Copper has been a cornerstone of human civilization, essential in electrical engineering, construction, and many industrial applications. When we talk about “high-purity copper powder,” we’re diving into a realm of materials that push the boundaries of purity and performance. High-purity copper powder isn’t just any material; it’s a specialized form of copper that offers unmatched qualities in conductivity, corrosion resistance, and thermal management, among other attributes. In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about high-purity copper powder, from its composition and characteristics to its various applications and the different models available on the market. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of this remarkable material and how it could benefit your projects.
Overview of High-Purity Copper Powder
High-purity copper powder refers to copper in powdered form with purity levels typically exceeding 99.9%. This powder is used in various industries, including electronics, metallurgy, chemical engineering, and advanced manufacturing, due to its superior conductivity, malleability, and resistance to corrosion. The production of high-purity copper powder involves several sophisticated processes, such as electrolysis, chemical reduction, and atomization, each ensuring the material’s purity and consistency.
In high-tech applications, where performance cannot be compromised, high-purity copper powder stands out for its exceptional properties. This guide aims to provide an in-depth look into the different types of high-purity copper powders available, their compositions, specific characteristics, and potential uses, along with an analysis of their advantages and limitations.
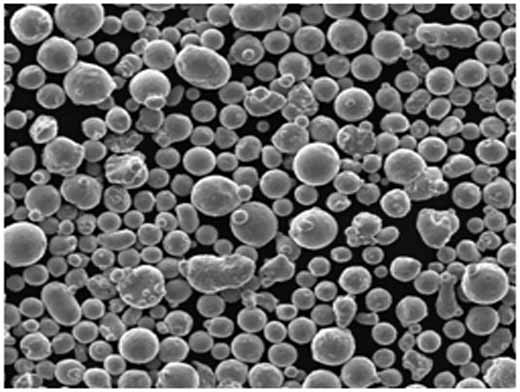
Types of High-Purity Copper Powder
Different types of high-purity copper powders are tailored for specific applications. Below is a table summarizing the key types and their distinct properties.
| Type | Purity Level | Particle Size (µm) | Production Method | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrolytic Copper Powder | 99.99% | 1-10 µm | Electrolytic Refining | Electronics, Sintering |
| Atomized Copper Powder | 99.95% | 5-50 µm | Atomization Process | 3D Printing, Thermal Management |
| Reduced Copper Powder | 99.9% | 10-100 µm | Chemical Reduction | Metallurgy, Catalysts |
| Precipitated Copper Powder | 99.95% | 0.5-10 µm | Precipitation Method | Conductive Pastes, Electronics |
| Nanopowder Copper | 99.999% | <100 nm | Chemical Synthesis | Nanotechnology, High-precision Components |
| Spherical Copper Powder | 99.9% | 15-45 µm | Gas Atomization | Additive Manufacturing, Conductive Inks |
| Flake Copper Powder | 99.9% | 1-15 µm | Milling | Conductive Coatings, Lubricants |
| Granular Copper Powder | 99.95% | 50-150 µm | Granulation | Powder Metallurgy, Bearings |
| Ultra-High-Purity Copper Powder | 99.9999% | 1-5 µm | Special Electrolytic Refining | Semiconductor Manufacturing |
| Fine Copper Powder | 99.97% | 5-20 µm | Mechanical Comminution | Surface Coating, Welding Materials |
Composition of High-Purity Copper Powder
High-purity copper powder’s composition is almost entirely copper, but the trace elements present can significantly affect its properties and performance. Understanding the composition helps in selecting the right type for specific applications.
| Component | Typical Concentration | Effect on Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Copper (Cu) | 99.9% – 99.9999% | Provides excellent electrical and thermal conductivity |
| Oxygen (O) | <0.001% | Higher levels can reduce conductivity and promote oxidation |
| Iron (Fe) | <0.0005% | Low levels are crucial for preventing corrosion and maintaining ductility |
| Lead (Pb) | <0.0001% | Must be minimized to avoid environmental and health risks |
| Sulfur (S) | <0.0002% | Affects the malleability and overall performance |
| Silver (Ag) | <0.0005% | Can enhance conductivity and corrosion resistance |
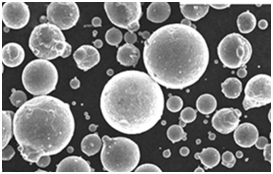
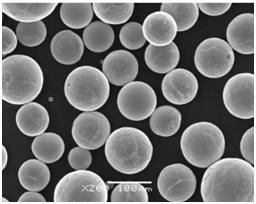
Characteristics of High-Purity Copper Powder
The characteristics of high-purity copper powder are what make it indispensable in so many advanced applications. Below, we detail some of the most critical characteristics that define its performance.
