal conductivity | Automotive parts, heat exchangers |
| CoCrMo | Cobalt, Chromium, Molybdenum | High wear resistance, biocompatibility | Medical implants, dental devices |
| Hastelloy X | Nickel, Chromium, Iron, Molybdenum | Excellent oxidation resistance, good formability | Gas turbine engines, chemical processing |
| Maraging Steel | Iron, Nickel, Cobalt, Molybdenum | Ultra-high strength, good toughness | Aerospace tooling, high-performance gears |
| Copper 85/15 | Copper, Tin | High electrical conductivity, good mechanical strength | Electrical components, thermal management systems |
| NiCrBSi | Nickel, Chromium, Boron, Silicon | Wear resistance, good hardness | Surface coatings, repair applications |
Composition of Spherical Gas Atomized Alloy Powder
Understanding the composition of these powders is crucial for selecting the right material for your specific application. Here’s a breakdown of the elemental makeup for some common powders.
| Model | Elemental Composition (%) |
|---|---|
| 316L | Fe: 62-72, Cr: 16-18, Ni: 10-14, Mo: 2-3 |
| 17-4PH | Fe: 65-75, Cr: 15-17, Ni: 3-5, Cu: 3-5 |
| Inconel 718 | Ni: 50-55, Cr: 17-21, Fe: Bal., Mo: 2.8-3.3 |
| Ti6Al4V | Ti: Bal., Al: 5.5-6.75, V: 3.5-4.5 |
| AlSi10Mg | Al: Bal., Si: 9-11, Mg: 0.2-0.4 |
| CoCrMo | Co: Bal., Cr: 27-30, Mo: 5-7 |
| Hastelloy X | Ni: 47-52, Cr: 20-23, Fe: 18-20, Mo: 8-10 |
| Maraging Steel | Fe: Bal., Ni: 18-19, Co: 8-9, Mo: 4-5 |
| Copper 85/15 | Cu: 85, Sn: 15 |
| NiCrBSi | Ni: Bal., Cr: 14-18, B: 2.5-3.5, Si: 3-4.5 |
Characteristics of Spherical Gas Atomized Alloy Powder
Physical Properties
Spherical gas atomized alloy powders exhibit specific physical characteristics that make them ideal for high-performance applications.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Particle Size Distribution | Uniform size distribution ensures consistent behavior during processing |
| Morphology | Spherical shape provides excellent flowability and packing density |
| Density | High bulk density compared to irregular powders |
| Surface Area | Lower surface area due to spherical shape, reducing oxidation and contamination |
Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties of these powders are tailored through their composition and atomization process.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | High tensile strength for demanding applications |
| Hardness | Superior hardness for wear resistance |
| Ductility | Good ductility allows for complex shape formation |
| Fatigue Resistance | Excellent fatigue resistance for long-lasting performance |



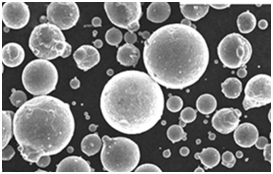

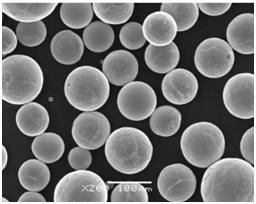
Applications of Spherical Gas Atomized Alloy Powder
Spherical gas atomized alloy powders find use across a variety of sectors due to their superior properties.
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, structural components, fasteners |
| Medical | Implants, prosthetics, dental devices |
| Automotive | Engine components, heat exchangers, lightweight structures |
| Additive Manufacturing | 3D printing of complex geometries, rapid prototyping |
| Thermal Spraying | Coatings for corrosion and wear resistance |
| Metal Injection Molding | Precision parts for electronics, firearms, and tools |
Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards
When selecting a spherical gas atomized alloy powder, it’s essential to consider various specifications and standards to ensure suitability for your application.
