Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) might sound like something straight out of a sci-fi novel, but it’s actually one of the most advanced methods for producing high-quality metal alloys. If you’ve ever wondered how some of the most critical components in aerospace, medical devices, and high-performance engines are made, look no further. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of VIM, from its basic principles to specific metal powder models, all while keeping things engaging and easy to understand. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of Vacuum Induction Melting!
Overview of Vacuum Induction Melting
Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) is a process used to melt and refine metals and alloys in a vacuum environment. This technique ensures the production of high-purity materials by minimizing contamination from gases and other impurities. The primary components of the VIM process include an induction furnace, a vacuum chamber, and various monitoring and control systems.
Key Features of VIM
- High Purity: The vacuum environment reduces contamination.
- Precise Control: Allows for accurate control of temperature and composition.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of metals and alloys.
- Efficiency: Reduces energy consumption compared to traditional melting methods.
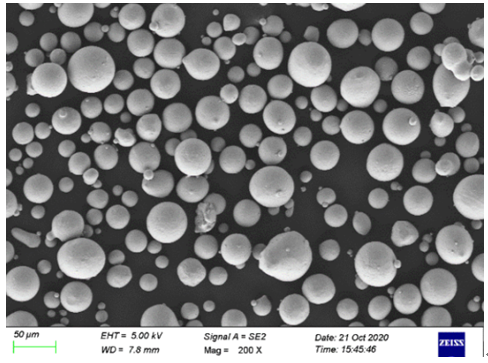
Types of Metals Processed by VIM
| Metal Type | Composition | Properties | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium Alloys | Ti, Al, V, Mo | High strength, corrosion resistance | Lightweight, high-temperature performance |
| Nickel Alloys | Ni, Cr, Fe, Mo, Al | High corrosion and heat resistance | Suitable for extreme environments |
| Stainless Steels | Fe, Cr, Ni, Mo, C | Corrosion resistance, strength | Used in medical, automotive, and aerospace sectors |
| Cobalt Alloys | Co, Cr, W, Ni | High wear resistance, toughness | Ideal for medical implants, cutting tools |
| Superalloys | Ni, Co, Fe, Cr, Mo, Al | Exceptional mechanical strength | Critical in jet engines, gas turbines |
| Copper Alloys | Cu, Zn, Sn, Pb | Good electrical and thermal conductivity | Widely used in electrical components |
| Aluminum Alloys | Al, Cu, Mg, Si, Zn | Lightweight, good corrosion resistance | Used in aerospace, automotive |
| Precious Metals | Au, Ag, Pt, Pd | High value, excellent conductivity | Used in electronics, jewelry |
| Specialty Alloys | Various metals | Tailored properties for specific applications | Customizable for unique industrial needs |
| Ferrous Alloys | Fe, C, Mn, Si | High strength, magnetic properties | Essential for construction, machinery |
Understanding Vacuum Induction Melting: The Process
1. Basic Principles of VIM
At its core, VIM involves melting metals using electromagnetic induction under a vacuum. This method minimizes the presence of gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen, which can cause defects in the metal.
2. The Melting Process
- Induction Heating: The metal charge is placed in a crucible within the induction furnace. An alternating current passes through a coil surrounding the crucible, generating an electromagnetic field that heats the metal.
- Vacuum Environment: As the metal heats up and begins to melt, the vacuum chamber reduces atmospheric pressure, preventing oxidation and contamination.
- Refining: The molten metal can be further refined by adding alloying elements and removing impurities.
3. Cooling and Solidification
Once the desired composition and temperature are achieved, the molten metal is poured into molds or cast into ingots. Controlled cooling allows the metal to solidify with minimal defects, resulting in a high-quality product.
Characteristics of Vacuum Induction Melting
VIM offers several unique characteristics that make it the go-to choice for producing high-performance metals.
Purity and Quality
By operating in a vacuum, VIM minimizes contamination from gases and other impurities, resulting in metals with exceptional purity and quality.
Precision and Control
The process allows for precise control over temperature and composition, ensuring consistent and reliable results.
Versatility
VIM is suitable for a wide range of metals and alloys, from common stainless steels to exotic superalloys and precious metals.
Energy Efficiency
Compared to traditional melting methods, VIM is more energy-efficient, reducing both operational costs and environmental impact.
