Tungsten silver powder, also known as tungsten metal powder coated with silver, is a unique material with applications across many industries. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of tungsten silver powder, its properties, production methods, applications, suppliers, and more.
Overview of Tungsten Silver Powder
Tungsten silver powder typically consists of tungsten microparticles coated with a layer of pure silver. The silver coating percentage can range from 10% to 60% by weight.
Here are the key details about tungsten silver powder:
Tungsten Core
- Pure tungsten microparticles ranging from 0.5 to 10 microns in size
- Provides density, thermal conductivity, temperature resistance
Silver Coating
- Thin layer of pure silver metallurgically bonded to tungsten
- Provides electrical conductivity, lubricity, sintering aid
Composite Material
- Combines desirable properties of both tungsten and silver
- Varied silver content allows tailoring properties as needed
- Provides unique benefits for electrical contacts, welding, brazing, and other applications
Typical Product Specifications
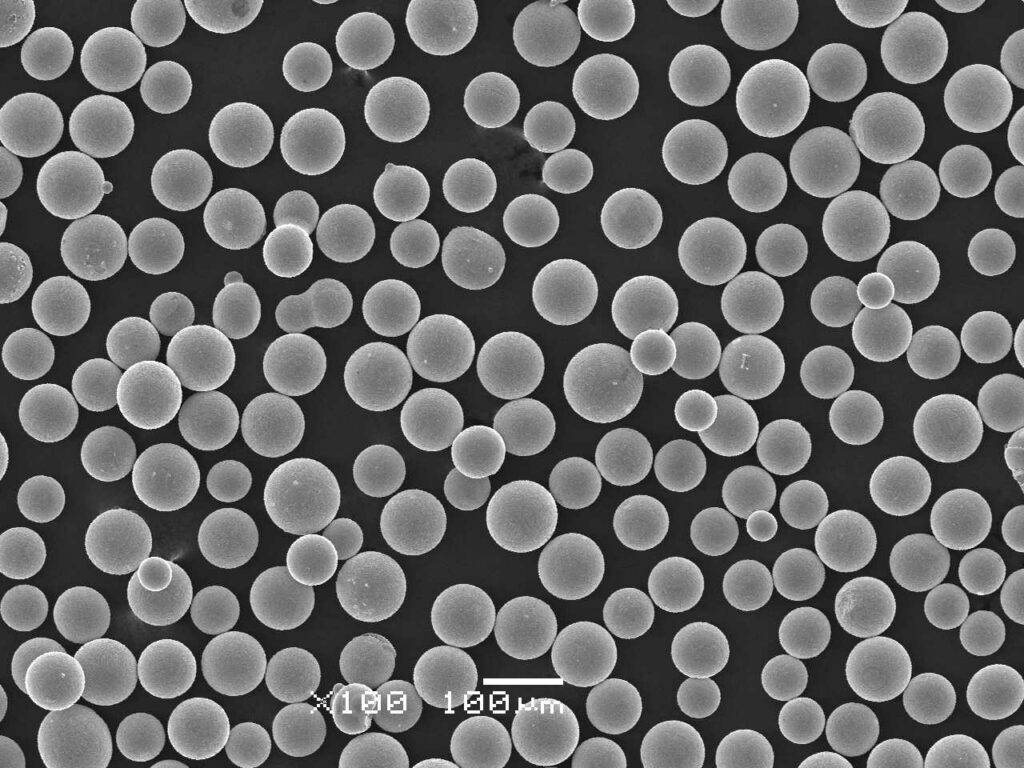
- Particle sizes: 0.5 to 10 microns
- Silver content: 10% to 60% by weight
- Apparent density: 9 to 11 g/cm3
- Tungsten core purity: ≥99.9%
- Silver coating purity: ≥99.9%
Key Characteristics
- High density similar to tungsten
- Good electrical and thermal conductivity
- Excellent lubricity and anti-welding from silver
- Withstands high temperatures like tungsten
- Low contact erosion rate
- Resists arc erosion and welding
Applications of Tungsten Silver Powder
Tungsten silver powder is a versatile material suitable for the following applications:
Electrical Contacts
- Relays, switches, circuit breakers
- Sliding electrical contacts
- Automotive ignition systems
- High current switches and relays
Welding Electrodes
- Low contact erosion welding electrodes
- Resistance welding electrodes
Silver Brazing and Soldering
- Braze pastes for metal joining
- Vacuum brazing of ceramics or diamonds
- High temperature electrical contacts
EMI/RFI Shielding
- Electrically conductive coatings and films
- Electromagnetic interference shielding
Conductive Plastics
- Electrodes for conductive polymer actuators
- Static charge dissipation
- Electrically conductive plastic composites
Thermal Management
- Thermal interface materials
- Heat spreaders
- Printed circuit board substrates
Other
- Vacuum interrupters, X-ray targets
- Electrical brushes, high voltage insulators
- Spark plug electrodes, arcing contacts
Tungsten silver’s unique properties make it suitable for applications requiring high density, temperature resistance, electrical conductivity, low contact erosion, and anti-welding characteristics.