| Model | Specifications | Sizes (µm) | Grades | Standards |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316L | ASTM F138, ISO 5832-1 | 15-45, 45-105 | Medical, Industrial | ASTM, ISO |
| 17-4PH | AMS 5604, ASTM A693 | 10-45, 45-150 | Aerospace, Industrial | AMS, ASTM |
| Inconel 718 | AMS 5662, ASTM B637 | 15-45, 45-105 | Aerospace, Industrial | AMS, ASTM |
| Ti6Al4V | ASTM F1472, ISO 5832-3 | 15-45, 45-105 | Medical, Aerospace | ASTM, ISO |
| AlSi10Mg | DIN 1712 | 20-63, 63-106 | Industrial | DIN |
| CoCrMo | ASTM F75, ISO 5832-12 | 10-45, 45-105 | Medical, Industrial | ASTM, ISO |
| Hastelloy X | AMS 5536, ASTM B435 | 15-45, 45-105 | Aerospace, Industrial | AMS, ASTM |
| Maraging Steel | AMS 6514, ASTM A538 | 10-45, 45-150 | Aerospace, Industrial | AMS, ASTM |
| Copper 85/15 | ASTM B505 | 15-45, 45-105 | Industrial | ASTM |
| NiCrBSi | AWS A5.21 | 10-53, 53-150 | Industrial | AWS |
Suppliers and Pricing Details
Pricing and availability are crucial factors when procuring spherical gas atomized alloy powders. Here are some prominent suppliers and an overview of pricing.
| Supplier | Model | Price (per kg) | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Höganäs AB | 316L, Ti6Al4V | $120-$150 | In stock |
| Carpenter Technology | 17-4PH, Inconel 718 | $150-$200 | In stock |
| Arcam AB | AlSi10Mg, CoCrMo | $100-$130 | In stock |
| LPW Technology | Hastelloy X, Maraging Steel | $180-$220 | In stock |
| GKN Hoeganaes | Copper 85/15, NiCrBSi | $90-$120 | In stock |
Comparing Pros and Cons of Different Powders
Each type of spherical gas atomized alloy powder comes with its own set of advantages and limitations. Here’s
a comparison to help you choose the right one for your needs.
| Model | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| 316L | Excellent corrosion resistance, good mechanical properties | Higher cost |
| 17-4PH | High strength, good corrosion resistance | Susceptible to stress corrosion cracking |
| Inconel 718 | High-temperature strength, oxidation resistance | Expensive |
| Ti6Al4V | High strength-to-weight ratio, biocompatibility | Difficult to machine |
| AlSi10Mg | Good casting properties, thermal conductivity | Lower strength compared to other alloys |
| CoCrMo | High wear resistance, biocompatibility | High cost |
| Hastelloy X | Excellent oxidation resistance, good formability | Expensive |
| Maraging Steel | Ultra-high strength, good toughness | High cost, requires aging treatment |
| Copper 85/15 | High electrical conductivity, good mechanical strength | Susceptible to corrosion |
| NiCrBSi | Wear resistance, good hardness | Brittleness in some applications |
FAQ
What is spherical gas atomized alloy powder?
Spherical gas atomized alloy powder is a fine metallic powder produced through gas atomization, where molten metal is dispersed into spherical particles using a high-pressure gas stream.
Why are spherical gas atomized alloy powders preferred?
Their spherical shape offers superior flowability and packing density, making them ideal for various industrial applications, including additive manufacturing and thermal spraying.
What are the common applications of these powders?
They are used in aerospace, medical, automotive, additive manufacturing, thermal spraying, and metal injection molding due to their excellent mechanical and physical properties.
How are these powders produced?
They are produced through gas atomization, where molten metal is dispersed into fine droplets using a high-pressure gas stream, resulting in spherical particles.
What factors should be considered when selecting a powder?
Considerations include composition, particle size distribution, mechanical properties, application requirements, and cost.
Where can I buy spherical gas atomized alloy powder?
Prominent suppliers include Höganäs AB, Carpenter Technology, Arcam AB, LPW Technology, and GKN Hoeganaes.
Are these powders expensive?
The cost varies depending on the alloy type and supplier, typically ranging from $90 to $220 per kilogram.
What are the benefits of using spherical powders in additive manufacturing?
Their superior flowability and packing density result in better layer adhesion and overall part quality in 3D printing processes.
Can these powders be used in medical applications?
Yes, powders like 316L and CoCrMo are commonly used for medical implants and devices due to their biocompatibility.
What are the limitations of these powders?
Some powders may have higher costs, be difficult to machine, or have specific weaknesses like stress corrosion cracking or brittleness in certain applications.
In conclusion, spherical gas atomized alloy powders offer a multitude of benefits for various industries. Their unique properties, derived from their composition and production process, make them indispensable for high-performance applications. Whether you’re in aerospace, medical, or additive manufacturing, understanding the intricacies of these powders will help you make informed decisions and leverage their full potential.
