In the realm of advanced materials, where innovation constantly seeks to push the boundaries of performance, the fusion of tungsten and titanium emerges as a formidable contender. Tungsten titanium powder, a blend of these two elements, is shaping industries across the board with its exceptional properties and applications. Let’s delve into the world of this remarkable alloy, uncovering its characteristics, production methods, advantages, challenges, and potential future trends.
Introduction to Tungsten Titanium Powder
Tungsten titanium powder, often referred to as WTi powder, is a cutting-edge alloy that marries the robustness of tungsten with the versatility of titanium. This alloy presents a unique amalgamation of properties that have garnered significant attention across industries seeking durable and high-performance materials.
Properties and Applications
Understanding Tungsten and Titanium
Tungsten, known for its remarkable density and strength, meets titanium, celebrated for its lightweight nature and corrosion resistance. The result? An alloy with a desirable combination of strength, toughness, and resistance to extreme conditions.
Alloying for Enhanced Performance
The process of alloying tungsten and titanium results in a synergy of properties that surpass those of individual elements. This alloy offers enhanced strength, excellent thermal stability, and the ability to withstand aggressive environments.
Applications in Various Industries
From aerospace engineering to medical advancements, tungsten titanium powder finds its place in diverse sectors. It’s a crucial material in manufacturing aircraft components, surgical implants, and sporting equipment due to its reliability and performance under stress.
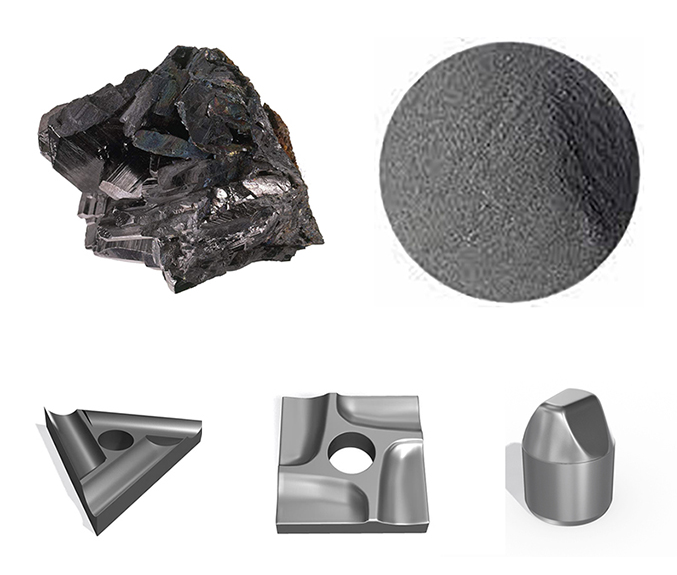

Production and Manufacturing
Powder Metallurgy Process
The production of tungsten titanium powder predominantly involves the powder metallurgy technique. This process enables the precise blending of tungsten and titanium particles at a microscopic level, ensuring uniform distribution of their respective properties.
Particle Size Control
Particle size plays a pivotal role in the alloy’s final properties. Manufacturers meticulously control particle size to tailor the alloy’s characteristics for specific applications.
Sintering Techniques
Sintering, a vital step, involves heating the blended powders to fuse them into a solid alloy. The chosen sintering technique significantly impacts the alloy’s density and mechanical properties.
Advantages and Benefits
High Strength and Toughness
Tungsten titanium alloy’s inherent strength and toughness make it invaluable for situations demanding reliability under extreme stress, such as aerospace engineering.
Corrosion Resistance
The alloy’s resistance to corrosion, coupled with its high strength, finds a sweet spot in applications that require both durability and longevity.
Thermal Stability
Tungsten titanium alloy’s remarkable thermal stability lends itself to applications involving high temperatures, including aerospace components subjected to intense heat during reentry.

Challenges in Usage
Cost Considerations
While tungsten titanium alloy offers unparalleled performance, its production cost can be a deterrent, particularly for budget-sensitive projects.
Machinability Challenges
The alloy’s high density and strength, while advantageous, can pose challenges during machining and fabrication processes.
Future Trends and Innovations
Research and Development
Continuous research seeks to optimize the alloy’s properties further and explore novel applications, opening doors to enhanced capabilities.
Emerging Applications
As industries evolve, new applications for tungsten titanium powder emerge, expanding its role in cutting-edge technologies.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Recycling and Reuse
Efforts are underway to develop recycling methods for tungsten titanium alloy, aligning with sustainable practices and minimizing waste.
Eco-Friendly Production Methods
Researchers are exploring environmentally friendly production techniques to mitigate the alloy’s carbon footprint.
Comparative Analysis with Other Materials
Tungsten Titanium vs. Traditional Alloys
A comparative analysis showcases how tungsten titanium alloy outperforms traditional materials, making it a compelling choice for advanced applications.
Tungsten Titanium vs. Other Advanced Materials
In the landscape of advanced materials, tungsten titanium alloy holds its ground against other high-performance substances, displaying its unique advantages.

How to Source Tungsten Titanium Powder
Trusted Suppliers and Manufacturers
Sourcing high-quality tungsten titanium powder demands collaboration with trusted suppliers and manufacturers with a proven track record.