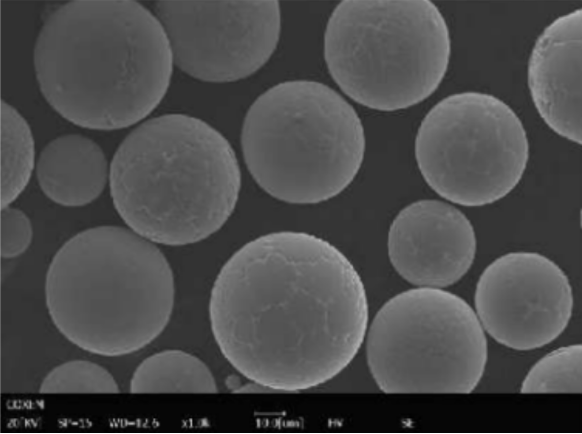

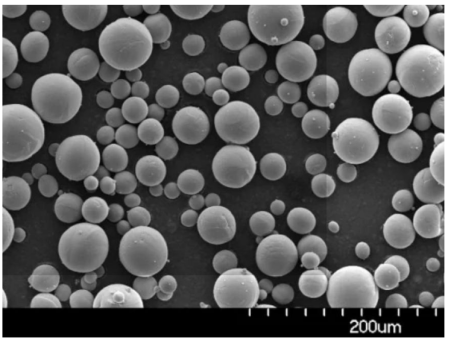
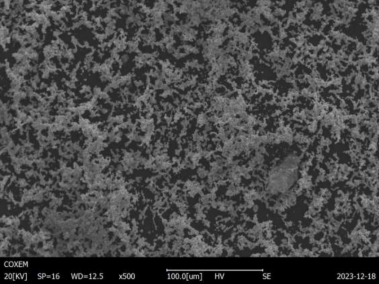

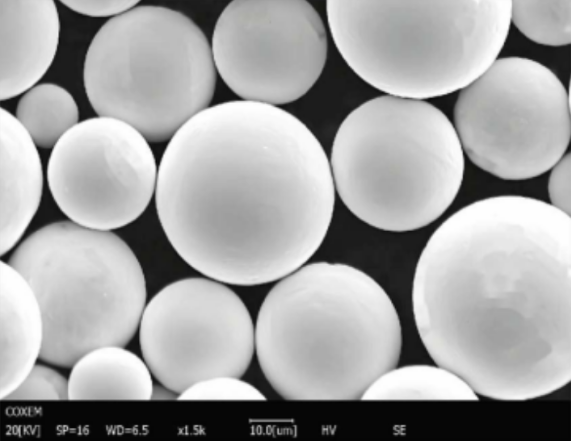

Applications of Vacuum Induction Melting
VIM is used across various industries to produce high-performance components that demand the highest levels of purity and precision.
| Industry | Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, engine components | High strength, heat resistance |
| Medical | Implants, surgical instruments | Biocompatibility, corrosion resistance |
| Automotive | High-performance engine parts | Durability, efficiency |
| Electronics | Conductive materials, connectors | High conductivity, reliability |
| Power Generation | Turbine components, nuclear reactor parts | Heat resistance, mechanical strength |
| Oil and Gas | Drilling equipment, subsea components | Corrosion resistance, toughness |
| Defense | Armor, weapon components | Strength, reliability |
| Industrial Machinery | Tooling, wear-resistant parts | Durability, wear resistance |
| Jewelry | High-value metal products | Aesthetic quality, value retention |
| Energy Storage | Battery components, superconductors | Efficiency, performance |
Grades of Vacuum Induction Melting
Different grades of metals produced through VIM cater to various industrial needs. Each grade has specific properties that make it suitable for particular applications.
| Metal Type | Grade | Composition | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium | Grade 5 | Ti-6Al-4V | High strength, lightweight | Aerospace, medical implants |
| Nickel | Inconel 718 | Ni-Cr-Fe-Mo-Nb | High strength, oxidation resistance | Turbine blades, aerospace |
| Stainless Steel | 316L | Fe-Cr-Ni-Mo | Corrosion resistance, biocompatibility | Medical devices, marine applications |
| Cobalt | CoCrMo | Co-Cr-Mo | Wear resistance, high strength | Medical implants, cutting tools |
| Superalloy | René 41 | Ni-Co-Cr-Mo | High temperature strength, oxidation resistance | Aerospace, gas turbines |
| Copper | C18200 | Cu-Cr | High conductivity, hardness | Electrical connectors, resistance welding |
| Aluminum | 6061-T6 | Al-Mg-Si | High strength, good machinability | Aerospace, automotive |
| Precious Metal | 24K Gold | Au | High purity, conductivity | Electronics, jewelry |
| Specialty Alloy | Haynes 230 | Ni-Cr-W-Mo | High temperature stability, oxidation resistance | Chemical processing, industrial heating |
| Ferrous Alloy | AISI 4140 | Fe-C-Mn-Si-Cr-Mo | High strength, toughness | Construction, machinery |
Suppliers and Pricing Details
Choosing the right supplier and understanding the pricing structure are crucial for businesses looking to utilize VIM-produced metals.