Manufacturing Tungsten Silver Powder
Tungsten silver powder is manufactured using various methods that coat tungsten particles with a thin layer of high purity silver. Here are the main production processes:
Mechanical Mixing
- Blending silver powder with tungsten powder
- Compacting the powder mixture into a perform
- Sintering perform to bond silver to tungsten
Electroless Plating
- Activating tungsten surface in an aqueous solution
- Immersing activated tungsten in silver chemical bath
- Silver ions are catalytically reduced onto tungsten
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
- Evaporating silver metal in a vacuum chamber
- Condensing silver vapor onto fluidized tungsten powder
- Provides uniform, controlled silver coating
Wet Chemistry Methods
- Tungsten particles immersed in a silver chemical bath
- Silver ions precipitate onto tungsten surface
- May involve additives or electrical current
The coating uniformity, silver content, and purity can be tailored by controlling the process parameters. Manufacturers select the method based on technical specifications and application requirements.
Specifications of Tungsten Silver Powder
Tungsten silver powder is available in different specifications optimized for various applications. Here are some key parameters:
Particle Size
- Range from 0.5 to 10 microns
- Smaller sizes preferred for better coating coverage
- Larger sizes provide higher density
Silver Content
- 10% to 60% silver by weight
- Higher silver increases conductivity
- Lower silver provides higher density
Apparent Density
- Typically 9 – 11 g/cm3
- Higher density improves wear resistance
- Lower porosity improves electrical contact
Purity
- Tungsten core purity ≥99.9%
- Silver coating purity ≥99.9%
- High purity minimizes contamination
Oxygen Content
- Below 100 ppm oxygen preferred
- Ensures good electrical conductivity
- Prevents embrittlement during sintering
Surface Area
- 0.5 to 3 m2/g common specification
- Higher surface area improves sintering
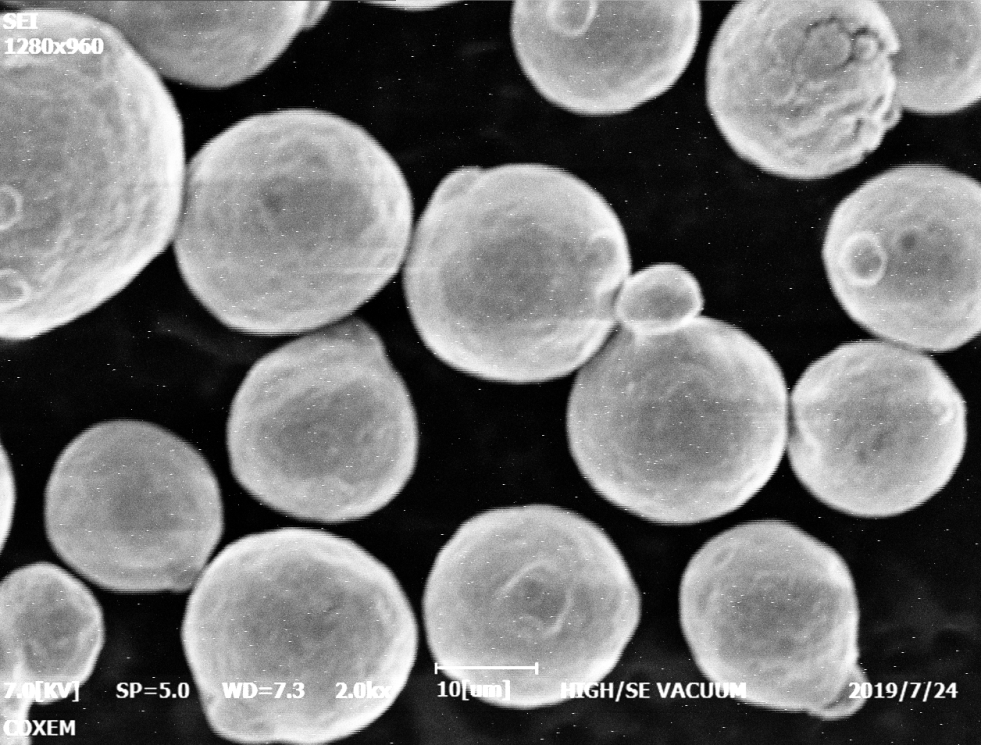
Coating Uniformity
- Uniform silver layer essential
- Ensures consistent properties and performance
Other Parameters
- Tap density, flow rate
- Compressibility and green strength
- Thermal conductivity
Design Considerations for Using Tungsten Silver Powder
Here are some key design factors to consider when selecting tungsten silver powder:
Operating Temperature
- Withstands up to 850°C in air
- Use minimum silver coating in highly oxidizing conditions
Electrical Conductivity
- Increases with higher silver content
- Tailor silver percentage based on conductivity needs
Density
- Decreases slightly with higher silver percentage
- Optimize density as per application requirements
Coating Uniformity
- Essential for reliable performance of contacts
- Verify manufacturer quality control protocols
Particle Shape
- Spherical, flaky, and angular options available
- Shape impacts density, flowability, and microstructure
Grain Size
- Finer grains improve strength
- Coarser grains improve conductivity
Degassed or Not
- Degassing reduces trapped gases
- Improves density and conductivity
Suppliers of Tungsten Silver Powder