Quality Assurance and Certifications
Ensuring quality through appropriate certifications and adherence to industry standards is paramount when sourcing this alloy.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Aerospace Industry Application
Exploring a case study where tungsten titanium alloy played a pivotal role in improving the efficiency and durability of aerospace components.
Medical Implants Application
Delving into the success story of how tungsten titanium alloy has revolutionized the field of medical implants with enhanced biocompatibility.
Expert Insights and Recommendations
Expert Opinions on Usage and Advantages
Industry experts provide insights into the alloy’s usage and highlight its advantages in various applications.
Precautions and Best Practices
Experts also share precautions and best practices to optimize the alloy’s performance and ensure safety during its utilization.

Conclusion
Tungsten titanium powder stands as a testament to the relentless pursuit of material innovation. Its unique blend of properties, applications across diverse sectors, and ongoing research and development efforts solidify its position as a transformative alloy.
FAQs
What distinguishes tungsten titanium powder from other alloys?
Tungsten titanium powder stands out due to its unique combination of properties derived from the two constituent elements. Tungsten contributes exceptional strength and density, while titanium brings lightweight corrosion resistance to the alloy. This blend of characteristics makes tungsten titanium powder particularly suitable for applications where a balance of strength, toughness, and resistance to extreme conditions is required.
Is tungsten titanium alloy cost-effective for small-scale applications?
Tungsten titanium alloy is renowned for its remarkable performance, but it’s important to note that its production can involve higher costs compared to traditional materials. This cost factor may be more pronounced for small-scale applications due to economies of scale. However, the alloy’s advantages in terms of durability, longevity, and performance under stress can often outweigh the initial investment, especially for critical components in sectors like aerospace and medical.
Can tungsten titanium alloy be recycled?
Yes, efforts are being made to develop recycling methods for tungsten titanium alloy. Recycling not only addresses environmental concerns but also helps mitigate the costs associated with acquiring new raw materials. By establishing efficient recycling processes, the industry aims to enhance the sustainability of this alloy while reducing its overall environmental footprint.
How does the machinability of tungsten titanium compare to traditional metals?
The high density and strength of tungsten titanium alloy can pose challenges in terms of machinability, especially when compared to traditional metals. The alloy’s toughness and resistance come from its density, which can make machining and fabrication more complex. However, advancements in machining techniques and technologies are continually improving the process, making it feasible to work with tungsten titanium alloy for various applications.
What are some cutting-edge applications on the horizon for this alloy?
Tungsten titanium powder is finding exciting applications in emerging technologies. In the aerospace industry, it’s contributing to the development of more efficient and durable aircraft components, pushing the boundaries of aviation. Additionally, the medical field is witnessing the alloy’s potential in producing biocompatible implants with enhanced longevity and reduced risk of rejection. As research and development efforts continue, new applications are likely to emerge, shaping industries in unforeseen ways.
know more 3D printing processes
Additional FAQs on Tungsten Titanium Powder
1) What W–Ti compositions are most common and why?
Typical ranges are 70–95 wt% W with 5–30 wt% Ti. Higher W boosts high-temperature strength, density, and radiation attenuation; higher Ti improves corrosion resistance, weldability, and reduces density. Specialized grades (e.g., W-10Ti, W-20Ti) are chosen per application and processing route.
2) Can tungsten titanium powder be 3D printed?
Yes. LPBF and binder jetting can process WTi powders when PSD is tightly controlled (often D10–D90 ≈ 15–45 μm for LPBF). Preheating, scan-parameter tuning, and post-HIP reduce residual stress and porosity. Binder-jetted parts typically require high-temp vacuum/H2 sintering and may be HIPed for >97% density.
3) How does WTi perform in corrosive or biomedical environments?
Ti additions enhance passivation in chloride-rich and physiological environments versus pure W. However, biocompatibility depends on composition, surface condition, and ion release; medical adoption requires ISO 10993 testing and application-specific validation.
4) What are key machining and finishing strategies for WTi parts?
Use rigid fixturing, PCBN/carbide tooling, generous coolant, and conservative speeds/feeds. For finishing: abrasive flow machining, electropolishing (on Ti-rich surfaces), or chemical-mechanical polishing to reach Ra < 0.2 μm when required.
5) How should tungsten titanium powder be stored and handled safely?
Store dry, inert the headspace if possible, and minimize dust. Use LEV with HEPA, antistatic PPE, grounded equipment, and Class D extinguishers. Follow SDS controls; avoid oxidizers and ignition sources. For AM, control O/N/H to protect mechanical and fatigue properties.
2025 Industry Trends for Tungsten Titanium Powder
- AM-ready feedstocks: Growth of spherical WTi powders with low oxygen (<0.10 wt%) for LPBF and finer cuts for binder jetting with sinter-HIP.
- Thermal management and RF: WTi graded with Cu or Mo interlayers to tailor CTE and thermal conductivity in power electronics and aerospace heat sinks.
- Radiation and high-temp use: Increased evaluation of WTi for x-ray/gamma shielding, plasma-facing components, and hot-structure fasteners where Ti improves toughness vs. refractory W alone.
