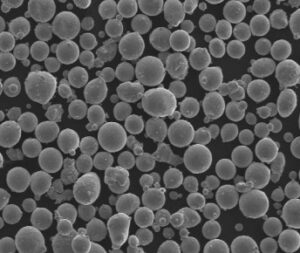
Overview of High Purity Powder
In the world of materials science, high purity powders are the building blocks of advanced manufacturing and technology. These finely milled particles—often metals or metal alloys—are prized for their exceptional purity, consistent particle size, and precise chemical composition. But what exactly is high purity powder? Why is it so important? And what are the different types you can find?
If you’re diving into the realm of high purity powders, it’s crucial to understand the ins and outs of this specialized material. In this guide, we’ll explore everything from the composition and properties of these powders to their applications, suppliers, and how to choose the best one for your needs.
What is High Purity Powder?
High purity powders are finely divided substances, typically metals or alloys, that boast a purity level of 99.9% or higher. These powders are crucial in industries where even the slightest impurity can lead to significant performance issues or failures, such as in electronics, aerospace, and pharmaceuticals.
Imagine trying to bake a cake with flour that has tiny bits of sand in it. The result wouldn’t be what you expect, right? The same logic applies to manufacturing processes that use metal powders—purity is paramount.
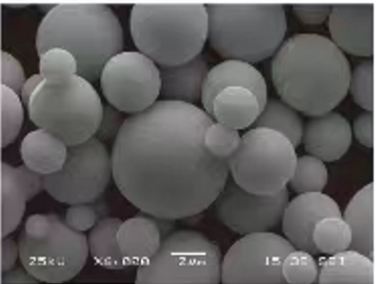
The Composition of High Purity Powder
High purity powders come in various compositions depending on the metal or alloy in question. Each type has its unique characteristics, making it suitable for specific applications. Below is a table detailing some of the most common high purity metal powders, their compositions, and key characteristics.
| Metal Powder | Composition | Purity Level | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Powder | Al (99.9% or higher) | 99.9% | Lightweight, high conductivity, corrosion-resistant |
| Copper Powder | Cu (99.99% or higher) | 99.99% | Excellent electrical conductivity, ductile |
| Titanium Powder | Ti (99.5% or higher) | 99.5% | High strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion-resistant |
| Silver Powder | Ag (99.99% or higher) | 99.99% | High thermal and electrical conductivity |
| Gold Powder | Au (99.99% or higher) | 99.99% | High corrosion resistance, excellent conductivity |
| Iron Powder | Fe (99.9% or higher) | 99.9% | Magnetic, easily alloyed with other metals |
| Nickel Powder | Ni (99.8% or higher) | 99.8% | High resistance to oxidation and corrosion |
| Zinc Powder | Zn (99.9% or higher) | 99.9% | Corrosion-resistant, used in galvanizing |
| Platinum Powder | Pt (99.95% or higher) | 99.95% | Extremely corrosion-resistant, catalytic properties |
| Palladium Powder | Pd (99.95% or higher) | 99.95% | Excellent catalytic properties, corrosion-resistant |
Characteristics of High Purity Powder
The characteristics of high purity powders are what make them so valuable in various industries. Here are some of the most important properties:
- Purity: High purity levels (99.9% and above) ensure that there are minimal impurities that could affect the material’s performance.
- Particle Size and Distribution: Consistent particle size and distribution are critical for achieving uniformity in the final product.
- Chemical Stability: These powders are chemically stable, meaning they won’t react easily with other substances, which is vital in environments where reactivity could lead to safety concerns or product failures.
- Flowability: The ability of the powder to flow smoothly is essential in manufacturing processes like 3D printing or powder metallurgy.
- Density: The density of the powder can affect the properties of the final product, such as strength and durability.
Types of High Purity Metal Powders
Let’s dive deeper into specific high purity metal powders, examining their unique properties, applications, and why they stand out.
1. Aluminum Powder
- Properties: Aluminum powder is known for its light weight and high electrical conductivity. It’s also corrosion-resistant, which makes it ideal for applications in the aerospace and automotive industries.
- Applications: Widely used in the production of paints, explosives, and as a component in metal coatings.
