Overview of Quality Metal Powder
Metal powders are finely divided solid materials that play a crucial role in various industrial applications. From additive manufacturing (3D printing) to powder metallurgy, these powders are the building blocks for creating advanced materials with specific properties. In this guide, we’ll dive deep into the world of quality metal powders, exploring their composition, properties, uses, and more.
We’ll cover everything from the basics to the most advanced details, helping you understand why quality matters in metal powders, and how to choose the right type for your specific needs.
What is Quality Metal Powder?
Quality metal powder is a term that encompasses various metal-based powders that have been refined, processed, and manufactured to meet specific standards for industrial and commercial applications. These powders are characterized by their purity, particle size, and uniformity, which ensure consistent performance in their end-use applications.
The Importance of Quality in Metal Powder
Why is quality so crucial when it comes to metal powders? Imagine trying to bake a cake with low-quality flour. The result would be inconsistent at best, and inedible at worst. Similarly, using subpar metal powder in manufacturing processes can lead to defects, reduced performance, and even catastrophic failure in critical applications.
High-quality metal powders ensure that the final products exhibit the desired strength, durability, and other key properties. They also contribute to efficient manufacturing processes by providing uniformity and consistency, reducing the need for rework or adjustments.
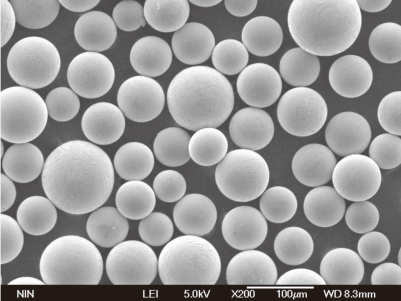
Types of Quality Metal Powders
When it comes to quality metal powders, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. Different applications require different types of metal powders, each with its unique composition, properties, and advantages. Let’s explore some of the most commonly used metal powders in the industry.
| Metal Powder | Composition | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Powder | Pure Aluminum (Al) | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, excellent thermal conductivity | Aerospace, automotive, pyrotechnics |
| Copper Powder | Pure Copper (Cu) | High electrical conductivity, excellent thermal conductivity | Electrical components, thermal management systems |
| Iron Powder | Pure Iron (Fe) | Magnetic properties, good strength, cost-effective | Powder metallurgy, magnetic materials, automotive parts |
| Stainless Steel Powder | Iron, Chromium, Nickel | Corrosion resistance, high strength, durability | Medical devices, aerospace components, automotive parts |
| Titanium Powder | Pure Titanium (Ti) | High strength-to-weight ratio, biocompatibility, corrosion resistance | Aerospace, medical implants, automotive components |
| Nickel Powder | Pure Nickel (Ni) | High-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, magnetic properties | Superalloys, batteries, electronics |
| Cobalt-Chromium Powder | Cobalt (Co), Chromium (Cr) | High wear resistance, biocompatibility, corrosion resistance | Medical implants, dental restorations, aerospace components |
| Tungsten Powder | Pure Tungsten (W) | High density, high melting point, excellent hardness | Cutting tools, radiation shielding, aerospace components |
| Magnesium Powder | Pure Magnesium (Mg) | Lightweight, good strength, high reactivity | Pyrotechnics, aerospace, automotive |
| Zinc Powder | Pure Zinc (Zn) | Good corrosion resistance, low melting point, sacrificial anode properties | Galvanizing, batteries, paints and coatings |
Aluminum Powder
Aluminum powder is one of the most widely used metal powders due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. It’s often employed in the aerospace and automotive industries, where reducing weight is crucial for improving fuel efficiency and performance. Additionally, aluminum powder is used in pyrotechnics to produce bright, white sparks.
Copper Powder
Copper powder is prized for its high electrical and thermal conductivity, making it ideal for electrical components and thermal management systems. Whether it’s in the production of conductive inks or as a component in friction materials, copper powder is essential for many high-tech applications.
Iron Powder
Iron powder, known for its magnetic properties and good strength, is a cost-effective option for various industrial applications. It’s extensively used in powder metallurgy to create complex shapes that would be difficult or expensive to produce using traditional methods. Additionally, iron powder is used in the automotive industry for making parts like gears and bearings.
