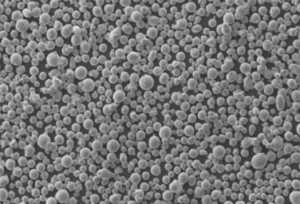
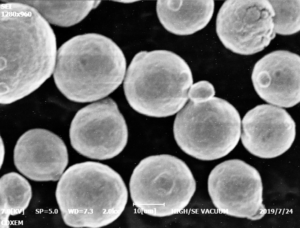
The Plasma-Rotating Electrode Process, often abbreviated as PREP, is a fascinating and highly specialized method for producing high-quality metal powders. This process, which involves a rotating electrode and a plasma arc, creates powders that are essential for various high-performance applications, including additive manufacturing, aerospace, and biomedical implants. Let’s dive into the details of this process, exploring its nuances, applications, and the different types of metal powders it can produce.
Overview of the Plasma-Rotating Electrode Process
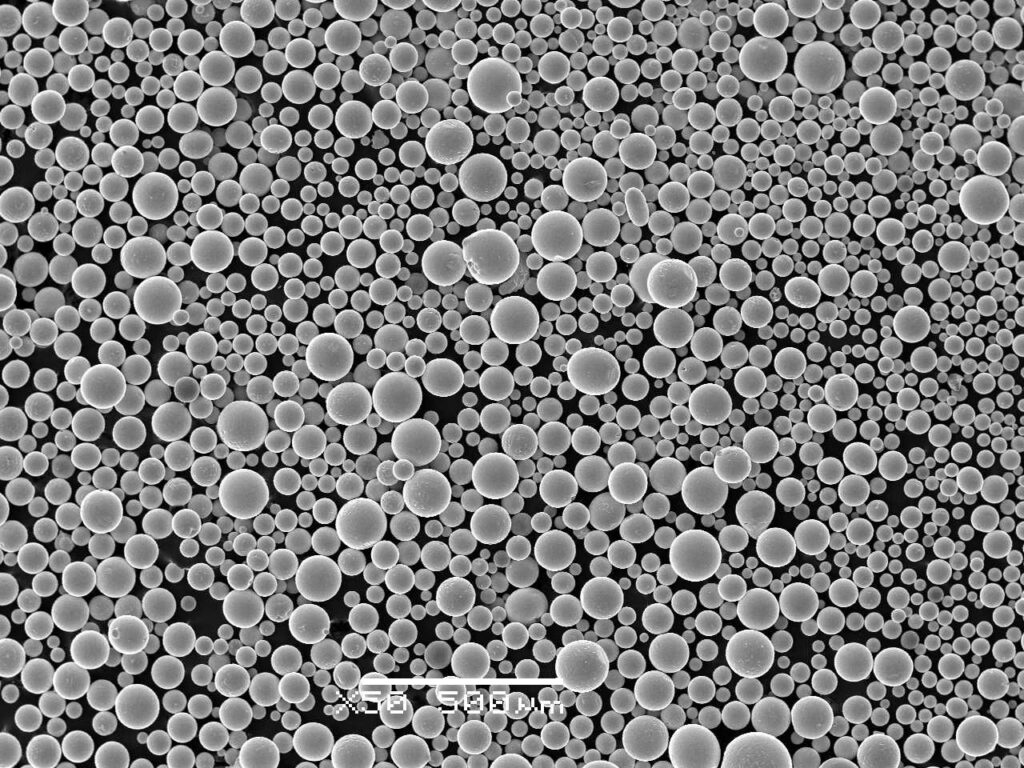
The Plasma-Rotating Electrode Process (PREP) is a cutting-edge technique used to produce spherical metal powders with high purity and uniform size distribution. This process involves melting a rotating electrode using a plasma arc, which then forms droplets that solidify into fine powders. Here’s a snapshot of what PREP entails:
- Technique: Melting of rotating electrode by plasma arc
- Result: High-quality, spherical metal powders
- Applications: Additive manufacturing, aerospace, biomedical implants, and more
- Advantages: High purity, uniform size, and excellent powder properties
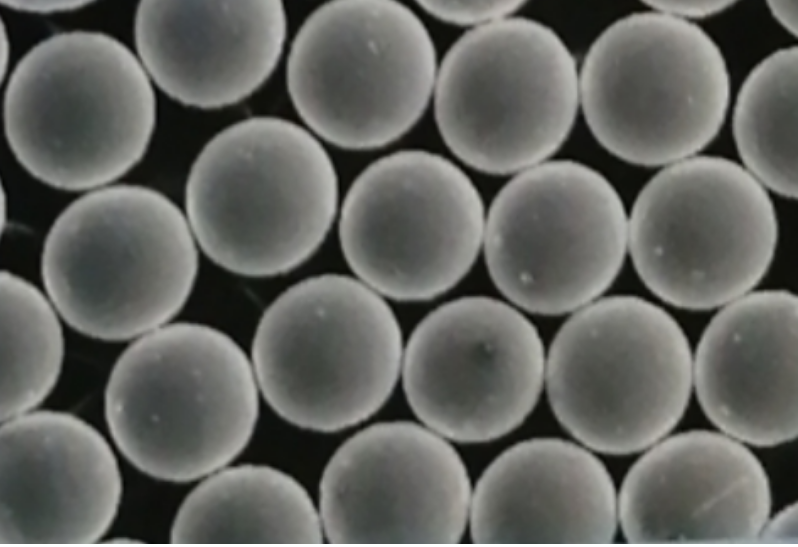
Types of Metal Powders Produced by PREP
1. Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V)
Description: Ti-6Al-4V is a titanium alloy known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. It is widely used in aerospace, medical devices, and high-performance engineering applications.
2. Stainless Steel (316L)
Description: 316L stainless steel is an austenitic stainless steel with high corrosion resistance and excellent mechanical properties. It is commonly used in marine environments, medical devices, and food processing equipment.
