Overview
Pure Copper (Cu) Powder is a metallic powder widely valued for its excellent conductivity, malleability, and versatility in industrial applications. Due to its high purity, Pure Cu Powder is a primary component in fields such as electronics, metallurgy, additive manufacturing, and chemical processes. With a typical composition exceeding 99.5% pure copper, this powder form of copper offers engineers, manufacturers, and researchers a valuable material with unique attributes.
What makes Pure Cu Powder truly valuable? Its combination of characteristics: high electrical and thermal conductivity, ductility, and the ability to be mixed with other materials or molded into a variety of forms. Whether you’re looking to produce intricate electronic components or sturdy structural parts, Pure Cu Powder provides a flexible and high-performing option.

Composition of Pure Cu Powder
Pure Cu Powder consists primarily of copper (Cu) in a finely milled form. However, depending on the application, small variations in purity levels, particle size, and shape may exist, allowing manufacturers to tailor the powder to specific needs. Here’s a breakdown:
| Component | Typical Composition (%) |
|---|---|
| Copper (Cu) | ≥ 99.5 |
| Oxygen (O) | < 0.3 |
| Iron (Fe) | < 0.05 |
| Other Impurities | < 0.15 |
This purity level ensures optimal performance, especially in electronic and conductive applications where copper’s electrical properties are critical. Most Pure Cu Powders are processed using atomization techniques, which allow for precise control over particle size and shape, thus influencing properties like flowability and compressibility.
Characteristics of Pure Cu Powder
To appreciate the full capabilities of Pure Cu Powder, let’s explore its core characteristics. Each characteristic plays a vital role, impacting how the powder behaves in different applications.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Copper’s conductivity is second only to silver, making Pure Cu Powder highly effective in electronic and thermal management applications. |
| Thermal Conductivity | With excellent thermal conductivity, Pure Cu Powder efficiently dissipates heat, crucial in electronics and heat exchangers. |
| Ductility | Ductility allows Pure Cu Powder to be molded and reshaped without fracturing, ideal for additive manufacturing and metallurgy. |
| Corrosion Resistance | While copper does develop a surface oxide layer, Pure Cu Powder resists deeper corrosion, protecting core functionality in various environments. |
| Particle Morphology | The morphology, typically spherical or irregular, affects flowability, density, and how the powder blends or packs within molds or additive processes. |
| Density | Pure Cu Powder has a density of approximately 8.96 g/cm³, which can affect how it mixes or compacts, especially in high-density applications. |
| Melting Point | Copper melts at 1,084°C, giving it high-temperature stability, which is essential in sintering and metal injection molding processes. |
Particle Shape and Size in Pure Cu Powder
The shape and size of the particles in Pure Cu Powder can vary, impacting properties like flow rate, compressibility, and even sintering behavior. Here are the most common shapes and their effects:
| Particle Shape | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Spherical | Provides uniform flow and packing density, ideal for 3D printing and coatings. | Frequently used in powder metallurgy and additive manufacturing for consistent layer deposition. |
| Irregular | Offers a higher surface area, enhancing bonding in composites or compounds. | Preferred in applications where a strong bond or mechanical interlock with other materials is needed. |
| Flake | Thin, flat particles that maximize surface contact. | Often used in conductive coatings and paints, where coverage and conductivity are critical. |
Applications of Pure Cu Powder
Pure Cu Powder finds itself in a myriad of industries, with each one harnessing its specific qualities. Here’s a look at its primary applications:
| Industry | Application | Why Pure Cu Powder? |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics | Conductive inks, printed circuits, and EMI shielding | Copper’s conductivity is ideal for precision electronic components. |
