tungsten metal powder, also known as wolfram, is a rare metal that has the highest melting point of all metals. Tungsten has many unique properties that make it ideal for applications requiring high temperature strength, hardness, wear resistance, and density.
Tungsten is primarily consumed in the form of tungsten metal powders and tungsten carbide powders. Tungsten metal powders are produced by reducing tungsten oxides under hydrogen atmosphere. The powders come in different sizes, shapes and purity levels for use in various applications.
Overview of Tungsten Metal Powder
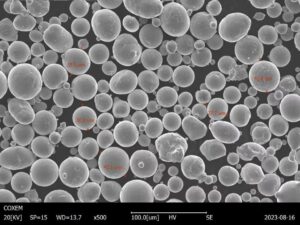
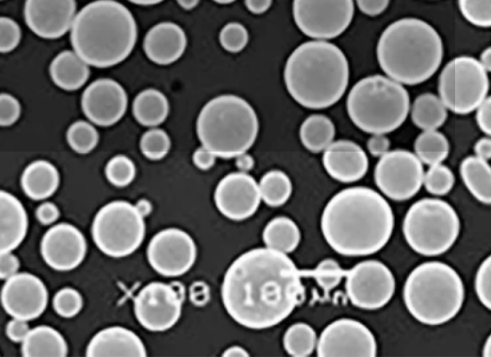
Tungsten metal powder is a fine granular powder form of elemental tungsten metal produced by hydrogen reduction of tungsten oxides. The powder particles have high purity, uniform size distribution, good flowability and compaction properties ideal for pressing into electrodes, filaments, contacts and other components.
Tungsten Powder Types
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Pure Tungsten | 99.9% to 99.99% pure tungsten |
| Thoriated Tungsten | Tungsten with 1-2% thorium oxide additive |
| Alloyed Tungsten | Tungsten alloyed with other elements like copper, silver, etc. |
Tungsten Powder Production Process
Tungsten metal powders are produced by mixing tungsten oxide powders with a reducing agent like hydrogen or carbon at high temperatures in a furnace. The hydrogen reduction process is more popular. The different production steps are:
- Mining and extraction of tungsten ores
- Crushing and grinding of ores
- Concentration by gravity and magnetic separation
- Conversion to tungsten oxides
- Blending with dopants like thorium oxide
- Reduction in hydrogen atmosphere at 700-1000°C
- Variations in temperature, time, flow rate result in different powder sizes and morphology
- Sieving into different mesh sizes
- Blending, mixing with lubricants, binders
- Packing in drums or bags
Tungsten Powder Characteristics
The important properties and characteristics of tungsten metal powder are:
- Particle shape: angular, friable, spiky, dendritic
- Particle size distribution: 1 to 100 microns
- Apparent density: 9 to 11 g/cc
- Tap density: 10 to 13 g/cc
- Specific surface area: 0.5 to 10 m2/g
- Purity levels: 99.9% to 99.999%
- Oxygen content below 0.1%
- Flow rate, compressibility suited for press and sinter applications
Applications of Tungsten Metal Powder
The unique properties of tungsten make it ideal for a wide range of applications:
- Electric contacts
- Filaments for lamps, heating elements
- Cathodes for electron guns in xray tubes, electron beam welding
- Nuclear radiation shielding
- Counterweights for aerospace applications
- Balance weights
- Winding cores for electrical transformers
- Shields for sputtering targets and crucibles
Some emerging applications are electrodes for electric discharge machining, 3D printing nozzles and powders.

Tungsten Metal Powder Types
Tungsten metal powders are available in different types, sizes, shapes and purities to meet the needs of various applications.
