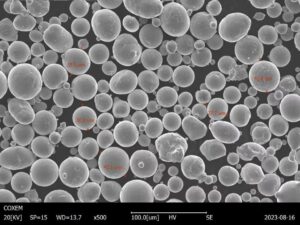
Electrode inert gas atomizers are integral to the manufacturing of high-quality metal powders used across various industries. These atomizers play a crucial role in ensuring the purity and consistency of metal powders, making them indispensable in fields like aerospace, automotive, and additive manufacturing.
In this detailed guide, we’ll delve into the complexities of electrode inert gas atomizers, exploring their types, compositions, properties, and applications. We’ll also compare various metal powder models, provide specifications, and discuss their advantages and limitations.
Overview of Electrode Inert Gas Atomizers
Electrode inert gas atomizers are advanced devices used in the production of fine metal powders. These atomizers employ an electric arc to melt metal, which is then dispersed into fine particles by a high-pressure inert gas, typically argon or nitrogen. This method ensures that the metal powder is free from contamination and possesses uniform particle size, making it ideal for high-precision applications.
Key Features of Electrode Inert Gas Atomizers:
- High Purity: Ensures minimal contamination during the atomization process.
- Uniform Particle Size: Produces metal powders with consistent particle distribution.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of metals and alloys.
- Efficiency: Capable of producing large quantities of metal powder quickly.

Types and Compositions of Electrode Inert Gas Atomizers
Electrode inert gas atomizers can be classified based on the types of metals and alloys they process. Here’s a breakdown of some of the most commonly used metal powder models:
| Metal Powder Model | Composition | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Iron (Fe) Powder | Pure Iron | High strength, magnetic |
| Nickel (Ni) Powder | Pure Nickel | Corrosion resistant, high melting point |
| Copper (Cu) Powder | Pure Copper | Excellent electrical conductivity |
| Aluminum (Al) Powder | Pure Aluminum | Lightweight, corrosion resistant |
| Titanium (Ti) Powder | Pure Titanium | High strength-to-weight ratio |
| Stainless Steel Powder | Fe-Cr-Ni Alloy | Corrosion resistant, durable |
| Cobalt (Co) Powder | Pure Cobalt | High temperature resistance |
| Zinc (Zn) Powder | Pure Zinc | Low melting point, galvanizing |
| Silver (Ag) Powder | Pure Silver | Highest electrical conductivity |
| Gold (Au) Powder | Pure Gold | High corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity |
These models are selected based on specific application requirements, such as strength, conductivity, and resistance to environmental factors.
Characteristics of Electrode Inert Gas Atomizers
To understand why electrode inert gas atomizers are preferred for metal powder production, let’s explore their key characteristics:
- Particle Size Distribution: Ensures a consistent and narrow particle size distribution.
- Morphology: Produces spherical particles that improve flowability and packing density.
- Purity Levels: Maintains high purity by avoiding contamination during the atomization process.
- Control Over Composition: Allows precise control over the alloy composition.
These characteristics make electrode inert gas atomizers ideal for applications that demand high-quality metal powders.
Applications of Electrode Inert Gas Atomizers
Metal powders produced using electrode inert gas atomizers are used in a variety of applications, including:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Additive Manufacturing | Used in 3D printing to create complex parts with high precision. |
| Powder Metallurgy | Utilized in creating components through compacting and sintering processes. |
| Thermal Spraying | Applied in coatings to protect against wear and corrosion. |
| Electronics | Used in conductive inks and pastes for electronic circuits. |
| Aerospace | Essential in the production of lightweight, high-strength components. |
| Automotive | Used in manufacturing parts that require high durability and precision. |
| Medical Devices | Utilized in the creation of biocompatible implants and prosthetics. |
These applications highlight the versatility and critical importance of high-quality metal powders in modern manufacturing and technology.




