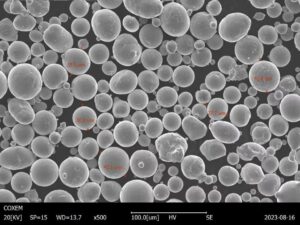
Uses of Titanium Alloy Powders
Titanium alloy powders are versatile materials with a wide range of applications. These powders find extensive use in industries such as aerospace, medical, automotive, and more. Due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, they are often used in manufacturing lightweight yet robust components for aircraft, spacecraft, and high-performance automotive parts.
Moreover, titanium alloy powders play a crucial role in the medical field, where biocompatibility is essential. They are employed in producing medical implants, such as dental implants, joint replacements, and bone plates. The unique combination of mechanical properties and biocompatibility makes titanium alloy powders a preferred choice for these applications.
Manufacturing Process of Titanium Alloy Powders
The manufacturing process of titanium alloy powders involves various techniques, with atomization being one of the most common methods. In atomization, molten titanium alloy is rapidly cooled, resulting in the formation of fine powders. This process allows for precise control over particle size and composition, ensuring the desired material properties.
Other methods include plasma atomization, which involves the use of a plasma jet to melt and atomize the alloy, and mechanical milling, where solid pieces of the alloy are milled into powders. Each method has its advantages and is selected based on factors such as the intended application and required powder characteristics.
Advantages of Titanium Alloys
Titanium alloys offer several distinct advantages that make them a sought-after choice in various industries. One of the primary benefits is their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, which allows for the creation of lightweight yet durable components. This property is particularly advantageous in aerospace and automotive applications, where reducing weight while maintaining structural integrity is crucial.
Additionally, titanium alloys exhibit remarkable corrosion resistance, even in aggressive environments. This corrosion resistance makes them suitable for use in marine, chemical, and medical applications, where materials must withstand harsh conditions over an extended period.

Corrosion Resistance of Titanium Alloy Powders
Titanium alloy powders are highly corrosion-resistant due to the formation of a protective oxide layer on their surface. This oxide layer prevents direct contact between the metal and corrosive agents, effectively inhibiting the degradation of the material. As a result, titanium alloy powders are extensively used in environments where corrosion is a significant concern.
Industries such as offshore oil and gas, chemical processing, and marine engineering rely on the corrosion-resistant properties of titanium alloy powders to ensure the longevity and reliability of their components.
Applications of Titanium Alloy Powders
The applications of titanium alloy powders span a wide range of industries and sectors. One notable application is in the aerospace industry, where titanium alloy powders are used to manufacture critical components such as aircraft engine parts, structural components, and landing gear.
In the medical field, these powders are utilized for producing biocompatible implants, including joint replacements, bone plates, and dental implants. The exceptional biocompatibility of titanium alloys ensures that the implants integrate well with the human body, minimizing the risk of rejection or adverse reactions.
Titanium Alloy Powders vs. Other Materials
Titanium alloy powders offer several advantages over other materials, making them a preferred choice for specific applications. When compared to steel, titanium alloys have a significantly lower density while maintaining comparable strength. This property makes titanium alloy powders ideal for applications where weight reduction is a priority without compromising structural integrity.
In contrast to aluminum, titanium alloys boast superior corrosion resistance and a higher strength-to-weight ratio. This makes them suitable for industries that require both lightweight components and resistance to harsh environments, such as marine and aerospace applications.
3D Printing with Titanium Alloy Powders
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has gained prominence in various industries, and titanium alloy powders are no exception to this trend. 3D printing with titanium alloy powders allows for the creation of complex geometries and customized components that may be challenging or impossible to achieve using traditional manufacturing methods.
This technology finds use in aerospace, medical, and automotive sectors, enabling the production of lightweight yet robust parts with intricate designs. The ability to create near-net-shape components reduces material waste and manufacturing time, making 3D printing with titanium alloy powders a cost-effective and innovative solution.