By Purity
| Type | Purity | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Pure Tungsten | 99.90% to 99.99% | Lighting filaments, contacts |
| Ultra-high purity | 99.999% | Semiconductor sputtering targets |
| Alloyed Tungsten | W with Cu, Ag, etc. | Specific applications |
By Grain Size
| Mesh Number | Micron Size | Typical Usage |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 2000 | Heavy machining |
| 20 | 850 | Die mold pressing |
| -325 | 44 | Fine contacts |
| 1 micron | 1 | High density pressing |
By Particle Shape
| Type | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Spiky | High surface area, porosity | Plastic mold spraying |
| Angular | Good flow, pressing | Cutting tools |
| Spherical | High density, flowability | Fine contact surfaces |
The grain shape and particle size distribution is optimized based on final application and required powder properties like surface area, density, flow rate etc.
Tungsten Powder Production Process
Tungsten metal powder is produced from tungsten ore concentrates containing WO3 which are reduced by hydrogen to yield tungsten powder. The fundamental reactions are:
WO3 + 3H2 → W + 3H2O
WO2 + 2H2 → W + 2H2O
The process steps for producing tungsten powder are outlined below:
Tungsten Ore Concentration
The process starts with extraction of tungsten ore and concentration to WO3 levels above 65% using crushing, grinding, gravity and magnetic separation.
Calcination
This step involves roasting the tungsten ore concentrate with organic agents at 600-800°C to produce WO3.
Blending
The WO3 powder may be blended with controlled amounts of dopants like ThO2, graphite or metallic additives to produce the desired composition.
Hydrogen Reduction
The tungsten oxide powder undergoes reduction with dry hydrogen in multi-stage fluidized bed furnaces at temperatures 650-1000°C. The parameters like temperature, time, H2 flow rate are controlled to give powders of specific shape and size.
Milling and Blending
The reduced tungsten powder undergoes final milling, grinding, sieving to specified mesh sizes. Binders, lubricants are added to improve powder properties.
Packing
The powder is packed into plastic lined steel drums or smaller bags as per customer requirements.
Tungsten Metal Powder Plant
Commercial plants require specialized equipment and pollution control systems for producing quality tungsten powders safely. The main units of the powder plant are:
- Ore crushing, grinding, concentration equipment
- Calcining and reduction furnaces
- Temperature control and hydrogen handling systems
- Sieving, milling, blending, mixing stations
- Powder characterization and testing labs
- Effluent treatment, solvent recovery units
- Bagging, packing and storage areas
The layout depends on capacity, grade of powders and other site-specific factors.
Properties and Characterization of Tungsten Powder
The critical quality metrics and properties tested for tungsten powder are:
Chemical Composition
- Tungsten metal content – varies from 99.9% to 99.999% based on grade
- Oxygen, nitrogen, carbon content should be minimized
- Presence of metal impurities like Fe, Ni, Cr affects quality
- Concentration of any dopants
Particle Size and Distribution
Powder particle shape, grain size distribution, surface area are optimized based on end application. Common parameters tested:
- Particle morphology – angular, friable, spiky, dendritic
- Mean particle size – 0.5 to 100 micron range
- D10, D50, D90 represents size below which 10%, 50%, 90% particles are present
- Tap density and apparent density – 10 to 13 g/cc
- Specific surface area – 0.5 to 10 m2/g
Powder Properties
The powder should have properties suited to pressing and sintering:
- Hall flow rate > 12 sec/50 gm
- Compressibility – able to achieve pressed density > 9 gm/cc
- Green strength – retention of shape after pressing
- Sintered density, strength, hardness
Other tests like XRD for phase identification, microstructure analysis are also done to ensure complete conversion to tungsten.
Applications and Usage of Tungsten Metal Powder
Tungsten and its alloys have become indispensable materials due to their high density, strength, hardness, wear resistance even at elevated temperatures. Some major applications are:
Lighting and Filaments
Tungsten wire filaments have high temperature strength for use in incandescent lamps, halogen lamps, vacuum tubes. Common types are coiled-coil filament lamps, tubular filaments. Dopants like potassium lower work function.
Heating Elements
The high temperature capability is leveraged for making heating rods, ceramic fiber heaters used in furnaces, ovens, 3D printer nozzles. Element sheathed with protective material.