2. Copper Powder
- Properties: With excellent electrical conductivity and ductility, copper powder is a key material in electronics.
- Applications: Used in the production of electrical components, conductive inks, and coatings.
3. Titanium Powder
- Properties: Titanium powder offers a high strength-to-weight ratio and is corrosion-resistant, making it perfect for medical implants and aerospace components.
- Applications: Commonly used in 3D printing, aerospace, and biomedical fields.
4. Silver Powder
- Properties: Silver powder is highly conductive and has antimicrobial properties, which makes it valuable in electronics and medical applications.
- Applications: Used in conductive pastes, solar cells, and antimicrobial coatings.
5. Gold Powder
- Properties: Gold powder is extremely resistant to corrosion and has excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for high-end electronics and medical devices.
- Applications: Used in electronics, jewelry, and as a catalyst in chemical reactions.
6. Iron Powder
- Properties: Iron powder is magnetic and easily alloyed, which allows for a wide range of applications in manufacturing and metallurgy.
- Applications: Used in automotive parts, magnetic materials, and as a catalyst in chemical reactions.
7. Nickel Powder
- Properties: Nickel powder is highly resistant to oxidation and corrosion, which makes it suitable for harsh environments.
- Applications: Used in batteries, superalloys, and as a catalyst in hydrogenation processes.
8. Zinc Powder
- Properties: Zinc powder is primarily known for its corrosion resistance and is often used in protective coatings.
- Applications: Widely used in galvanizing, as an anti-corrosion agent, and in the production of batteries.
9. Platinum Powder
- Properties: Platinum powder is incredibly corrosion-resistant and possesses excellent catalytic properties, making it valuable in both industrial and medical fields.
- Applications: Used in catalytic converters, fuel cells, and as a catalyst in various chemical reactions.
10. Palladium Powder
- Properties: Palladium powder is known for its catalytic properties and resistance to tarnishing, making it ideal for a variety of chemical processes.
- Applications: Commonly used in electronics, catalytic converters, and hydrogen purification.
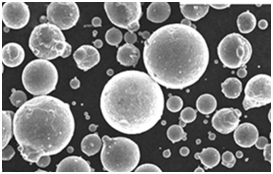

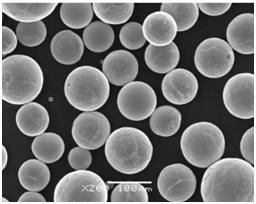



Applications of High Purity Powder
High purity powders are used in a variety of industries, each requiring different properties depending on the application. Here’s a breakdown of how these powders are utilized across various fields:
| Industry | Common Applications | Examples of Powders Used |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics | Conductive inks, printed circuit boards (PCBs), semiconductors | Copper, Silver, Gold, Palladium |
| Aerospace | Lightweight components, coatings, 3D printed parts | Aluminum, Titanium, Nickel |
| Automotive | Engine components, catalytic converters, battery electrodes | Platinum, Palladium, Zinc, Iron |
| Medical | Implants, prosthetics, antimicrobial coatings | Titanium, Silver, Gold, Platinum |
| Energy | Fuel cells, solar panels, batteries | Platinum, Nickel, Copper, Silver |
| Chemical | Catalysts, hydrogenation processes | Palladium, Platinum, Nickel |
| Jewelry | High-end jewelry, corrosion-resistant coatings | Gold, Silver, Platinum |
Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards
Understanding the specifications, sizes, and grades of high purity powders is critical for selecting the right material for your needs. Below is a table that outlines the key specifications for each metal powder.
