Overview of Gas Atomizer Equipment
Gas atomizer equipment plays a crucial role in the production of metal powders, which are essential in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics. These devices use high-pressure gas to break down molten metal into fine particles, resulting in high-purity, uniform powder with excellent flowability. This process is vital for applications requiring precision and consistency in material properties.
Gas atomization ensures that the produced metal powders have desirable characteristics such as controlled particle size distribution, high purity, and spherical morphology. These properties make gas-atomized powders ideal for additive manufacturing (3D printing), metal injection molding (MIM), and other advanced manufacturing techniques.

Types, Composition, Properties, and Characteristics of Gas Atomizer Equipment
Types of Gas Atomizer Equipment
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Inert Gas Atomizers | Use inert gases like argon or nitrogen to prevent oxidation of metals during the atomization process. |
| Reactive Gas Atomizers | Utilize reactive gases such as hydrogen to produce specific alloys or to modify powder characteristics. |
| Water Atomizers | Employ high-pressure water jets instead of gas, suitable for metals that are less reactive with water. |
| Vacuum Atomizers | Operate in a vacuum to prevent contamination, ideal for high-purity powder production. |
Composition of Gas Atomizer Equipment
| Component | Material | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Atomizing Nozzle | Tungsten Carbide, Steel | Directs the gas flow to break up molten metal. |
| Gas Supply System | Stainless Steel, Alloys | Provides and regulates the flow of gas. |
| Melting Furnace | Graphite, Ceramic Linings | Melts the metal feedstock before atomization. |
| Powder Collection System | Stainless Steel, Polymers | Collects and stores the metal powder. |
Properties and Characteristics of Gas Atomizer Equipment
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
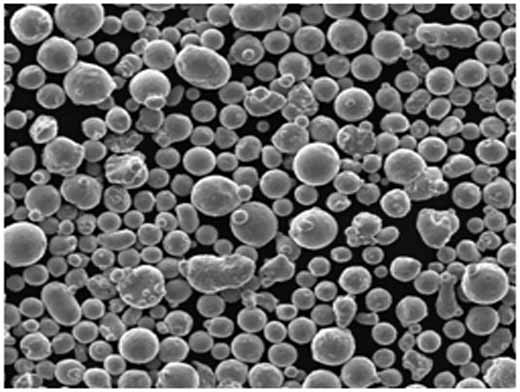
| Particle Size Distribution | Uniform and controlled, typically ranging from 10 to 150 microns. |
| Powder Morphology | Spherical particles with smooth surfaces for improved flowability and packing density. |
| Purity Levels | High purity with minimal contamination due to inert atmosphere processing. |
| Production Capacity | Varies from small laboratory-scale units to large industrial systems. |
| Efficiency | High efficiency in converting metal feedstock into powder form. |
Applications and Uses of Gas Atomizer Equipment
Applications of Gas Atomized Powders
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Production of lightweight, high-strength components. |
| Automotive | Manufacturing of parts with complex geometries. |
| Medical | Creation of biocompatible implants and surgical tools. |
| Electronics | Fabrication of conductive pastes and components. |
| Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) | Production of prototypes and end-use parts. |
| Metal Injection Molding (MIM) | Forming intricate metal parts with precision. |
Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards of Gas Atomizer Equipment
Specifications of Gas Atomizer Equipment
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Gas Pressure | Ranges from 10 to 50 bars depending on the model. |
| Nozzle Diameter | Typically between 0.2 to 2 mm. |
| Melting Capacity | From 1 kg to several tons per batch. |
| Powder Yield | Up to 95% efficiency in powder production. |
Sizes and Grades of Metal Powders
| Grade | Size Range (microns) | Typical Composition |
|---|---|---|
| Fine | 10 – 30 | High-purity metals and alloys. |
| Medium | 30 – 60 | General-purpose metal powders. |
| Coarse | 60 – 150 | Structural and heavy-duty parts. |
Standards for Gas Atomized Powders
| Standard | Organization | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM B243 | ASTM International | Standard terminology of powder metallurgy. |
| ISO 4497 | International Organization for Standardization | Determination of particle size distribution by sieving. |
| MPIF Standard 35 | Metal Powder Industries Federation | Material standards for metal powders. |