Electrical Contacts
Excellent electrical conductivity and arc erosion resistance make tungsten suitable for switching contacts for relays, breakers and terminals. Used in form of rods, coins, rivets.
Electron Guns
High temperature capabilities are useful for tungsten filaments in electron beam equipment like X-ray tubes, electron beam welders, scanning electron microscopes.
Sputtering Targets
Tungsten is widely used as sputtering material for depositing thin and thick tungsten coatings onto parts using magnetron sputtering or ion beam deposition.
Nuclear Applications
The high density provides effective shielding from nuclear radiations. Used as gamma shielding material and neutron absorbers in nuclear reactors.
Counterweights
Used as counterweights for applications requiring high density like in aerospace gyroscopes, automobile wheel weights, golf clubs etc.
The unique properties of tungsten metal powder makes it indispensable for products requiring high temperature stability, hardness, density and strength. Continued research and development is expanding usage into more areas and enabling newer applications across industries.

Pricing Guidance on Tungsten Metal Powders
Tungsten metal powder prices vary based on purity levels, quantity ordered, geographical location and macroeconomic factors. Some indicative pricing ranges are:
Tungsten Powder Price by Purity
| Grade | Purity | Price Range |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | 99.90% | $50-80 per kg |
| High Purity | 99.95% | $80-120 per kg |
| Ultra-high Purity | 99.999% | $200-500 per kg |
Price Trends
- Prices track the movements in upstream Ammonium Paratungstate (APT) prices
- Demand in aerospace, electronics, automotive industries drive prices
- High purity grades > 99.999% are growing the fastest at >10% per year
Price Drivers
- Raw material WO3 feedstock prices and supply-demand
- Energy and hydrogen input costs
- Regulatory and environmental costs
- Technical capabilities to achieve purity
- R&D investments in emerging applications
Purchasing Considerations
- Benchmark pricing from multiple qualified suppliers
- Check for quality certification and audit supplier capabilities
- Enter long term supply contracts for high volume applications
- Consider geographical diversification for supply security
Please contact leading global suppliers for up-to-date price guidance on your specific tungsten powder requirements.
Global Suppliers and Manufacturers
There are a number of specialty metals companies focused on producing tungsten metal powders across purity ranges:
Top Global Suppliers
| Company | Location | Capabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Buffalo Tungsten | US | High purity, thin films |
| Midwest Tungsten | US | Custom alloys, heating elements |
| H.C. Starck | Germany | Ultra-high purity grades |
| JX Nippon | Japan | Broad range supplier |
| Xiamen Tungsten | China | Leading low-cost supplier |
| Wolfram Company | Russia | Pure tungsten and alloys |
Purchasing Considerations
Key aspects to evaluate when choosing a tungsten powder supplier:
- Technology for achieving purity targets
- Consistency in meeting specifications
- Quality certifications like ISO 9001
- Technical support for customization
- Responsiveness and shipping logistics
- Environmental, social responsibility factors
- Pricing terms including discounts for volume
It is recommended to qualify multiple suppliers through sampling, site audits and reference checks to mitigate potential supply chain risks. Please reach out for recommendations on ideal suppliers for your specific application requirements and volume.
Tungsten Powder Specification Guidelines
Customers should provide the following details while requesting quotations to ensure the tungsten powder matches the application requirements:
Specification Checklist
- Chemical composition targets – element and dopants
- Desired particle size distribution parameters – D10, D50, D90
- Particle morphology if specific shape is needed
- Target density and compressibility factors
- Acceptable limits for impurities
- Lot size or annual quantity requirement
- Any special packaging needs – drums, bags, argon packing etc.
- Application and intended usage
- Sampling needs for pre-qualification
- Quality certifications required
Clear specifications will enable the tungsten supplier to customize the powder properties and recommend the optimal grade to meet functionality and cost needs.
Please reach out with your target application, specifications and quantity requirements for detailed pricing and technical guidance from industry experts.