There are a number of reputable manufacturers and suppliers of tungsten silver powder:
Major Global Suppliers
- H.C. Starck
- Inframat Advanced Materials
- American Elements
- Atlantic Equipment Engineers
- Eco-Tec Ltd.
China-based Manufacturers
- Zhuzhou Cemented Carbide Group
- Luoyang Tongrun Info Technology
- Miyou Group
- Sichuan Anxian Yinhee Tungsten
- Chengdu Nuclear
Pricing
- Ranges from $50 – $500 per kg
- Varies by purity, silver content, particle size
- Quotes available from suppliers
When selecting a tungsten silver powder supplier, buyers should evaluate quality certifications, manufacturing capacity, pricing, and responsiveness.
Installation and Operation of Tungsten Silver Powder-based Components
For applications like electrical contacts and welding electrodes using tungsten silver powder, following proper installation and operation guidelines is critical:
- Carefully inspect components for any damage prior to installation
- Ensure mating surfaces are clean and free of contaminants
- Apply manufacturer recommended torque for fastening hardware
- Follow any break-in or conditioning procedures
- Operate within rated voltage and current limits
- Avoid excessive arcing or sparking during operation
- Periodically clean surfaces according to application guidelines
- Inspect for wear, erosion, or welding after scheduled maintenance cycles
- Replace contacts once maximum erosion limit is reached
- Recondition mating surfaces according to manufacturer instructions
Adhering to these best practices will maximize service life and optimize performance. Consult application manuals for specific procedures.

Maintenance and Inspection of Tungsten Silver Contacts
Regular inspection and maintenance is necessary for tungsten silver electrical contacts:
Inspection Schedule
- Initial inspection after 100 cycles or 1 month
- Routine inspection every 1000 cycles or 6 months
Visual Inspection
- Check for signs of wear, pitting, or erosion
- Look for electrical arcing damage
- Inspect for debris, contaminants, or welding
Dimensional Inspection
- Measure contact thickness in wear areas
- Compare readings to baseline values
- Measure mating gaps against specs
Electrical Testing
- Check resistance with low current
- Perform millivolt drop tests
- Verify ratings are still met
Cleaning Method
- Use solvents or abrasives as suitable
- Avoid damaging silver coating
- Remove any oil, films, or oxides
Reconditioning
- Dress or machine as per procedure
- May involve silver electroplating
- Replace if erosion limit exceeded
Documentation
- Record results of measurements
- Note any deviations from specs
- Update maintenance logs
Choosing a Tungsten Silver Powder Supplier
Here are key factors to consider when selecting a supplier of tungsten silver powder:
Product Quality
- Experience in manufacturing the powder
- Process capabilities and controls
- Quality certifications
- Reliability and consistency
Technical Expertise
- Knowledge of production processes
- Expertise in powder metallurgy
- Understanding of product applications
- Guidance on proper material selection
Range of Options
- Ability to tailor silver content, particle size, purity, etc.
