Introduction
Molybdenum, an essential transition metal, plays a vital role in various industries owing to its exceptional properties. In this article, we explore the fascinating world of molybdenum powder, an integral form of this element that is highly sought after in numerous industrial applications. From its definition to production methods, market trends, and future prospects, we uncover the versatility of molybdenum powder and its significance in shaping modern technologies.
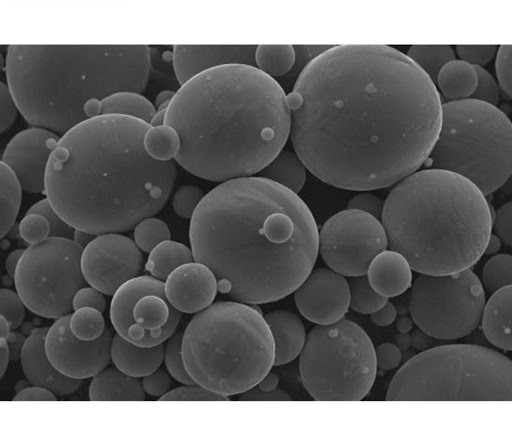
What is Molybdenum Powder?
Molybdenum powder is a finely divided form of molybdenum metal, distinguished by its small particle size and high purity levels. It is obtained through various production methods and possesses remarkable physical and chemical characteristics that make it invaluable in many industries.

Uses of Molybdenum Powder
Metallurgy and Alloy Production
Molybdenum powder serves as a key component in the production of high-strength alloys, including stainless steel and superalloys. Its addition enhances the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of these alloys, making them ideal for applications in aerospace, construction, and more.
Industrial Lubricants
Due to its low coefficient of friction and excellent high-temperature stability, molybdenum powder is used in manufacturing industrial lubricants and greases. These lubricants find use in heavy machinery, automotive parts, and other equipment operating under extreme conditions.
Electronics and Semiconductors
The semiconductor industry relies on molybdenum powder for the production of thin films and electronic components. It is widely used in creating gate contacts, interconnects, and metallization layers in integrated circuits.
Chemical Applications
Molybdenum powder finds applications in various chemical processes, such as catalysts for petrochemical refining and desulfurization. Its catalytic properties are crucial in promoting chemical reactions with high efficiency.
Properties of Molybdenum Powder
High Melting Point and Strength
Molybdenum powder exhibits an exceptionally high melting point, making it suitable for applications involving high temperatures, such as in aerospace propulsion systems and high-temperature furnaces. It also imparts improved strength to alloys when used as an additive.
Thermal Conductivity
One of the outstanding properties of molybdenum powder is its high thermal conductivity, which makes it valuable in heat sinks, electronic cooling devices, and applications requiring efficient heat dissipation.
Corrosion Resistance
Molybdenum powder provides enhanced corrosion resistance to alloys, particularly in harsh environments like marine and chemical processing, ensuring prolonged material durability.
Electrical Conductivity
Its moderate electrical conductivity makes molybdenum powder an excellent choice for electronic and electrical applications, where it can act as a conductive element in circuitry.