3. Inconel 718
Description: Inconel 718 is a nickel-chromium alloy known for its high strength and corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures. It is extensively used in gas turbines, aerospace, and chemical processing.
4. Aluminum Alloy (AlSi10Mg)
Description: AlSi10Mg is an aluminum-silicon-magnesium alloy with good casting properties and high thermal conductivity. It is often used in automotive and aerospace applications.
5. Cobalt-Chromium Alloy (CoCrMo)
Description: CoCrMo is a cobalt-chromium-molybdenum alloy known for its wear resistance and biocompatibility. It is primarily used in medical implants and dental prosthetics.
6. Copper Alloy (CuCrZr)
Description: CuCrZr is a copper alloy with chromium and zirconium, offering high strength and excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. It is used in electrical and thermal management applications.
7. Tool Steel (H13)
Description: H13 is a chromium-molybdenum hot work tool steel with high toughness and resistance to thermal fatigue. It is used in die casting and extrusion tooling.
8. Maraging Steel (18Ni300)
Description: 18Ni300 is a maraging steel known for its ultra-high strength and toughness. It is used in aerospace components, tooling, and high-performance engineering parts.
9. Tantalum
Description: Tantalum is a rare metal with high corrosion resistance and excellent biocompatibility. It is used in medical implants, electronics, and chemical processing equipment.
10. Nickel Alloy (Hastelloy X)
Description: Hastelloy X is a nickel-based superalloy with outstanding oxidation and high-temperature strength. It is used in gas turbine engines, chemical processing, and industrial heating.