Stainless Steel Powder
Stainless steel powder is a blend of iron, chromium, and nickel, offering excellent corrosion resistance and high strength. This makes it perfect for medical devices, aerospace components, and automotive parts that need to withstand harsh environments.
Titanium Powder
Titanium powder is renowned for its high strength-to-weight ratio, making it a preferred material in aerospace and medical applications. Its biocompatibility also makes it suitable for medical implants, while its corrosion resistance ensures longevity in demanding environments.
Nickel Powder
Nickel powder is valued for its high-temperature resistance and corrosion resistance, making it a key component in superalloys used in the aerospace industry. It’s also used in batteries and electronics, where its magnetic properties are advantageous.
Cobalt-Chromium Powder
Cobalt-chromium powder combines the wear resistance of cobalt with the corrosion resistance of chromium, making it ideal for medical implants and dental restorations. Its biocompatibility ensures that it performs well inside the human body, while its durability makes it a reliable choice for aerospace components.
Tungsten Powder
Tungsten powder is known for its high density, high melting point, and excellent hardness. These properties make it suitable for cutting tools, radiation shielding, and aerospace components that need to withstand extreme conditions.
Magnesium Powder
Magnesium powder is the go-to choice for applications where weight reduction is critical. It’s lightweight, yet strong, making it ideal for aerospace and automotive industries. Additionally, magnesium powder is highly reactive, making it a key ingredient in pyrotechnics.
Zinc Powder
Zinc powder is widely used for its corrosion resistance and sacrificial anode properties, making it essential in galvanizing processes to protect steel from rusting. It’s also used in batteries, paints, and coatings for its protective and conductive properties.
Composition of Quality Metal Powder
The composition of metal powders is a critical factor that determines their properties and suitability for different applications. Metal powders can be pure metals, alloys, or a combination of different materials to achieve specific characteristics.
| Metal Powder | Primary Elements | Additional Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Powder | Aluminum (Al) | Silicon (Si), Iron (Fe), Titanium (Ti) |
| Copper Powder | Copper (Cu) | Phosphorus (P), Nickel (Ni), Zinc (Zn) |
| Iron Powder | Iron (Fe) | Carbon (C), Manganese (Mn), Sulfur (S) |
| Stainless Steel Powder | Iron (Fe), Chromium (Cr), Nickel (Ni) | Molybdenum (Mo), Carbon (C), Manganese (Mn) |
| Titanium Powder | Titanium (Ti) | Aluminum (Al), Vanadium (V) |
| Nickel Powder | Nickel (Ni) | Chromium (Cr), Iron (Fe), Molybdenum (Mo) |
| Cobalt-Chromium Powder | Cobalt (Co), Chromium (Cr) | Molybdenum (Mo), Tungsten (W), Nickel (Ni) |
| Tungsten Powder | Tungsten (W) | Carbon (C), Nickel (Ni), Iron (Fe) |
| Magnesium Powder | Magnesium (Mg) | Aluminum (Al), Zinc (Zn), Manganese (Mn) |
| Zinc Powder | Zinc (Zn) | Aluminum (Al), Copper (Cu), Iron (Fe) |
Each metal powder’s composition is carefully controlled to meet specific standards and performance criteria. For example, the addition of elements like silicon and iron in aluminum powder can enhance its strength and hardness, while the presence of chromium and nickel in stainless steel powder provides corrosion resistance.
Properties of Quality Metal Powder
The properties of metal powders are determined by their composition, particle size, and shape. These properties influence how the powders behave during processing and how they perform in their final applications.