- Range of powder specifications supported
- Customization services available
Production Capacity
- Ability to meet demand requirements
- Capacity for large volume orders
Pricing
- Competitive pricing for product grade
- Discounts for bulk orders
- Stable long term pricing
Responsiveness
- Quick response to inquiries and requests
- Fast delivery times
- Willingness to meet unique needs
Procuring Tungsten Silver Powder
Follow these best practices when procuring tungsten silver powder:
- Provide detailed specifications to suppliers
- Request product datasheets and certifications
- Ask for representative samples for evaluation
- Clarify any customization or tailoring options
- Obtain pricing quotes from multiple suppliers
- Evaluate suppliers based on selection criteria
- Place initial trial orders to qualify supplier
- Test samples and audit supplier processes
- Negotiate pricing for higher volume orders
- Agree to long term supply agreements if suitable
- Review quality and consistency over time
Properly procuring tungsten silver powder ensures you get the right product quality from a reputable supplier at a reasonable price.
Advantages and Limitations of Tungsten Silver Powder
Advantages
- Combines beneficial properties of tungsten and silver
- Withstands high temperature oxidizing conditions
- Provides excellent electrical conductivity
- Resists arc erosion and contact welding
- Easy to manufacture using various methods
- Can be tailored to achieve desired density and conductivity
Limitations
- More expensive than pure tungsten or silver
- Not suitable for highly corrosive environments
- Lower thermal conductivity than pure silver
- Susceptible to embrittlement if overheated
- Contact erosion still occurs over time
- Silver migration can occur under DC current
FAQs
Q: What is tungsten silver powder used for?
A: The main uses are for electrical contact materials, welding electrodes, silver brazing alloys, conductive coatings, and other applications requiring a combination of high density, temperature resistance, electrical conductivity, and anti-welding properties.
Q: How is the silver bonded to the tungsten particles?
A: Manufacturing processes like sintering, electroless plating, and PVD result in metallurgical bonding between the silver coating and tungsten core at the atomic level. This creates a composite material.
Q: What affects the electrical conductivity of tungsten silver powder?
A: The silver content primarily controls the conductivity. Higher silver percentages result in higher conductivity. The uniformity of the silver coating and the porosity after sintering also impact conductivity.
Q: Does tungsten silver powder require sintering?
A: Yes, tungsten silver powder is commonly consolidated using powder metallurgy which involves compacting the powder and then sintering at high temperature to achieve full density. This fuses the particles together.
Q: What is the difference between tungsten silver and silver tungsten?
A: The convention is to list the core material first. So tungsten silver powder has a tungsten core with a silver coating, while silver tungsten would have a silver core and tungsten coating.
Q: How is tungsten silver powder made?
A: Common manufacturing methods include mechanical mixing, electroless plating, physical vapor deposition, and wet chemistry processes that precipitate silver onto tungsten powder particles.
Q: What particle size of tungsten silver powder is best?
A: For good silver coating coverage, smaller sizes below 5 microns are preferred. However, larger particle sizes above 5 microns will provide higher density in the finished component. The optimal size depends on the application.
Q: Is tungsten silver powder hazardous?
A: Tungsten and silver metals are generally non-hazardous materials. However, manufacturers recommend handling powder in ventilated areas and using protective equipment to minimize dust exposure during handling.
Q: Does tungsten silver powder go by any other names?
A: It may be referred to as silver coated tungsten powder, AgW powder, or SW powder. The tungsten percentage is sometimes listed first, for example 90W10Ag indicates 90wt% tungsten with 10wt% silver.
know more 3D printing processes
Additional FAQs: Tungsten Silver Powder
1) How should silver content be selected for different electrical contact uses?
- Low-voltage signal contacts: 30–60 wt% Ag for low resistance.
- Medium/high current switching and arcing: 15–35 wt% Ag to balance conductivity with arc‑erosion resistance and density.
- Sliding/brush contacts: 25–45 wt% Ag for lubricity and wear balance.
2) What particle size distribution is optimal for sintered Ag‑coated W components?
- For press-and-sinter contacts, D50 ≈ 2–6 µm improves coating continuity and sinter necking; larger secondary fraction (8–12 µm) can enhance packing density. Target high sphericity and narrow PSD.
3) Can Tungsten Silver Powder be used in additive manufacturing?
- It is feasible in binder jetting with post‑sinter/infiltration and in paste-based printing for thick films. Direct LPBF is challenging due to immiscibility, density contrast, and reflectivity; specialized process parameters or composite approaches are required.
4) How do oxygen and carbon impurities impact performance?
- Elevated O/C increase interfacial oxides and porosity, raising contact resistance and reducing mechanical integrity. Typical specs: O ≤ 0.10 wt%, C ≤ 0.05 wt% for high-performance contacts; verify via inert gas fusion analysis.
5) What post-processing improves contact life for Ag‑coated W parts?