| Metal Powder | Particle Size Range (µm) | Purity Grade | Standards |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Powder | 1 – 100 | 99.9% (High Purity) | ASTM B928/B928M-15 |
| Copper Powder | 0.5 – 75 | 99.99% (Ultra High Purity) | ASTM B170 |
| Titanium Powder | 5 – 45 | 99.5% (High Purity) | ASTM F67, ASTM F136 |
| Silver Powder | 1 – 50 | 99.99% (Ultra High Purity) | ASTM B832 |
| Gold Powder | 1 – 10 | 99.99% (Ultra High Purity) | ASTM B488 |
| Iron Powder | 10 – 150 | 99.9% (High Purity) | ASTM A575, ASTM A876 |
| Nickel Powder | 5 – 20 | 99.8% (High Purity) | ASTM B330 |
| Zinc Powder | 1 – 50 | 99.9% (High Purity) | ASTM B822 |
| Platinum Powder | 1 – 25 | 99.95% (Ultra High Purity) | ASTM B562 |
| Palladium Powder | 0.5 – 5 | 99.95% (Ultra High Purity) | ASTM B563 |
Suppliers and Pricing Details for High Purity Powders
When it comes to sourcing high purity powders, several reputable suppliers offer a range of products. Prices can vary significantly depending on the purity, particle size, and quantity purchased.
| Supplier | Available Powders | Price Range (per kg) | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| American Elements | Aluminum, Copper, Titanium, Nickel | $150 – $800 | USA |
| Advanced Materials Inc | Silver, Gold, Platinum, Palladium | $500 – $2,000 | USA |
| Goodfellow | Zinc, Iron, Copper, Nickel | $100 – $600 | UK |
| Alfa Aesar | Titanium, Aluminum, Gold, Silver | $200 – $1,500 | USA |
| Metal Powders USA | Copper, Zinc, Nickel, Palladium | $250 – $1,200 | USA |
Comparing High Purity Powders: Advantages and Limitations
Choosing the right high purity powder often involves comparing the advantages and limitations of each option. Here’s a table that breaks down these factors for each metal powder discussed.
| Metal Powder | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Powder | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, conductive | Oxidizes easily, lower melting point |
| Copper Powder | Excellent conductivity, ductile | Prone to oxidation, relatively expensive |
| Titanium Powder | High strength-to-weight ratio, biocompatible | Expensive, challenging to process |
| Silver Powder | Superior conductivity, antimicrobial properties | Expensive, tarnishes over time |
| Gold Powder | Excellent conductivity, corrosion-resistant | Very expensive, heavy |
| Iron Powder | Magnetic, easily alloyed | Prone to rusting, heavy |
| Nickel Powder | Corrosion-resistant, high melting point | Allergic reactions in some applications |
| Zinc Powder | Corrosion-resistant, affordable | Low melting point, not very strong |
| Platinum Powder | Extremely corrosion-resistant, excellent catalytic properties | Extremely expensive, heavy |
| Palladium Powder | High catalytic efficiency, tarnish-resistant | Very expensive, limited availability |

FAQs
Here are some common questions about high purity powders, along with detailed answers.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What defines a high purity powder? | High purity powders have a purity level of 99.9% or higher, ensuring minimal impurities. |
| Why is purity important in metal powders? | Purity is crucial because impurities can affect the performance, conductivity, and safety of the final product. |
| What industries use high purity powders? | High purity powders are used in electronics, aerospace, automotive, medical, energy, and chemical industries. |
| How do I choose the right high purity powder? | Consider the specific application, required properties, and budget to select the appropriate powder. |
| What are the challenges in handling high purity powders? | Handling can be challenging due to their fine particle size and potential reactivity. Proper storage and handling practices are essential. |
| Are high purity powders expensive? | Yes, high purity powders tend to be more expensive due to the complex manufacturing process and the need for high-quality materials. |
| How are high purity powders produced? | They are typically produced through processes like atomization, chemical reduction, and electrolysis to ensure high purity and consistency. |
| Can high purity powders be customized? | Yes, many suppliers offer customization options in terms of particle size, distribution, and purity levels. |
| What are the environmental concerns with high purity powders? | The production and disposal of high purity powders must be managed carefully to avoid environmental contamination. Recycling and responsible sourcing can mitigate these concerns. |
| Are there any alternatives to high purity powders? | Depending on the application, lower purity powders or different materials might be used, but they may not offer the same level of performance. |
Conclusion
High purity powders are the unsung heroes of advanced manufacturing and technology. With their exceptional purity and unique properties, these powders play a critical role in industries ranging from aerospace to electronics. Whether you’re looking to enhance the performance of a product or develop cutting-edge technologies, understanding the nuances of high purity powders is essential. By choosing the right powder for your application, you can ensure optimal performance, reliability, and efficiency in your projects.