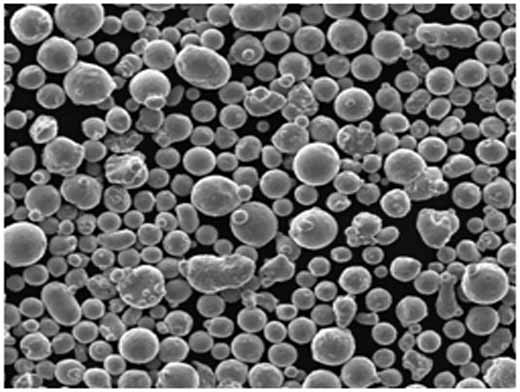

Specifications and Standards for Electrode Inert Gas Atomizers
Specifications for metal powders vary depending on the application and the desired properties. Here’s a detailed look at the specifications, sizes, grades, and standards:
| Metal Powder Model | Size Range (µm) | Grade | Standards |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iron (Fe) Powder | 10-150 | Industrial | ASTM B213, ISO 4497 |
| Nickel (Ni) Powder | 5-100 | High Purity | ASTM B330, ISO 10070 |
| Copper (Cu) Powder | 20-200 | Conductive | ASTM B216, ISO 4492 |
| Aluminum (Al) Powder | 15-100 | Lightweight | ASTM B328, ISO 4498 |
| Titanium (Ti) Powder | 10-150 | Aerospace | ASTM B299, ISO 3923 |
| Stainless Steel Powder | 10-150 | Corrosion Res. | ASTM B243, ISO 3923 |
| Cobalt (Co) Powder | 5-150 | High Temp | ASTM B964, ISO 4499 |
| Zinc (Zn) Powder | 20-100 | Galvanizing | ASTM B527, ISO 4496 |
| Silver (Ag) Powder | 1-50 | Electronic | ASTM B214, ISO 3924 |
| Gold (Au) Powder | 1-10 | Electronic | ASTM B482, ISO 3925 |
These standards ensure that the metal powders meet the necessary quality and performance requirements for their intended applications.
Suppliers and Pricing Details of Electrode Inert Gas Atomizers
Selecting the right supplier for electrode inert gas atomizers and metal powders is crucial. Here’s a look at some prominent suppliers and their pricing details:
| Supplier | Metal Powder Models | Pricing (per kg) | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Höganäs AB | Iron, Nickel, Copper | $20 – $150 | Sweden |
| Carpenter Technology | Titanium, Stainless Steel | $50 – $500 | USA |
| Sandvik | Aluminum, Cobalt | $30 – $200 | Sweden |
| GKN Powder Metallurgy | Iron, Stainless Steel | $25 – $180 | Germany |
| Advanced Powder & Coatings | Copper, Silver | $100 – $700 | USA |
| Ametek Inc. | Nickel, Cobalt | $40 – $300 | USA |
| Metal Powder Products | Zinc, Aluminum | $15 – $100 | USA |
| Rio Tinto Metal Powders | Iron, Stainless Steel | $20 – $170 | Canada |
| Eramet Group | Nickel, Cobalt | $35 – $250 | France |
| ATI Powder Metals | Titanium, Iron | $45 – $400 | USA |
These suppliers are known for their high-quality metal powders and reliable delivery, ensuring that manufacturers receive the best materials for their production needs.
Comparing Pros and Cons of Electrode Inert Gas Atomizers
When choosing an electrode inert gas atomizer, it’s essential to weigh the advantages and limitations. Here’s a comparison to help you make an informed decision:
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | High purity levels, minimal contamination | Requires high-quality raw materials |
| Particle Size | Consistent and uniform particle size | Initial setup cost can be high |
| Efficiency | Fast production rates | Maintenance and operational costs |
| Versatility | Suitable for various metals and alloys | Requires skilled operators |
| Quality Control | Precise control over composition and properties | High energy consumption |
| Environmental Impact | Uses inert gases, reducing oxidation | Disposal of used gases |
| Cost | Can be cost-effective for large-scale production | Expensive for small-scale operations |
Understanding these factors can help you determine if electrode inert gas atomizers are the right choice for your metal powder production needs.

FAQ
Here are some common questions about electrode inert gas atomizers and their applications:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is an electrode inert gas atomizer? | A device that melts metal using an electric arc and disperses it into fine particles using an inert gas. |
| Which metals can be processed using this method? | Various metals including iron, nickel, copper, aluminum, titanium, stainless steel, and more. |
| What are the benefits of using inert gas? | Inert gases prevent oxidation and contamination, ensuring high purity and quality of the metal powder. |
| How is particle size controlled? | By adjusting the gas pressure, nozzle design, and other parameters during the atomization process. |
| What industries use metal powders from these atomizers? | Industries such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, medical devices, and additive manufacturing. |
| Are there environmental concerns with this process? | While inert gases reduce oxidation, proper disposal of used gases and energy consumption are concerns. |
| How does this method compare to other atomization techniques? | It offers higher purity and better control over particle size but can be more expensive and energy-intensive. |
Conclusion
Electrode inert gas atomizers are a pivotal technology in the production of high-quality metal powders. Their ability to produce consistent, pure, and versatile metal powders makes them indispensable across various high-precision industries. By understanding their types, characteristics, applications, and the pros and cons, manufacturers can make informed decisions to optimize their production processes and achieve the best possible results.
Whether you’re in aerospace, automotive, or additive manufacturing, electrode inert gas atomizers offer the reliability and performance needed to meet the highest standards. So, why not explore this technology further and see how it can revolutionize your production capabilities?