| Metallurgy | Powder metallurgy, sintering, and brazing | The powder form enables molding and compaction in complex shapes with excellent mechanical strength. |
| Additive Manufacturing | 3D printing of functional parts and prototypes | Pure Cu Powder’s flowability and malleability suit intricate design production and structural integrity. |
| Automotive | Heat sinks, friction materials, and fuel cells | Pure Cu Powder dissipates heat effectively, making it an excellent choice for automotive thermal management and energy solutions. |
| Chemical Industry | Catalysts and conductive coatings | Copper’s reactivity with certain compounds and excellent conductivity enhances chemical reactions and product durability. |
| Medical Devices | Antimicrobial surfaces and implants | Copper has natural antimicrobial properties, crucial in medical equipment to reduce infection risks. |

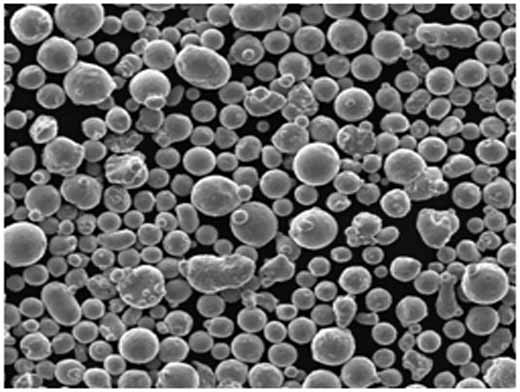



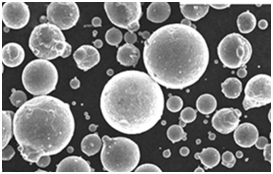
Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards of Pure Cu Powder
Understanding the specifications, sizes, grades, and standards of Pure Cu Powder can help you select the right material for a specific project. The purity, particle size, and form significantly impact performance in each application.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Purity | ≥ 99.5% (often up to 99.9% for high-end applications) |
| Particle Size | Ranges from nano-scale (<100 nm) to microns (up to 100 μm) |
| Density | 8.96 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1,084°C |
| Conductivity | Approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m |
| Standard Grades | ASTM B212, ASTM B848, ISO 4287 |
| Morphology | Available in spherical, flake, and irregular shapes |
Each of these grades and specifications aligns with international standards like ASTM and ISO, ensuring that the powder meets high-performance requirements. Here’s a breakdown of popular sizes and grades:
Common Sizes and Grades
| Grade | Purity (%) | Typical Particle Size Range (μm) | Best for Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| CP1 | 99.5 | 10-45 | Conductive inks, printed circuits |
| CP2 | 99.8 | 20-60 | Powder metallurgy, sintering |
| CP3 | 99.9 | 1-15 | Catalysts, specialized coatings |
| Nano-Cu | 99.9 | <0.1 | Advanced electronics, nanotechnology |
| Flake Cu | 99.5 | 15-45 | Conductive paints, EMI shielding |
| Spherical Cu | 99.7 | 20-100 | Additive manufacturing, 3D printing |
Advantages and Limitations of Pure Cu Powder
Choosing Pure Cu Powder over other metal powders like silver, aluminum, or even nickel brings unique advantages, but there are also some limitations to consider. Here’s a comparative analysis:
| Aspect | Advantages of Pure Cu Powder | Limitations of Pure Cu Powder |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | Superior electrical and thermal conductivity (close to silver) | Lower than silver, but much higher than aluminum or nickel |
| Cost | Less expensive than silver while providing comparable conductivity | More expensive than aluminum, especially for high-purity grades |
| Malleability | Highly ductile, making it suitable for molding and forming | Malleability can lead to deformation under stress |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good corrosion resistance in non-acidic environments | Susceptible to oxidation, which affects surface conductivity |
| Availability | Widely available in various grades, particle sizes, and shapes | Some specialty sizes and shapes may be more costly |
| Reactivity | Less reactive than other metals in moderate environments | Can react with certain chemicals, limiting its use in some applications |
Top Pure Cu Powder Models and Their Specific Applications
Let’s dive into some of the top Pure Cu Powder models currently available, each designed for specific industrial applications. Each model brings unique features to the table, tailored to meet the demands of particular processes, from high-precision 3D printing to conductive coatings and high-performance electronics.