- Vacuum or H2 sintering with controlled dew point, hot forging/coinage to densify the contact face, surface finishing (micro-machining, lapping), optional silver flash plating, and stress-relief heat treatments.
2025 Industry Trends: Tungsten Silver Powder
- Reliability under electrification: EV relays/contactors push demand for Ag–W composites with lower arc erosion and stable millivolt drop across high cycle counts.
- Digital genealogy: Batch tracking of PSD, Ag wt%, and O/C content is being mandated by OEMs for safety-critical switching gear.
- Sustainability: More closed-loop silver recovery from scrap contacts; Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) requested in RFQs.
- Process control: Movement from electroless-only to hybrid coating routes (PVD + chemical) to tighten coating uniformity and reduce satellite agglomerates.
- Standards alignment: Wider adoption of IEC/ASTM test protocols for arc erosion, contact resistance, and weld force in qualification.
2025 Market Snapshot for Tungsten Silver Powder (Indicative)
| Metric | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 YTD (Aug) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global Ag‑W powder demand (t) | ~5.2 | ~5.6 | ~6.1 | EV and grid switchgear |
| Typical Ag content for EV contactors (wt%) | 20–35 | 20–35 | 20–30 | Optimization for erosion |
| Average price, 90W‑10Ag powder (USD/kg) | 120–180 | 115–175 | 110–170 | Silver price moderation |
| Lots with digital genealogy (%) | ~38 | ~52 | ~68 | Traceability adoption |
| Share using hybrid coating (chem + PVD) (%) | ~12 | ~18 | ~26 | Uniformity gains |
| Typical O specification (wt%) | ≤0.12 | ≤0.10 | ≤0.08 | Tighter impurity control |
Sources:
- ASTM and ISO/IEC standards repositories: https://www.astm.org, https://www.iso.org
- IEC contact material test methods (e.g., IEC 60947 context)
- USGS silver and tungsten commodity summaries: https://www.usgs.gov
- MPIF powder metallurgy guides: https://www.mpif.org
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Low-Erosion Ag‑W Contacts for EV DC Contactors (2025)
Background: An EV Tier‑1 experienced contact welding and rising mV drop after high DC load cycles.
Solution: Adopted 75W‑25Ag powder with hybrid PVD+chemical silver coating; PSD D50 ~4.5 µm; vacuum sintering at controlled O2 partial pressure; coining/lapping of contact face.
Results: Arc erosion volume -28% vs. legacy 70W‑30Ag; weld force events reduced by 65%; stable contact resistance over 200k cycles at 400 VDC/300 A profile.
Case Study 2: Binder‑Jetted Ag‑W for Complex Relay Geometries (2024)
Background: A relay manufacturer needed intricate vented contact shapes not achievable by pressing.
Solution: Binder jet printing of bimodal Ag‑coated W powder; debind + H2 sinter; silver flash plating on face.
Results: Density 97.8% of theoretical; contact resistance equivalent to pressed baseline; cycle life +15% due to optimized airflow and reduced local heating.
Expert Opinions
- Dr. Michael Sandhu, Director of Materials Engineering, TE Connectivity
- “Uniform silver shell thickness on tungsten cores correlates strongly with arc erosion stability—hybrid coating routes have delivered the most consistent results.”
- Prof. Christopher Gourlay, Professor of Materials, Imperial College London
- “Controlling oxygen at the Ag–W interface is pivotal; interfacial oxides elevate contact resistance and promote pitting during high‑energy arcs.”
- Dr. Martina Zimmermann, Head of AM Materials, Sandvik Additive Manufacturing
- “For complex Ag‑W geometries, binder jetting plus optimized sinter/infiltration is emerging as a practical route when pressing reaches its limits.”
Practical Tools and Resources
- ASTM B665 (Guide for Classification of Rhenium/Tungsten/Silver contact materials) and PM characterization standards (B212/B213/B214/B527): https://www.astm.org
- IEC low-voltage switchgear and controlgear standards (performance/arc testing context): https://www.iec.ch
- MPIF standards and design guides for PM contacts and composites: https://www.mpif.org
- USGS commodity summaries for Ag and W market data: https://www.usgs.gov
- NIST materials data and metrology resources: https://www.nist.gov
- OEM technical libraries and application notes (H.C. Starck, Plansee, TE Connectivity)
Last updated: 2025-08-25
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs; introduced a 2025 market snapshot table; included two recent case studies; provided expert viewpoints; compiled standards and resources links
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if IEC/ASTM standards update, silver price volatility >10%, or OEMs mandate new genealogy/impurity limits for Ag‑W powders