Composition of Metal Powders in PREP
The composition of metal powders produced via PREP is crucial for their performance in specific applications. Here’s a breakdown of the primary elements found in each type of metal powder:
| Metal Powder | Composition |
|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V | Ti (90%), Al (6%), V (4%) |
| 316L | Fe (65%), Cr (17%), Ni (12%), Mo (2.5%), Mn (2%) |
| Inconel 718 | Ni (50-55%), Cr (17-21%), Fe (balance), Nb (4.75-5.5%), Mo (2.8-3.3%) |
| AlSi10Mg | Al (90-92%), Si (9-10%), Mg (0.3-0.5%) |
| CoCrMo | Co (60-65%), Cr (27-30%), Mo (5-7%) |
| CuCrZr | Cu (97-99%), Cr (0.5-1.2%), Zr (0.03-0.3%) |
| H13 | Fe (balance), Cr (5%), Mo (1.3%), Si (1%) |
| 18Ni300 | Fe (balance), Ni (18-19%), Co (8-9%), Mo (4.5-5%) |
| Tantalum | Ta (99.95% min) |
| Hastelloy X | Ni (47-50%), Cr (20-23%), Fe (18-20%), Mo (8-10%) |
Characteristics of PREP Metal Powders
The properties of metal powders produced by the Plasma-Rotating Electrode Process make them highly sought after in various industries. Let’s examine these characteristics:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Particle Size | Fine, spherical particles with narrow size distribution |
| Purity | High purity with minimal contamination |
| Morphology | Uniform spherical shape for consistent flow and packing |
| Density | High packing density suitable for powder bed fusion and other additive manufacturing techniques |
| Oxidation | Low oxidation levels due to inert gas environment during production |
| Flowability | Excellent flow properties for uniform layering in 3D printing |


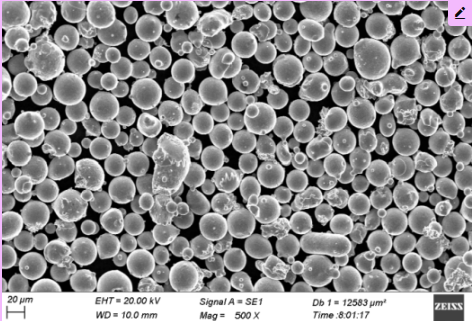



Applications of PREP Metal Powders
Metal powders produced via PREP are used in a wide range of applications due to their superior quality and properties. Here’s a look at some of the key applications:
| Application | Metal Powder | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Additive Manufacturing | Ti-6Al-4V, 316L, Inconel 718 | Used in 3D printing for complex, high-performance parts |
| Aerospace Components | Ti-6Al-4V, Inconel 718, H13 | High-strength, lightweight parts for aircraft and spacecraft |
| Medical Implants | CoCrMo, Ti-6Al-4V, Tantalum | Biocompatible materials for implants and prosthetics |
| Automotive Parts | AlSi10Mg, 316L | Lightweight, high-strength components for vehicles |
| Electrical Conductors | CuCrZr | High conductivity materials for electrical and thermal applications |
| Tooling and Dies | H13, 18Ni300 | Durable materials for manufacturing tools and dies |
| Chemical Processing | Hastelloy X, Inconel 718 | Corrosion-resistant materials for harsh chemical environments |
Specifications and Standards for PREP Metal Powders
Metal powders produced via PREP must meet specific standards and specifications to ensure their quality and suitability for various applications. Here are some typical specifications:
| Metal Powder | Particle Size Range | Purity | Standards |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V | 15-45 µm | 99.5% min | ASTM F2924, AMS 4998 |
| 316L | 10-50 µm | 99.9% min | ASTM A276, AMS 5648 |
| Inconel 718 | 20-60 µm | 99.0% min | AMS 5662, ASTM B637 |
| AlSi10Mg | 20-60 µm | 99.8% min | EN 1706, ASTM B247 |
| CoCrMo | 15-45 µm | 99.0% min | ASTM F75, ISO 5832-4 |
| CuCrZr | 10-50 µm | 99.9% min | ASTM B224, AMS 4534 |
| H13 | 20-60 µm | 99.5% min | ASTM A681, AMS 6408 |
| 18Ni300 | 15-45 µm | 99.0% min | ASTM A579, AMS 6514 |
| Tantalum | 10-40 µm | 99.95% min | ASTM B521, AMS 7847 |
| Hastelloy X | 20-60 µm | 99.0% min | AMS 5754, ASTM B435 |
Suppliers and Pricing of PREP Metal Powders
The market for PREP metal powders includes a range of suppliers, each offering various grades and sizes at different price points. Here’s an
overview:
| Supplier | Metal Powder | Price Range (per kg) |
|---|---|---|
| AP&C (GE Additive) | Ti-6Al-4V, 316L, Inconel 718 | $300 – $700 |
| Höganäs AB | AlSi10Mg, CoCrMo, H13 | $200 – $600 |
| Sandvik Osprey | CuCrZr, 18Ni300, Hastelloy X | $250 – $800 |
| Praxair Surface Technologies | Ti-6Al-4V, Inconel 718, Tantalum | $400 – $900 |