Cost Considerations of Titanium Alloy Powders
The cost of titanium alloy powders can vary based on factors such as alloy composition, powder particle size, and production method. Titanium alloys are generally more expensive than traditional materials like steel and aluminum due to the complexity of their production processes and the intrinsic value of titanium.
The benefits offered by titanium alloys, such as their superior strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, often outweigh the initial material cost. Industries that prioritize performance, longevity, and reduced maintenance costs are willing to invest in titanium alloy powders to achieve these advantages.
Health and Safety Considerations
While titanium alloy powders offer exceptional mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, it’s important to address health and safety considerations when working with these materials. Fine powders can pose inhalation risks, potentially leading to respiratory issues.
Employers and workers should adhere to safety protocols, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) such as masks and gloves, proper ventilation in work areas, and regular training on safe handling practices. Proper storage and disposal of titanium alloy powders are also crucial to minimize potential hazards.
FAQ
Q1: What are the main uses of titanium alloy powders?
Titanium alloy powders find applications in aerospace, medical, automotive, and marine industries for producing lightweight and corrosion-resistant components.
Q2: How are titanium alloy powders manufactured?
Titanium alloy powders are manufactured through techniques like atomization, plasma atomization, and mechanical milling, allowing precise control over particle size and composition.
Q3: What advantages do titanium alloys offer?
Titanium alloys offer advantages such as high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility, making them ideal for diverse applications.
Q4: Can titanium alloy powders be 3D printed?
Yes, 3D printing with titanium alloy powders enables the creation of complex, lightweight, and customized components for various industries.
Q5: How do titanium alloys compare to other materials like steel and aluminum?
Titanium alloys surpass steel and aluminum in terms of strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility, making them suitable for specific applications.
Q6: What are the health and safety considerations when working with titanium alloy powders?
Workers should follow safety guidelines, use appropriate PPE, ensure proper ventilation, and receive regular training to safely handle titanium alloy powders and minimize inhalation risks.
Q7: What factors influence the cost of titanium alloy powders?
The cost of titanium alloy powders depends on factors like alloy composition, particle size, and production method, with the benefits of the material often justifying the investment.
Summary Table
| Step | Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | Uses of Titanium Alloy Powders | Aerospace, medical, and automotive applications; lightweight, corrosion-resistant components. |
| 3 | Manufacturing Process of Titanium Alloys | Atomization, plasma atomization, mechanical milling; control over particle size, composition. |
| 4 | Advantages of Titanium Alloys | High strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance; ideal for aerospace, automotive, medical sectors. |
| 5 | Corrosion Resistance of Titanium Alloy Powders | Protective oxide layer prevents corrosion; suitable for marine, chemical, and medical applications. |
| 6 | Applications of Titanium Alloy Powders | Aerospace engine parts, medical implants; biocompatibility, strength. |
| 7 | Titanium Alloy Powders vs. Other Materials | Superior strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance over steel, aluminum; aerospace, marine uses. |
| 8 | 3D Printing with Titanium Alloy Powders | Additive manufacturing for complex, lightweight parts; aerospace, medical, automotive applications. |
| 9 | Cost Considerations of Titanium Alloy Powders | Variable cost based on composition, size; long-term benefits outweigh initial material cost. |
| 10 | Health and Safety Considerations | Inhalation risks, proper PPE, ventilation, training, storage; ensure safe handling of titanium powders. |
| FAQ | Frequently Asked Questions | Main uses, manufacturing, advantages, 3D printing, cost factors, industries, selection, recycling, limitations. |
Exploring the world of titanium alloy powders reveals their exceptional properties and wide-ranging applications across industries. From aerospace to medicine, these powders contribute to lighter, stronger, and more corrosion-resistant components, pushing the boundaries of innovation. As industries continue to harness the potential of titanium alloy powders, understanding their properties, benefits, and safety considerations remains crucial for successful and sustainable applications.