Physical Properties
| Property | Aluminum Powder | Copper Powder | Iron Powder | Stainless Steel Powder | Titanium Powder |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm³) | 2.7 | 8.9 | 7.8 | 7.9 | 4.5 |
| Melting Point (°C) | 660 | 1,085 | 1,538 | 1,400-1,530 | 1,668 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | 237 | 401 | 80 | 15-30 | 22 |
| Electrical Conductivity (S/m) | 37 x 10^6 | 58 x 10^6 | 10 x 10^6 | 1-10 x 10^6 | 2 x 10^6 |
| Particle Size (µm) | 10-50 | 5-100 | 5-50 | 10-100 | 10-50 |
Mechanical Properties
| Property | Aluminum Powder | Copper Powder | Iron Powder | Stainless Steel Powder | Titanium Powder |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV) | 45-100 | 60-140 | 60-90 | 150-250 | 250-350 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 70-150 | 200-350 | 150-250 | 600-1,200 | 800-1,200 |
| Elongation (%) | 3-12 | 20-45 | 2-10 | 25-50 | 15-25 |
Chemical Properties
| Property | Aluminum Powder | Copper Powder | Iron Powder | Stainless Steel Powder | Titanium Powder |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Moderate | Low | Excellent | High |
| Oxidation Resistance | Moderate | Low | High | Excellent | Excellent |





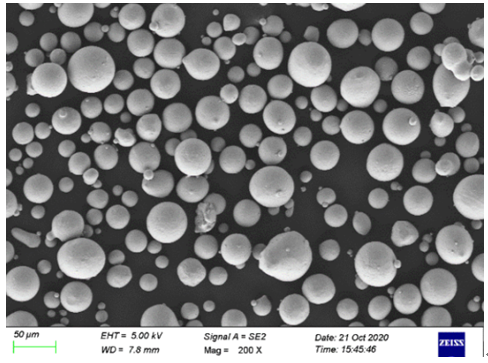
Applications of Quality Metal Powders
Metal powders are used in a wide range of applications, each exploiting their unique properties. Here’s a look at some common applications and the metal powders that best fit those needs:
| Application | Metal Powder | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) | Aluminum, Titanium, Stainless Steel | These powders are used to create complex geometries and parts with high strength and precision. |
| Powder Metallurgy | Iron, Stainless Steel, Copper | Used to produce parts with high precision and complex shapes that are cost-effective to produce. |
| Aerospace Components | Titanium, Aluminum, Cobalt-Chromium | Critical for parts that require high strength-to-weight ratios and resistance to extreme conditions. |
| Automotive Parts | Iron, Stainless Steel, Aluminum | For manufacturing durable and high-performance parts like engine components and transmission gears. |
| Medical Implants | Titanium, Cobalt-Chromium | Biocompatible materials used for implants and prosthetics. |
| Electronic Components | Copper, Nickel | Essential for high-conductivity components such as connectors and circuit boards. |
| Thermal Management Systems | Copper, Aluminum | Used in heat sinks and thermal interface materials to manage heat dissipation. |
| Cutting Tools | Tungsten, Cobalt-Chromium | Known for their hardness and wear resistance, ideal for cutting tools and drill bits. |
| Pyrotechnics | Magnesium, Aluminum | For creating flares and fireworks with bright colors and intense effects. |
| Galvanizing | Zinc | Provides corrosion protection for steel and iron products. |
Specifications, Sizes, and Grades of Metal Powders
The specifications, sizes, and grades of metal powders can significantly affect their performance in various applications. Here’s a detailed look:
| Metal Powder | Sizes Available | Grades | Specifications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Powder | 10-500 µm | Standard, Fine, Ultra-Fine | ASTM B211, ISO 3250 |
| Copper Powder | 5-200 µm | Standard, High Purity | ASTM B244, ISO 2740 |
| Iron Powder | 5-100 µm | Standard, High Purity | ASTM A595, ISO 3290 |
| Stainless Steel Powder | 10-150 µm | 316L, 304L, 17-4PH | ASTM A313, ISO 5832 |
| Titanium Powder | 10-100 µm | CP Ti, Ti-6Al-4V | ASTM B348, ISO 5832 |
| Nickel Powder | 10-200 µm | Standard, High Purity | ASTM B679, ISO 6207 |
| Cobalt-Chromium Powder | 10-150 µm | Co-Cr-Mo, Co-Cr-WC | ASTM F75, ISO 5832 |