| Model | Purity | Particle Size (μm) | Shape | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu-Powder CP1 | 99.5% | 10-45 | Irregular | Conductive inks, printed circuits, and basic electronic applications |
| Cu-Powder CP2 | 99.8% | 20-60 | Spherical | Suitable for powder metallurgy and sintering due to its flowability |
| Cu-Powder CP3 | 99.9% | 1-15 | Fine Flake | High-end conductive coatings and specialized electronic components |
| Nano-Cu 99.9 | 99.9% | <0.1 | Nano | Advanced electronic devices, sensors, nanotechnology, and catalysis |
| Cu-Sph 45 | 99.7% | 15-45 | Spherical | 3D printing, additive manufacturing, and precision part fabrication |
| Cu-Flake 99.5 | 99.5% | 15-45 | Flake | Conductive paints, EMI shielding, and coatings requiring large surface area coverage |
| Cu-Powder 80 | 99.8% | 45-80 | Spherical | Ideal for structural parts in additive manufacturing due to density and strength |
| High-Purity Cu 100 | 99.99% | 10-30 | Spherical | High-performance electronics, particularly in sensitive or miniaturized devices |
| Cu-Powder M10 | 99.7% | 10-50 | Mixed | Used in automotive parts, fuel cells, and friction materials |
| Cu-Catalyst 99.8 | 99.8% | 1-5 | Fine Powder | Specialized in chemical and pharmaceutical industry for catalytic applications |
Suppliers and Pricing Information for Pure Cu Powder
Pricing and supplier availability are crucial when planning to use Pure Cu Powder in large-scale applications. Below is a table comparing common suppliers, their products, and approximate pricing ranges, which can vary based on quantity and specific grade requirements.
| Supplier | Model Availability | Pricing (Approximate) | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| American Elements | CP1, CP2, Nano-Cu, Spherical | $50-200/kg | Known for high-purity powder; customized sizing |
| Goodfellow Corporation | High-Purity Cu, Nano-Cu | $150-400/kg | High-end models for medical and advanced electronics |
| Metal Powder Co. Ltd. | CP3, Flake Cu | $70-150/kg | Offers large volumes and flexible sizing options |
| SkySpring Nanomaterials | Nano-Cu, High-Purity Cu | $250-500/kg | Specializes in nanomaterials; premium pricing |
| Valimet | Spherical Cu | $80-220/kg | Large selection for additive manufacturing uses |
| Nanografi Nano Technology | Cu-Catalyst, Nano-Cu | $200-450/kg | Known for research-grade powders with high purity |

FAQ
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is Pure Cu Powder used for? | Pure Cu Powder is primarily used in electronics, metallurgy, additive manufacturing, automotive parts, and as a catalyst in the chemical industry. |
| Why is copper powder preferred in electronics? | Copper powder offers excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, essential for conductive inks, printed circuits, and EMI shielding in electronic components. |
| How is Pure Cu Powder produced? | It’s commonly made through atomization, where molten copper is dispersed into fine droplets that cool and solidify into powder form, controlling size and shape. |
| What are the particle shapes available, and why do they matter? | Available shapes include spherical, flake, and irregular. Spherical particles flow better and pack densely, ideal for 3D printing, while flakes offer greater surface area for coatings. |
| What are the benefits of high-purity copper powder? | High-purity copper powder (99.9% or higher) provides better conductivity and fewer impurities, essential for sensitive applications like advanced electronics and catalysts. |
| Is copper powder safe to handle? | Yes, with standard precautions like wearing gloves and masks. Copper powder is non-toxic, but inhaling fine particles can be harmful, so dust control is advised. |
| Can copper powder oxidize, and how does it affect applications? | Yes, copper powder can oxidize, especially in high humidity. Oxidation may impact conductivity, so powders are often stored in low-oxygen environments or treated with protective coatings. |
| What are the main standards for copper powder? | Standards include ASTM B212, ASTM B848, and ISO 4287, which define quality, purity, particle size, and other specifications, ensuring it meets industrial requirements. |
| How is particle size measured, and why is it important? | Particle size is measured using laser diffraction or microscopy. Size affects flowability, packing density, and surface area, impacting performance in specific applications. |
| Where can I buy Pure Cu Powder, and what should I consider? | Many suppliers like American Elements, Goodfellow, and Valimet offer Pure Cu Powder. When purchasing, consider purity, particle size, intended application, and supplier reputation. |
| How does copper powder compare to other metal powders like silver or nickel? | Copper is highly conductive and less expensive than silver. It’s more conductive than nickel but has lower corrosion resistance, making it suitable for cost-sensitive, conductive applications. |
| Can Pure Cu Powder be used in 3D printing? | Absolutely! Spherical Pure Cu Powder is widely used in metal 3D printing due to its excellent flowability and density, ideal for forming strong, detailed parts. |
| Is copper powder recyclable? | Yes, copper powder is recyclable, making it environmentally friendly. Scrap or unused powder can often be refined and reused in other applications. |