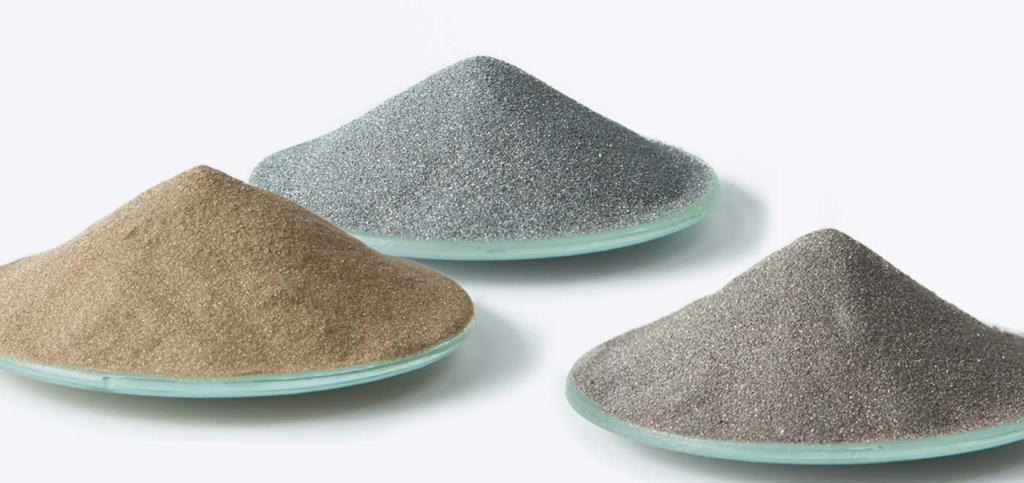

Production Methods of Molybdenum Powder
Reduction of Molybdenum Oxide
One of the common methods to produce molybdenum powder involves reducing molybdenum oxide with hydrogen or carbon at high temperatures, resulting in the formation of molybdenum metal.
Atomization
Atomization is a process that utilizes high-pressure gas or liquid jets to break molten molybdenum into tiny droplets, which then solidify into fine powder particles.
Mechanical Crushing
In this method, molybdenum ingots are crushed into fine particles, producing molybdenum powder with specific particle size distributions.
Grades and Specifications of Molybdenum Powder
Particle Size
Molybdenum powder is available in various particle sizes, ranging from micrometers to nanometers, catering to different industrial requirements.
Purity Levels
High purity is crucial in many applications, and molybdenum powder can be obtained with purity levels of 99.9% and above, ensuring top performance in critical industries like electronics and aerospace.
Application-specific Grades
Manufacturers produce molybdenum powder with tailored properties to meet specific application needs, customizing features like hardness, compressibility, and particle shape.

Market Trends and Applications
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace sector extensively utilizes molybdenum powder in turbine engines, airframe components, and rocket propulsion systems, benefiting from its high strength and resistance to extreme temperatures.
Energy Sector
In power generation and transmission, molybdenum powder plays a crucial role in manufacturing electrical contacts, switches, and power semiconductors, contributing to efficient energy utilization.
Medical Applications
Molybdenum powder is utilized in medical imaging devices and radiation therapy equipment due to its excellent X-ray shielding properties and biocompatibility.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, molybdenum powder finds application in engine components, exhaust systems, and catalytic converters, enhancing performance and reducing emissions.
Benefits and Advantages of Molybdenum Powder
Improved Strength and Toughness
Molybdenum powder’s addition to alloys significantly improves their strength and toughness, making them more durable and capable of withstanding harsh operating conditions. This property is particularly valuable in the aerospace and automotive industries, where components are exposed to extreme stresses.
High-Temperature Applications
Due to its exceptional high melting point, molybdenum powder is perfect for applications that involve elevated temperatures. It is extensively used in the aerospace and energy sectors, where components must withstand extreme heat without compromising performance.
Enhanced Corrosion Resistance
Molybdenum powder enhances the corrosion resistance of alloys, protecting them from degradation caused by exposure to corrosive environments. This property makes it highly desirable in marine, chemical, and oil and gas industries.
Safety Considerations
Handling and Storage
Safety is of utmost importance when dealing with molybdenum powder. Proper handling and storage procedures should be followed to prevent accidents and exposure to harmful particles.
Workplace Safety
Industrial settings that handle molybdenum powder should implement safety measures to protect workers from inhalation and skin contact. Proper ventilation and personal protective equipment (PPE) are crucial for employee well-being.
Environmental Impact
Recycling and Sustainability
The recycling of molybdenum powder and molybdenum-based products helps reduce the demand for virgin materials and minimizes environmental impact. Sustainable practices are vital to ensure responsible resource utilization.
Waste Management
Proper waste management is essential to prevent the release of molybdenum particles into the environment. Industries must adhere to regulations for the safe disposal and recycling of molybdenum-containing waste.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Nanotechnology Applications
The unique properties of molybdenum powder make it a promising material in the field of nanotechnology. Researchers are exploring its potential in nanocomposites, nanoelectronics, and other advanced applications.
Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is revolutionizing various industries. Molybdenum powder’s compatibility with this manufacturing technique opens up new possibilities for complex designs and lightweight structures.
Conclusion
Molybdenum powder stands as a true wonder in the world of industrial applications. Its exceptional properties and versatility make it indispensable in key sectors like aerospace, electronics, and energy. As technology continues to advance, molybdenum powder is likely to play an even more significant role in shaping our future, propelling innovation and progress across various industries.
FAQs
1. Is molybdenum powder the same as molybdenum oxide?
No, molybdenum powder is the elemental form of molybdenum, whereas molybdenum oxide is a compound that contains oxygen and molybdenum.
2. Can molybdenum powder be used in medical implants?
While molybdenum powder itself is not used directly in medical implants, molybdenum-based alloys are utilized in certain medical devices and implants due to their biocompatibility and corrosion resistance.
3. What safety precautions should be taken when handling molybdenum powder?
Workers should wear appropriate protective equipment, such as gloves and masks, to prevent inhalation and skin contact. Proper ventilation in the workplace is also essential to reduce exposure to airborne particles.
4. How does molybdenum powder contribute to sustainability?
Molybdenum powder can be recycled and reused, reducing the demand for new raw materials and promoting sustainable practices in various industries.
5. Can molybdenum powder be used in 3D printing?
Yes, molybdenum powder is compatible with additive manufacturing techniques like 3D printing, enabling the creation of intricate designs and innovative components.
know more 3D printing processes
Additional FAQs on Molybdenum Powder
1) What particle sizes are best for different processes (PM, MIM, AM)?
- Press-and-sinter PM: typically 20–150 μm with good flowability.
- Metal injection molding (MIM): 5–20 μm for high sintered density.
- Laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) AM: spherical 15–45 μm (D10–D90) for stable recoating and density.
2) How do oxygen and carbon impurities affect properties?
Elevated O/C increases brittleness and raises ductile-to-brittle transition temperature, degrading toughness and conductivity. Control with high-purity feedstock, vacuum/H2 reduction steps, and inert handling.
3) Can molybdenum powder be alloyed for better high-temperature strength?
Yes. Mo–Hf–C (MHC) and TZM (Mo–Ti–Zr–C) powders improve creep resistance and recrystallization temperature for hot tooling, furnace hardware, and aerospace thermal parts.
4) Is molybdenum powder suitable for thermal management in electronics?
Mo and Mo-based laminates offer high thermal conductivity with a coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) closer to semiconductors (e.g., Mo-Cu, Mo-Graphite composites), reducing thermal stress in power modules.
5) What are best practices for sintering molybdenum powder?
Dewax in dry H2 or vacuum, sinter at 1600–2000°C under high vacuum or flowing H2, minimize oxygen pickup, and consider HIP for near-full density. Slow cooling can help reduce residual stresses.
2025 Industry Trends in Molybdenum Powder
- Power electronics growth: Higher demand for Mo, TZM, and Mo-Cu composites in SiC/GaN packages and high-reliability heat spreaders.
- AM adoption: Spherical Mo powders for LPBF and binder jetting mature; post-HIP workflows deliver 98–99.5% density for complex thermal hardware.
- Hydrogen economy: Mo-based catalysts for hydrodesulfurization and emerging roles in green H2 production and storage R&D.
- Sustainability and traceability: Wider use of recycled Mo from hardmetal scrap; EPDs and material passports integrated with MES.