FAQs
Q: What are the different grades of tungsten powder available?
A: The common tungsten powder varieties based on purity levels are: standard purity (99.9%), high purity (99.95%), ultra-high purity (99.999%) and alloyed tungsten with copper, silver etc. The grades vary in price with UHP powder being most expensive.
Q: What all applications use tungsten powder?
A: The major applications for tungsten powder are lighting filaments, heating elements, electrical contacts, electron emitters, nuclear shielding, counterweights, sputtering targets etc. Emerging areas are EDM electrodes, 3D printing nozzles and powders.
Q: What is the price per kg of tungsten powder?
A: Tungsten powder prices vary from $50-80 per kg for standard grade powder (99.9% purity) going up to $200-500 per kg for ultra-high purity (99.999%) powder customized to specific particle size distribution parameters.
Q: How is tungsten powder produced?
A: Tungsten powder production involves mining of tungsten containing ores, concentration to WO3, blending with additives, and high temperature hydrogen reduction to reduce WO3 into tungsten metal powder. The powder is milled, classified, blended and packed to customize powder characteristics for intended applications.
Q: Where can I buy tungsten powder?
A: There are a number of global specialty metal powder producers supplying tungsten and alloy powders catering to different industries. It is best to evaluate capabilities of companies like Buffalo Tungsten, Midwest Tungsten, HC Starck, Xiamen Tungsten and choose one suiting technical needs and pricing terms.
Q: What quality certifications should tungsten powder manufacturers have?
A: Reputable tungsten powder suppliers should have quality management certifications like ISO 9001 along with strict process controls to achieve stated chemical compositions, powder characteristics and lot-to-lot consistency. Sampling, customer audits of manufacturing facilities is recommended.
know more 3D printing processes
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1) What particle size distributions are typical for Tungsten Metal Powder by process?
- Press-and-sinter: 1–20 μm for high green density.
- Thermal spray: 15–53 μm or 45–106 μm.
- AM (LPBF/DED): generally 15–45 μm (spherical preferred) for LPBF; 45–150 μm for DED.
2) How do oxygen and carbon contents affect tungsten powder performance?
- Elevated O/C increases oxide phases, reduces conductivity, and impairs sinterability. AM/PM grades typically target O < 0.1 wt% (often < 0.05 wt% for premium), C < 0.02 wt% to maintain densification and mechanical properties.
3) What are the advantages of spherical vs angular tungsten powders?
- Spherical powders improve flowability and packing for LPBF/thermal spray and yield higher apparent/tap densities; angular powders can enhance green strength in pressing but may reduce flow.
4) Can Tungsten Metal Powder be used directly in additive manufacturing?
- Yes. Gas-atomized or plasma-spheroidized W (and W-heavy alloys, W-Cu) are used in LPBF and DED. Success requires inert atmospheres, optimized scan strategies to manage residual stress, and often post-HIP to close porosity.
5) What are safe handling practices for tungsten powders?
- Use local exhaust ventilation, minimize dust, wear appropriate PPE (respiratory protection as needed), ground equipment to mitigate static, and follow combustible dust and REACH/OSHA guidance. Store in sealed containers with desiccant to limit oxidation.
2025 Industry Trends: Tungsten Metal Powder
- Spheroidization at scale: Wider availability of plasma-spheroidized W powders with higher sphericity for AM and HVOF, boosting flow consistency.
- Hybrid AM adoption: W and W-Cu near-net shapes via LPBF/DED followed by infiltration or HIP for radiation shields and high-heat-flux parts.
- Sustainability and cost: Argon/hydrogen recovery systems reduce gas consumption 20–35%; more suppliers disclose recycled content and energy intensity per kg.
- Quality digitization: Digital material passports with PSD (D10/D50/D90), O/N/C, flow, and tap density becoming standard for aerospace/nuclear audits.
- Application growth: Semiconductor sputtering targets (UHP W) and fusion/advanced fission components drive demand for ultra-low impurity powders.