1. Electrical Conductivity
High-purity copper powder is renowned for its outstanding electrical conductivity, often used in applications requiring efficient electron flow, such as electrical contacts and conductive inks.
2. Thermal Conductivity
Copper’s ability to conduct heat efficiently makes high-purity copper powder a preferred material in heat sinks and other thermal management components, particularly in electronics.
3. Corrosion Resistance
Despite being highly conductive, high-purity copper powder also offers excellent resistance to corrosion, especially when free of impurities like sulfur and iron.
4. Ductility and Malleability
The ductility and malleability of high-purity copper powder enable it to be formed into complex shapes without cracking, which is vital in sintering and additive manufacturing processes.
5. Purity Levels
The purity level directly impacts the performance, with ultra-high-purity copper powder (99.9999% purity) being essential for applications in semiconductor manufacturing, where even the slightest impurity can cause significant defects.




Advantages of High-Purity Copper Powder
Choosing high-purity copper powder offers several advantages over lower-purity options, particularly in high-performance applications. Here’s a detailed look at some of the benefits.
| Advantage | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Superior Electrical Conductivity | Ensures efficient current flow in electrical and electronic components. |
| High Thermal Conductivity | Ideal for heat dissipation in high-power devices and thermal management systems. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Long-lasting performance in corrosive environments, reducing maintenance costs. |
| Enhanced Ductility | Can be easily shaped into intricate designs, essential for micro-components in electronics. |
| Ultra-Pure Grades Available | Suitable for use in semiconductor and nanotechnology applications where purity is critical. |
Applications of High-Purity Copper Powder
High-purity copper powder finds its way into a myriad of applications across various industries. Here’s a table summarizing some of the most common uses.
| Industry | Application | Type of Copper Powder Used |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics | Conductive Inks, PCBs, EMI Shielding | Nanopowder Copper, Electrolytic Copper Powder |
| Additive Manufacturing | 3D Printing of Metal Parts | Spherical Copper Powder, Atomized Copper Powder |
| Metallurgy | Sintering, Powder Metallurgy | Granular Copper Powder, Reduced Copper Powder |
| Aerospace | Thermal Management Components | Ultra-High-Purity Copper Powder |
| Automotive | Brake Pads, Bearings | Fine Copper Powder, Flake Copper Powder |
| Nanotechnology | High-Precision Devices | Nanopowder Copper |
| Medical Devices | Antimicrobial Coatings | Precipitated Copper Powder |
| Renewable Energy | Solar Cell Components | Electrolytic Copper Powder |
| Welding | Brazing Pastes, Welding Rods | Fine Copper Powder, Granular Copper Powder |
| Chemical Engineering | Catalysts | Reduced Copper Powder, Precipitated Copper Powder |
Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards of High-Purity Copper Powder
When selecting high-purity copper powder for specific applications, understanding the specifications, sizes, grades, and standards is crucial. Below is a detailed table outlining these parameters.
| Specification | Range/Grade | Standard | Size Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purity | 99.9% – 99.9999% | ASTM B170, ISO 431 | Customizable (1 µm – 150 µm) |
| Particle Size | 0.1 µm – 150 µm | ASTM E11 | Fine, Coarse, Nanoparticle |
| Shape | Spherical, Flake, Granular | ASTM B822 | Various Shapes Available |
| Density | 2.0 – 8.9 g/cm³ | ISO 3923 | Bulk Density, Tap Density |
| Flowability | 5 – 25 s/50g | ISO 4490 | Free-Flowing, Non-Free-Flowing |
| Oxygen Content | <0.001% | ISO 5832 | Ultra-Low Oxygen Options |
| Conductivity | > 99% IACS | ASTM B193 | High Conductivity Grades |
Suppliers and Pricing Details of High-Purity Copper Powder
Purchasing high-purity copper powder involves considering both the supplier’s reputation and the pricing structure. Below is a table summarizing the details of some top suppliers and their pricing.