- Price stabilization efforts: Supply diversification and recycling buffers volatility tied to energy costs and mining outputs.
| 2025 Metric | Typical Range/Value | Relevance/Notes | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| LPBF Mo relative density | 97–99.5% (post-HIP) | Complex thermal parts, thin walls | Peer-reviewed AM studies; OEM notes |
| Thermal conductivity (bulk Mo) | 130–150 W/m·K | Heat sinks/spreaders benchmark | ASM Handbook; MatWeb |
| TZM typical tensile strength (RT) | 700–950 MPa | High-temp tooling components | ASM data |
| Binder-jetted Mo final density | 95–99% (sinter/HIP) | Cost-efficient complex shapes | Vendor case reports |
| Recycled share of Mo supply | ~30–40% | Scrap recovery reduces footprint | USGS; ITIA-style summaries |
| Indicative price, spherical AM-grade Mo | $120–$220/kg | PSD, sphericity, certs impact | Market trackers; supplier quotes |
Authoritative references and further reading:
- USGS Mineral Commodity Summaries (Molybdenum): https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs
- ASM Handbook: https://www.asminternational.org
- International Molybdenum Association (IMOA): https://www.imoa.info
- ISO/ASTM AM standards (52907 feedstock, 52910 design): https://www.astm.org and https://www.iso.org
- NIST materials data: https://www.nist.gov
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: LPBF-Manufactured TZM Heat Spreader for SiC Inverters (2025)
Background: An EV power electronics supplier needed a low-CTE, high-conductivity spreader with integrated micro-channels.
Solution: Used spherical TZM powder (15–45 μm), high-temperature platform preheat, followed by HIP and stress relief; internal channels optimized for two-phase cooling.
Results: 20% lower junction temperature at 1.2 kW, 2.5× thermal-cycle life (−40 to 175°C), and 17% weight reduction versus machined Mo-Cu plate with drilled channels.
Case Study 2: Binder-Jetted Molybdenum Collimator for Radiotherapy (2024)
Background: A medical OEM sought complex, high-attenuation collimators with shorter lead times.
Solution: Fine-cut Mo powder binder jetted, debound and vacuum sintered >1800°C, optional HIP; incorporated lattice stiffeners to reduce mass.
Results: 97–98% density, equivalent attenuation to legacy W-based units with 12% mass reduction, 30% lead-time reduction, and improved geometric fidelity of channel geometry.
Expert Opinions
- Dr. Douglas G. Ivey, Professor of Materials Engineering, University of Alberta
Key viewpoint: “Interstitial control—especially oxygen—is decisive for molybdenum’s ductility and conductivity; vacuum/H2 processing and clean handling are non-negotiable.” - Dr. Elena López, Head of Additive Manufacturing, AIMEN Technology Centre
Key viewpoint: “For AM molybdenum and TZM, platform preheat and HIP are essential to mitigate cracking, while topology optimization unlocks unique thermal designs.” - Richard Preston, Technical Director, International Molybdenum Association (IMOA)
Key viewpoint: “Demand growth in power electronics and hydrogen-related catalysts is broadening molybdenum powder’s strategic role across energy transition supply chains.”
Citations for expert profiles:
- University of Alberta: https://www.ualberta.ca
- AIMEN Technology Centre: https://www.aimen.es
- IMOA: https://www.imoa.info
Practical Tools and Resources
- Standards and data
- ASTM B387 (Mo products), ASM Handbook volumes on refractory metals: https://www.asminternational.org
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (feedstock), 52910 (DFAM): https://www.astm.org
- Design/simulation
- COMSOL Multiphysics (Heat Transfer, AC/DC): https://www.comsol.com
- Ansys Additive + Mechanical (distortion, thermal): https://www.ansys.com
- nTopology (lattices for cooling): https://ntop.com
- Powder QC and processing
- LECO O/N/H analyzers: https://www.leco.com
- Bodycote HIP services and high-temp vacuum heat treat: https://www.bodycote.com
- Senvol Database (machines/materials): https://senvol.com/database
- Industry and market intelligence
- USGS molybdenum statistics: https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs
- IMOA technical brochures and corrosion guidance: https://www.imoa.info
Last updated: 2025-08-21
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs, 2025 trend table with metrics and sources, two recent molybdenum powder case studies, expert viewpoints with citations, and a practical resources list.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if USGS/IMOA market data shifts materially, new AM/HIP processing guidance for Mo/TZM is released, or standards (ASTM/ISO) affecting powder specs are updated.