Suppliers and Pricing Details of Gas Atomizer Equipment
Suppliers of Gas Atomizer Equipment
| Supplier | Location | Specialization |
|---|---|---|
| Höganäs AB | Sweden | High-quality metal powders and atomizing equipment. |
| Sandvik AB | Sweden | Advanced atomization technology for various metals. |
| Praxair Surface Technologies | USA | Industrial gas solutions and atomizer equipment. |
| AP&C (GE Additive) | Canada | Aerospace-grade metal powders and atomizing systems. |
Pricing Details
| Equipment Type | Price Range |
|---|---|
| Laboratory Scale Atomizers | $50,000 – $200,000 USD |
| Industrial Scale Atomizers | $500,000 – $5,000,000 USD |
| Custom-Built Systems | Varies based on specifications |
Pros and Cons of Gas Atomizer Equipment
Advantages of Gas Atomizer Equipment
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| High Purity | Produces metal powders with minimal contamination. |
| Uniform Particle Size | Ensures consistent quality and performance in applications. |
| Versatility | Can process a wide range of metals and alloys. |
| Scalability | Suitable for both small-scale and large-scale production. |
Limitations of Gas Atomizer Equipment
| Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
| High Initial Cost | Significant investment required for equipment setup. |
| Complex Operation | Requires skilled operators and stringent process control. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed to ensure optimal performance. |
| Energy Consumption | High energy usage during the atomization process. |
Specific Metal Powder Models
- Inconel 625
- Composition: Nickel, Chromium, Molybdenum
- Properties: High corrosion resistance, excellent fatigue and thermal-fatigue strength, oxidation resistant.
- Applications: Aerospace, marine, chemical processing.
- Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V)
- Composition: Titanium, Aluminum, Vanadium
- Properties: High strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, biocompatible.
- Applications: Medical implants, aerospace components, automotive parts.
- 316L Stainless Steel
- Composition: Iron, Chromium, Nickel, Molybdenum
- Properties: Excellent corrosion resistance, good mechanical properties.
- Applications: Medical devices, food processing equipment, chemical containers.
- Aluminum Alloy (AlSi10Mg)
- Composition: Aluminum, Silicon, Magnesium
- Properties: High strength, lightweight, good thermal properties.
- Applications: Automotive, aerospace, structural components.
- Cobalt-Chrome (CoCr)
- Composition: Cobalt, Chromium, Molybdenum
- Properties: High wear resistance, biocompatibility, excellent mechanical properties.
- Applications: Medical implants, dental devices, aerospace.
- Copper Alloy (CuNi2SiCr)
- Composition: Copper, Nickel, Silicon, Chromium
- Properties: High thermal and electrical conductivity, good mechanical properties.
- Applications: Electrical components, heat exchangers, aerospace.
- Maraging Steel
- Composition: Iron, Nickel, Cobalt, Molybdenum, Titanium
- Properties: Ultra-high strength, good toughness, easy to heat treat.
- Applications: Tooling, aerospace, high-performance engineering.
- Hastelloy X
- Composition: Nickel, Chromium, Molybdenum, Iron
- Properties: Excellent oxidation resistance, high-temperature strength.
- Applications: Aerospace, gas turbines, industrial furnace applications.
- Nickel Alloy 718
- Composition: Nickel, Chromium, Iron, Niobium, Molybdenum
- Properties: High tensile, yield, and creep-
rupture properties.
- Applications: Jet engines, high-stress components, oil and gas.
- Tool Steel (H13)
- Composition: Iron, Chromium, Molybdenum, Vanadium
- Properties: High toughness, good thermal fatigue resistance.
- Applications: Tooling, molds, dies for hot work applications.
Comparative Analysis of Gas Atomizer Equipment
| Feature | Inert Gas Atomizers | Reactive Gas Atomizers | Water Atomizers | Vacuum Atomizers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purity of Powder | High | Moderate to high | Moderate | Very high |
| Particle Morphology | Spherical | Spherical | Irregular | Spherical |
| Cost | Moderate to high | High | Low to moderate | Very high |
| Suitable Metals | Wide range | Specific alloys | Less reactive metals | High-purity metals |
| Oxidation Prevention | Excellent | Good | Requires post-treatment | Excellent |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Type
| Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Gas Atomizers | High purity, wide applicability | Higher operational cost, requires inert gas supply |
| Reactive Gas Atomizers | Allows alloying during atomization | Higher complexity, specialized gas handling required |
| Water Atomizers | Lower cost, simpler setup | Produces irregular particles, risk of contamination |
| Vacuum Atomizers | Highest purity, prevents oxidation and contamination | Very high cost, complex maintenance |

FAQ
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is gas atomization? | Gas atomization is a process where molten metal is disintegrated into fine droplets by a high-pressure gas stream, forming metal powders. |
| Why use inert gases in atomization? | Inert gases like argon prevent oxidation and contamination of the metal powders, ensuring high purity and quality. |
| Can gas atomizers handle all types of metals? | Most gas atomizers can handle a wide range of metals and alloys, but specific setups may be required for reactive or high-melting-point metals. |
| What industries benefit from gas atomized powders? | Aerospace, automotive, medical, electronics, and additive manufacturing industries benefit significantly from gas atomized powders. |
| How does particle size affect the application of metal powders? | Smaller, uniform particles are preferred for precision applications like 3D printing, while larger particles may be used in conventional processes. |
| What are the environmental considerations of gas atomization? | Gas atomization typically has lower environmental impact compared to other methods, especially when using inert gases that do not react with metals. |
| How is the quality of metal powders ensured during production? | Quality is ensured through controlled atmospheres, precise gas flow regulation, and stringent post-production testing for particle size and composition. |
| What is the difference between gas atomization and water atomization? | Gas atomization uses high-pressure gas for finer, spherical powders, whereas water atomization uses water jets, producing more irregular shapes. |
| Are there any new advancements in gas atomization technology? | Yes, advancements include improved nozzle designs, better gas flow control, and integration with digital monitoring systems for enhanced precision. |
| How can I choose the right gas atomizer for my needs? | Consider factors like the type of metal, required purity, particle size distribution, production capacity, and budget when choosing a gas atomizer. |