| Supplier | Location | Specialties | Pricing (per kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carpenter Technology | USA | High-performance alloys | $50 – $200 |
| ATI Metals | USA | Specialty metals and components | $40 – $180 |
| Haynes International | USA | High-temperature alloys | $45 – $190 |
| Allegheny Technologies | USA | Titanium and nickel-based alloys | $55 – $220 |
| VSMPO-AVISMA | Russia | Titanium products | $60 – $210 |
| Daido Steel | Japan | Specialty steel, superalloys | $50 – $200 |
| Sandvik Materials | Sweden | Stainless steel, special alloys | $45 – $185 |
| Oerlikon Metco | Switzerland | Surface solutions, advanced materials | $50 – $195 |
| Precision Castparts | USA | Complex metal components | $60 – $220 |
| Plansee Group | Austria | Refractory metals, high-performance materials | $55 – $215 |
Pros and Cons of Vacuum Induction Melting
Every process has its advantages and limitations. Let’s take a closer look at the pros and cons of VIM.
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| High purity of metals produced | High initial setup costs |
| Precise control over composition and temperature | Requires skilled operators |
| Versatility in processing various metals | Limited to small to medium batch sizes |
| Energy efficiency | Vacuum equipment maintenance |
| Reduced contamination and defects | Longer processing times |
Metal Powder Models Produced by VIM
VIM is also instrumental in producing metal powders for additive manufacturing (3D printing) and other advanced applications. Here are some specific models and their descriptions:
- Ti-6Al-4V Powder
- Composition: Titanium, Aluminum, Vanadium
- Applications: Aerospace, medical implants
- Properties: High strength, lightweight, corrosion-resistant
- Inconel 625 Powder
- Composition: Nickel, Chromium, Molybdenum, Niobium
- Applications: Aerospace, chemical processing
- Properties: High strength, oxidation and corrosion-resistant
- 316L Stainless Steel Powder
- Composition: Iron, Chromium, Nickel, Molybdenum
- Applications: Medical devices, marine components
- Properties: Corrosion-resistant, biocompatible
- CoCrMo Powder
- Composition: Cobalt, Chromium, Molybdenum
- Applications: Medical implants, dental applications
- Properties: High wear resistance, biocompatibility
- René 41 Powder
- Composition: Nickel, Chromium, Cobalt, Molybdenum
- Applications: Aerospace, gas turbines
- Properties: High temperature strength, oxidation resistance
- 6061 Aluminum Powder
- Composition: Aluminum, Magnesium, Silicon
- Applications: Aerospace, automotive
- Properties: High strength, good machinability
- Haynes 230 Powder
- Composition: Nickel, Chromium, Tungsten, Molybdenum
- Applications: Chemical processing, industrial heating
- Properties: High temperature stability, oxidation resistance
- C18200 Copper Powder
- Composition: Copper, Chromium
- Applications: Electrical connectors, resistance welding
- Properties: High conductivity, hardness
- 24K Gold Powder
- Composition: Gold
- Applications: Electronics, jewelry
- Properties: High purity, conductivity
- AISI 4140 Powder
- Composition: Iron, Carbon, Manganese, Silicon, Chromium, Molybdenum
- Applications: Construction, machinery
- Properties: High strength, toughness

FAQ
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is Vacuum Induction Melting? | VIM is a process that melts and refines metals in a vacuum environment using electromagnetic induction. |
| Why use a vacuum in VIM? | The vacuum minimizes contamination from gases and other impurities, ensuring high-purity metals. |
| What metals can be processed with VIM? | Metals like titanium, nickel, stainless steel, cobalt, superalloys, copper, aluminum, and precious metals. |
| What are the benefits of VIM? | High purity, precise control, versatility, and energy efficiency are some key benefits. |
| Are there any limitations to VIM? | High setup costs, skilled operator requirement, and limited batch sizes are some limitations. |
| How does VIM compare to traditional melting methods? | VIM offers better purity and control but can be more expensive and time-consuming. |
| What industries use VIM? | Aerospace, medical, automotive, electronics, power generation, oil and gas, defense, and more. |
| What are some specific metal powders produced by VIM? | Ti-6Al-4V, Inconel 625, 316L Stainless Steel, CoCrMo, René 41, 6061 Aluminum, Haynes 230, etc. |
| How does VIM ensure high quality? | The vacuum environment and precise control over temperature and composition help ensure high quality. |
| Where can I buy VIM-processed metals? | Suppliers like Carpenter Technology, ATI Metals, Haynes International, and others offer VIM-processed metals. |
Conclusion
Vacuum Induction Melting stands as a testament to the advancements in metal processing technology. Its ability to produce high-purity, high-performance metals makes it indispensable in industries where quality and reliability are paramount. Whether you’re in aerospace, medical, or any other field that demands the best materials, understanding VIM can give you an edge. The future of metal processing is here, and it’s vacuum-inducted!
So, the next time you marvel at the intricate parts of a jet engine or the precision of a medical implant, remember the incredible process that made it possible: Vacuum Induction Melting.