| Supplier | Product | Price Range (per kg) | Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| American Elements | Ultra-High-Purity Copper Powder | $500 – $700 | 1 kg | USA |
| Höganäs AB | Atomized Copper Powder | $300 – $500 | 5 kg | Sweden |
| Tekna | Spherical Copper Powder | $400 – $600 | 2 kg | Canada |
| Mitsui Mining & Smelting | Electrolytic Copper Powder | $250 – $450 | 10 kg | Japan |
| Umicore | Nanopowder Copper | $700 – $1000 | 0.5 kg | Belgium |
| Shanghai CNPC | Reduced Copper Powder | $200 – $400 | 20 kg | China |
| GGP Metal Powder | Flake Copper Powder | $150 – $350 | 15 kg | India |
| Kymera International | Granular Copper Powder | $300 – $550 | 3 kg | USA |
| Nanochemazone | Precipitated Copper Powder | $450 – $650 | 1 kg | Canada |
| Sumitomo Metal Mining | Fine Copper Powder | $350 – $550 | 5 kg | Japan |
Advantages and Limitations of High-Purity Copper Powder
Understanding both the strengths and weaknesses of high-purity copper powder can help in making informed decisions about its use.
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Superior Conductivity | Higher Cost: The ultra-high-purity grades can be expensive. |
| High Thermal Management | Oxidation: Though corrosion-resistant, it can still oxidize over time. |
| Excellent Malleability | Powder Handling: Fine powders can pose challenges in handling and processing. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Availability: Some high-purity grades may have limited availability depending on the supplier. |
| Wide Application Range | Health Risks: Nanopowders require careful handling due to potential health hazards. |

FAQ
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is high-purity copper powder used for? | High-purity copper powder is used in electronics, metallurgy, additive manufacturing, nanotechnology, and more due to its excellent electrical and thermal properties. |
| How is high-purity copper powder made? | It is produced through methods such as electrolysis, chemical reduction, atomization, and precipitation, ensuring high purity levels. |
| What purity levels are available? | Purity levels typically range from 99.9% to 99.9999%, depending on the application. |
| Why is high-purity copper powder expensive? | The cost reflects the sophisticated production processes required to achieve high purity and the critical role of copper in advanced technologies. |
| Can high-purity copper powder be used in 3D printing? | Yes, spherical high-purity copper powders are widely used in additive manufacturing for creating metal parts. |
| Is high-purity copper powder safe to handle? | While generally safe, nanopowders require careful handling due to potential inhalation risks. Proper safety protocols should be followed. |
| Where can I buy high-purity copper powder? | Several suppliers, such as American Elements, Höganäs AB, and Tekna, offer high-purity copper powder. Pricing varies by purity, particle size, and supplier. |
| What are the alternatives to high-purity copper powder? | Alternatives include silver powder for conductivity, aluminum powder for lightweight applications, and nickel powder for specific industrial uses. |
| How does purity affect the properties of copper powder? | Higher purity enhances electrical and thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and ductility, making it ideal for high-tech applications. |
| What are the challenges of using high-purity copper powder? | Challenges include higher costs, potential oxidation, and handling issues with very fine powders. |
Conclusion
High-purity copper powder is an essential material for industries that require precision, efficiency, and reliability. Whether it’s for making high-performance electronic components, enabling advanced manufacturing techniques like 3D printing, or enhancing thermal management in aerospace applications, the role of high-purity copper powder cannot be overstated. Understanding its various types, compositions, properties, and applications can guide you in selecting the right material for your specific needs. While the cost and handling challenges may pose some limitations, the benefits of using high-purity copper powder often outweigh these drawbacks, especially in high-performance applications where quality cannot be compromised.
As technology continues to evolve, the demand for materials like high-purity copper powder will only increase. Staying informed about the latest advancements and suppliers can give you a competitive edge, ensuring that your products are built with the best materials available.