- Sustainability and traceability: Material passports connecting powder lots to part serials; higher recycled content targets for Ti inputs; closed-loop powder recovery.
- Cost-down: Multi-laser LPBF, sinter-HIP consolidation, and near-net shaping reduce machining of ultra-hard W-rich alloys.
| 2025 Metric (WTi unless noted) | Typical Range/Value | Relevance/Notes | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| LPBF relative density (WTi) | 96–99.5% after HIP | Preheat + optimized scans; contour strategies | Peer-reviewed AM studies; OEM app notes |
| Binder-jetted WTi final density | 94–98% (sinter/HIP) | Complex shielding/thermal parts | Vendor case data; journals |
| Tensile strength at RT (W-10–20Ti, HIPed) | 700–1100 MPa | Alloy and porosity dependent | ASM data; literature ranges |
| Thermal conductivity (WTi) | 40–120 W/m·K | Decreases with Ti; design for heat paths | Materials handbooks |
| Oxygen content in AM feedstock | ≤0.05–0.12 wt% | Target to maintain ductility | ISO/ASTM 52907 practices |
| Indicative powder price (spherical WTi) | $80–$180/kg | PSD, sphericity, certification affect price | Market trackers; supplier quotes |
Authoritative references and further reading:
- International Tungsten Industry Association (ITIA): https://www.itia.info
- ASTM/ISO AM standards (ISO/ASTM 52907, 52910): https://www.astm.org and https://www.iso.org
- ASM Handbook (Properties of Refractory and Titanium Alloys): https://www.asminternational.org
- NIST materials data: https://www.nist.gov
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: LPBF W-15Ti Heat Sink with Graded WTi–Cu Interface (2025)
Background: A power electronics supplier needed a heat sink with low CTE mismatch to SiC modules and improved thermal cycling durability.
Solution: Printed a W-15Ti core via LPBF using spherical 15–45 μm powder (O ≤0.09 wt%), followed by infiltrated Cu interlayer and HIP; topology-optimized fin geometry.
Results: 22% lower junction temperature at 1 kW load, 3× thermal-cycle life (−40 to 150°C), and 18% mass reduction vs. machined W/Cu composite baseline.
Case Study 2: Binder-Jetted W-10Ti Collimator for CT Imaging (2024)
Background: Medical OEM sought complex collimator channels with reduced machining.
Solution: Binder jetting of fine-cut W-10Ti powder; debind + vacuum sinter at >1400°C and HIP; internal channels designed with lattice supports.
Results: 97% final density, channel straightness within ±50 μm, 15% weight reduction, and equivalent attenuation to denser WHA control; 20% cost reduction in low-volume builds.
Expert Opinions
- Dr. Subhash Mahajan, Regents’ Professor Emeritus, Arizona State University (materials science)
Key viewpoint: “Ti additions toughen tungsten by altering grain boundary chemistry and promoting crack-bridging mechanisms, which is especially beneficial for additively manufactured W-rich components.” - Dr. Martina Zimmermann, Head of Additive Manufacturing Materials, Fraunhofer IWM
Key viewpoint: “Achieving repeatable WTi properties hinges on interstitial control and thermal history. Preheat and HIP are non-negotiable for crack mitigation in LPBF W-rich alloys.” - Prof. Iain Todd, Professor of Metallurgy and Materials Processing, University of Sheffield
Key viewpoint: “Functionally graded WTi interfaces to copper or titanium dramatically reduce thermal stresses, enabling reliable, repairable thermal hardware for aerospace and power electronics.”
Citations for expert profiles:
- ASU Engineering: https://engineering.asu.edu
- Fraunhofer IWM: https://www.iwm.fraunhofer.de
- University of Sheffield: https://www.sheffield.ac.uk
Practical Tools and Resources
- Standards and specifications
- ASTM B777 (WHA context), ISO/ASTM 52907 (feedstock), 52910 (DFAM): https://www.astm.org and https://www.iso.org
- ITIA technical briefs on tungsten alloys: https://www.itia.info
- Design and simulation
- Ansys Additive + Ansys Mechanical (distortion, thermal stress): https://www.ansys.com
- COMSOL Multiphysics (Heat Transfer, AC/DC Modules): https://www.comsol.com
- nTopology for lattice and graded interfaces: https://ntop.com
- Powder QC and processing
- LECO O/N/H analysis: https://www.leco.com
- HIP service providers and parameters (WTi): https://www.bodycote.com
- Senvol Database (machines/materials): https://senvol.com/database
- Regulatory and biomedical
- ISO 10993 biocompatibility framework: https://www.iso.org
- FDA device database for imaging components and implants: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfpmn/pmn.cfm
Last updated: 2025-08-21
Changelog: Added 5 WTi-focused FAQs, 2025 trend table with metrics and sources, two recent application case studies, expert viewpoints with credible affiliations, and a curated tools/resources list relevant to tungsten titanium powder.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ISO/ASTM AM standards update, new WTi AM parameter sets or HIP cycles are published by OEMs, or market prices for W/Ti powders shift >10% QoQ.