| Tungsten Powder | 10-100 µm | Pure, Alloyed | ASTM B777, ISO 1176 |
| Magnesium Powder | 10-200 µm | Standard, High Purity | ASTM B93, ISO 1625 |
| Zinc Powder | 10-150 µm | Standard, High Purity | ASTM B6, ISO 1407 |
Suppliers and Pricing of Metal Powders
Finding reliable suppliers and understanding pricing is crucial for sourcing quality metal powders. Here’s an overview:
| Supplier | Metal Powder | Pricing (per kg) | Contact Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alcoa | Aluminum Powder | $10 – $50 | www.alcoa.com |
| Umicore | Copper Powder | $20 – $80 | www.umicore.com |
| Höganäs | Iron Powder | $15 – $60 | www.hoganas.com |
| BASF | Stainless Steel Powder | $25 – $100 | www.basf.com |
| ATI | Titanium Powder | $100 – $300 | www.atimetals.com |
| SGL Carbon | Nickel Powder | $50 – $150 | www.sglcarbon.com |
| Elementum | Cobalt-Chromium Powder | $150 – $500 | www.elementum3d.com |
| Global Tungsten & Powders | Tungsten Powder | $200 – $600 | www.globaltungsten.com |
| American Elements | Magnesium Powder | $30 – $120 | www.americanelements.com |
| Zinc Oxide | Zinc Powder | $20 – $70 | www.zincoxide.com |
Pricing can vary based on purity, particle size, and order volume. It’s essential to get quotes directly from suppliers to ensure you’re getting the best deal for your specific needs.
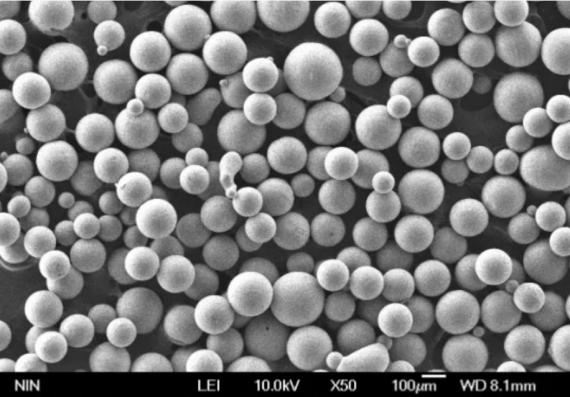
Comparing Quality Metal Powders
When choosing between different metal powders, it’s important to weigh the pros and cons of each option based on their properties, applications, and costs.
| Metal Powder | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Powder | Lightweight, excellent corrosion resistance, cost-effective | Lower strength compared to other metals |
| Copper Powder | High electrical and thermal conductivity, good machinability | Expensive, can tarnish over time |
| Iron Powder | Cost-effective, good strength, magnetic properties | Less corrosion resistance, can be brittle |
| Stainless Steel Powder | Corrosion resistance, high strength, durable | More expensive, can be difficult to process |
| Titanium Powder | High strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion-resistant, biocompatible | Very expensive, challenging to process |
| Nickel Powder | High-temperature resistance, good corrosion resistance | Expensive, can be difficult to work with |
| Cobalt-Chromium Powder | Excellent wear and corrosion resistance, biocompatible | Very expensive, limited availability |
| Tungsten Powder | Extremely hard, high melting point, dense | Very expensive, brittle |
| Magnesium Powder | Lightweight, good strength, reactive | Highly reactive, can be difficult to handle |
| Zinc Powder | Good corrosion protection, cost-effective | Less durable compared to other metals |
FAQ
Here are some common questions and answers about quality metal powders:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the most commonly used metal powder? | Aluminum powder is widely used due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. |
| How do I choose the right metal powder for my application? | Consider the properties required for your application, such as strength, conductivity, or corrosion resistance. |
| Are there environmental concerns with metal powders? | Some metal powders can be hazardous if not handled properly. Always follow safety guidelines and regulations. |
| Can metal powders be recycled? | Yes, many metal powders can be recycled, though the process depends on the type of metal and contamination levels. |
| What factors affect the price of metal powders? | Factors include purity, particle size, quantity ordered, and market demand. |