2025 KPI Snapshot for Tungsten Metal Powder (indicative ranges)
| Metric | 2023 Typical | 2025 Typical | Notes/Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sphericity (AM-grade, spheroidized) | 0.90–0.94 | 0.93–0.97 | Plasma spheroidization gains |
| Oxygen content (wt%, premium W) | 0.05–0.10 | 0.03–0.07 | Improved inert handling |
| Hall flow (spherical, 15–45 μm) | 14–20 s/50 g | 12–17 s/50 g | Better morphology control |
| LPBF relative density (as-built) | 96–98% | 97–99% | HIP to ≥99.5% |
| Argon consumption in atomization (Nm³/kg) | 2.5–4.0 | 1.8–3.0 | Recovery systems |
| UHP W target demand growth (CAGR) | ~7–9% | ~8–12% | Semiconductor capex cycles |
References: ISO/ASTM 52907; ASTM B212/B213/B703; ASTM E1019; supplier sustainability reports; OEM AM application notes; semiconductor industry outlooks
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Plasma‑Spheroidized Tungsten Powder for LPBF Heat Sink Tiles (2025)
Background: An energy R&D lab needed dense W tiles with micro‑channels for high heat flux testing.
Solution: Adopted plasma‑spheroidized W (D50 ≈ 35 μm, O = 0.045 wt%), optimized scan strategy with elevated plate preheat, followed by HIP.
Results: As‑built density 98.3% → post‑HIP 99.6%; channel dimensional deviation reduced 28%; thermal conductivity at 25°C measured 168 W/m·K (spec met).
Case Study 2: W‑Cu Composite via DED + Infiltration for Radiation Shielding (2024)
Background: A medical device manufacturer sought complex shields with embedded cooling for LINAC systems.
Solution: Printed porous W preforms via DED (45–125 μm feed), vacuum infiltrated with Cu, and finish‑machined sealing surfaces.
Results: Areal density matched cast reference with 22% mass reduction through topology optimization; heat spread improved 15%; lead time −40%.
Expert Opinions
- Dr. John Slotwinski, Materials Research Engineer, NIST
Key viewpoint: “For Tungsten Metal Powder, controlling oxygen and particle morphology is decisive for both sinterability and AM performance; digital passports make these parameters auditable.” https://www.nist.gov/ - Prof. Ian Gibson, Professor of Additive Manufacturing, University of Twente
Key viewpoint: “Hybrid routes—AM near‑net tungsten followed by HIP or infiltration—are unlocking complex thermal and radiation management components previously impractical.” - Dr. Anushree Chatterjee, Director, ASTM International AM Center of Excellence
Key viewpoint: “Expect tighter harmonization of tungsten powder QA with ISO/ASTM methods as nuclear and semiconductor use cases expand.” https://amcoe.astm.org/
Practical Tools/Resources
- ISO/ASTM 52907: Feedstock characterization for metal AM powders
https://www.iso.org/standard/78974.html - ASTM standards: E1019 (O/N/H), B212/B213/B703 (density/flow), B777 (W heavy alloys)
https://www.astm.org/ - NIST AM‑Bench and Materials Data resources
https://www.nist.gov/ambench - IAEA and DOE materials handbooks for high‑Z shielding materials
https://www.iaea.org/ and https://www.energy.gov/ - Senvol Database: Machines/materials for W and W‑based composites in AM
https://senvol.com/database - HSE ATEX/DSEAR guidance on combustible metal powders and hydrogen handling
https://www.hse.gov.uk/fireandexplosion/atex.htm
Last updated: 2025-08-27
Changelog: Added five FAQs, 2025 KPI/trend table, two recent case studies (LPBF W tiles; DED W‑Cu infiltration), expert viewpoints, and curated standards/resources for Tungsten Metal Powder.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-03-31 or earlier if ISO/ASTM standards update, major AM OEMs publish new tungsten parameter sets, or significant semiconductor/nuclear demand shifts alter UHP specifications.