| Carpenter Technology | 316L, H13, 18Ni300 | $250 – $700 |
Comparing Pros and Cons of PREP Metal Powders
Every material and process has its advantages and limitations. Let’s compare the pros and cons of metal powders produced by PREP:
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Morphology | Spherical particles enhance flow and packing density | Complex and costly process |
| Purity | High purity with minimal contamination | Requires high-quality raw materials |
| Size Distribution | Narrow size distribution ensures uniformity | Limited to specific particle size ranges |
| Mechanical Properties | Superior mechanical properties suitable for high-performance applications | Some materials may still require post-processing treatments |
| Production Cost | Cost-effective for high-performance applications | High initial setup and operational costs |
| Application Range | Versatile across various industries | Not all metals and alloys are suitable for PREP |
FAQs
1. What is the Plasma-Rotating Electrode Process (PREP)?
Answer: The Plasma-Rotating Electrode Process (PREP) is a method used to produce high-quality, spherical metal powders by melting a rotating electrode with a plasma arc.
2. What are the main applications of PREP metal powders?
Answer: PREP metal powders are used in additive manufacturing, aerospace, medical implants, automotive parts, electrical conductors, tooling and dies, and chemical processing.
3. What are the advantages of using PREP for producing metal powders?
Answer: PREP offers advantages such as high purity, uniform particle size, excellent flow properties, and superior mechanical properties of the resulting powders.
4. What types of metals can be processed using PREP?
Answer: Various metals and alloys can be processed using PREP, including titanium alloys, stainless steels, nickel alloys, aluminum alloys, cobalt-chromium alloys, copper alloys, tool steels, maraging steels, tantalum, and more.
5. How does the cost of PREP metal powders compare to other powder production methods?
Answer: While the initial setup and operational costs of PREP are high, it is cost-effective for producing high-performance powders due to the superior quality and properties of the resulting products.
6. Are there any limitations to the Plasma-Rotating Electrode Process?
Answer: Yes, the limitations include the complexity and cost of the process, the need for high-quality raw materials, and the restriction to specific particle size ranges.
7. How do PREP metal powders benefit additive manufacturing?
Answer: PREP metal powders benefit additive manufacturing by providing fine, spherical particles with high purity and excellent flowability, leading to better layer deposition and superior mechanical properties in the final printed parts.
8. Can all metals and alloys be produced using PREP?
Answer: Not all metals and alloys are suitable for PREP. The process is most effective for materials that can form fine, spherical powders when melted and solidified.
9. What are some common standards and specifications for PREP metal powders?
Answer: Common standards and specifications for PREP metal powders include ASTM, AMS, and ISO standards, which ensure the quality and consistency of the powders for various applications.
10. Where can I buy PREP metal powders?
Answer: PREP metal powders can be purchased from suppliers such as AP&C (GE Additive), Höganäs AB, Sandvik Osprey, Praxair Surface Technologies, and Carpenter Technology, among others.
In conclusion, the Plasma-Rotating Electrode Process is a vital technology in the production of high-quality metal powders. These powders are essential for various high-performance applications, from aerospace to biomedical implants. By understanding the intricacies of this process, its applications, and the specific metal powders it produces, we can appreciate its significant impact on modern manufacturing and engineering. Whether you are a manufacturer, an engineer, or simply curious about advanced materials, the Plasma-Rotating Electrode Process offers a fascinating glimpse into the future of material science and technology.