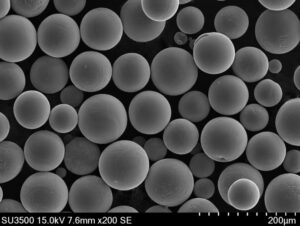
Overview
Gas atomization is a key technique in the production of metal powders, which are essential in various industries including additive manufacturing, metallurgy, and material science. This method involves the disintegration of molten metal into fine droplets using high-pressure gas jets. Once solidified, these droplets form a uniform and high-quality metal powder. But what makes gas atomization so crucial? Let’s dive into the world of gas atomizers, explore their working principles, advantages, specific models, and more.
What is Gas Atomization?
Gas atomization is a process where molten metal is broken up into fine particles using a high-velocity gas stream. The basic principle involves melting the metal, directing it through a nozzle, and then using a gas (like nitrogen, argon, or air) to atomize the liquid stream into fine droplets. These droplets quickly solidify into powder particles.

Types of Gas Atomizers for Metal Powder Production
To understand the various gas atomizers, it’s essential to look at their different types and how they function. Here are some popular models used in the industry:
Common Gas Atomizer Models
| Model | Description |
|---|---|
| GA-500 | High-capacity atomizer suitable for large-scale production of ferrous and non-ferrous powders. |
| Atomizer-X | Versatile atomizer designed for a wide range of metal powders, including aluminum and titanium alloys. |
| MicroJet 3000 | Compact atomizer ideal for research and small-scale production with high precision. |
| UltraFine 1500 | Specialized in producing ultra-fine powders for high-performance applications in aerospace and electronics. |
| EcoAtom 600 | Energy-efficient model optimized for reducing operational costs and environmental impact. |
| TitanMax 2000 | Robust atomizer designed specifically for titanium and its alloys, ensuring high purity and consistency. |
| SteelPro 400 | Engineered for steel and stainless steel powders, offering excellent particle size control. |
| AlloyMaster 750 | Versatile atomizer suitable for producing a variety of alloy powders, including high-entropy alloys. |
| NanoSpray 500 | Focuses on producing nano-sized particles for advanced material applications. |
| ArgonFlow 900 | Utilizes argon gas for inert atmosphere atomization, ideal for reactive metals like aluminum and magnesium. |
Composition of Gas Atomizers for Metal Powder Production
Gas atomizers consist of several critical components, each playing a crucial role in the atomization process. Let’s break down these components and their functions:
Key Components and Their Functions
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Nozzle | Directs the flow of molten metal and gas for precise atomization. |
| Crucible | Contains and melts the metal before atomization. |
| Gas Delivery System | Supplies and controls the gas used for atomizing the molten metal. |
| Cooling Chamber | Cools the atomized metal droplets rapidly to solidify them into powder. |
| Collector | Collects the solidified metal powder particles for further processing. |
| Control System | Manages the entire atomization process, ensuring optimal parameters for consistent powder quality. |
| Filters and Separators | Remove impurities and classify the powder particles based on size. |
Characteristics of Gas Atomizers for Metal Powder Production
Understanding the characteristics of gas atomizers is crucial for selecting the right model for your needs. Here are some important attributes:
Key Characteristics
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Particle Size Distribution | Determines the range and uniformity of powder particle sizes, critical for specific applications. |
| Purity | High purity levels are essential, especially for sensitive applications like aerospace and medical implants. |
| Yield | The efficiency of converting molten metal into powder. |
| Production Capacity | Varies based on the model, affecting the scale of operations. |
| Gas Consumption | Impacts operational costs and efficiency. |
| Flexibility | Ability to process different types of metals and alloys. |

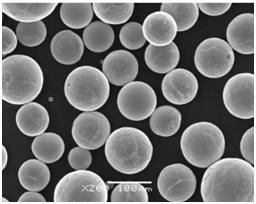
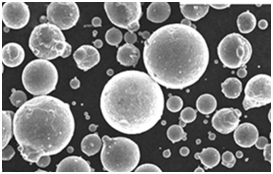



Advantages of Gas Atomizers for Metal Powder Production
Gas atomization offers several benefits over other powder production methods. Here’s why it’s preferred:
Why Choose Gas Atomization?
- High Purity Powders: The inert gas atmosphere minimizes oxidation and contamination.
- Uniform Particle Size: Ensures consistent quality, crucial for high-performance applications.
- Versatility: Can produce powders from a wide range of metals and alloys.
- Scalability: Suitable for both small-scale and large-scale production.
- Efficiency: High yield and low waste, making it cost-effective.
Applications of Metal Powders Produced by Gas Atomizers
Metal powders produced via gas atomization have a wide range of applications across various industries. Here’s a look at some key uses:
Industry Applications
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| Additive Manufacturing | 3D printing of complex metal parts and prototypes. |
| Aerospace | Manufacturing of lightweight, high-strength components. |
| Automotive | Production of wear-resistant and high-performance parts. |
| Medical | Fabrication of implants and surgical instruments. |
| Electronics | Creation of conductive and magnetic components. |
| Energy | Development of efficient and durable components for energy systems. |
| Tooling | Manufacturing of high-hardness tools and dies. |
Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards
When selecting a gas atomizer and the resulting metal powders, it’s important to consider various specifications and standards:
Specifications Overview
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Particle Size Range | Typically ranges from 1 to 150 micrometers, depending on the application. |
| Purity Levels | Varies based on the metal and process, generally exceeding 99.9% for high-purity applications. |
| Production Capacity | Can range from a few kilograms to several tons per hour. |
| Gas Types | Common gases used include nitrogen, argon, and air. |
| Standards | Compliance with international standards such as ASTM, ISO, and AMS. |
Suppliers and Pricing Details
Choosing the right supplier is crucial for ensuring quality and cost-efficiency. Here are some leading suppliers and a general pricing overview:
Leading Suppliers and Price Ranges
| Supplier | Description | Price Range |
|---|---|---|
| Höganäs AB | Renowned for high-quality metal powders for various industries. | $50 – $200 per kg |
| Carpenter Additive | Specializes in powders for additive manufacturing and high-performance applications. | $70 – $250 per kg |
| Sandvik | Offers a wide range of metal powders with high purity and consistency. | $60 – $220 per kg |
| GKN Additive | Known for innovative solutions and high-quality powders. | $80 – $300 per kg |
| LPW Technology | Focuses on metal powders for 3D printing and advanced manufacturing. | $75 – $280 per kg |
Advantages and Limitations of Gas Atomizers
Gas atomizers come with their own set of pros and cons. Here’s a comparison:
Pros and Cons Comparison
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| High Purity | High Initial Cost: Gas atomizers are generally expensive to purchase and set up. |
| Uniform Particle Size | Gas Consumption: High gas consumption can lead to increased operational costs. |
| Versatility | Complex Operation: Requires skilled operators and precise control systems. |
| Scalability | Maintenance: Regular maintenance is needed to ensure consistent performance. |
| Efficiency | Material Limitations: Not all metals and alloys are suitable for gas atomization. |
How to Choose the Right Gas Atomizer for Your Needs
Selecting the right gas atomizer involves considering several factors. Here are some tips to guide you:
Factors to Consider
- Material Compatibility: Ensure the atomizer can handle the metals and alloys you need to process.
- Production Capacity: Match the atomizer’s capacity with your production requirements.
- Purity Requirements: Choose an atomizer that can produce powders with the necessary purity levels.
- Cost Efficiency: Consider both the initial investment and ongoing operational costs.
- Supplier Reputation: Opt for reputable suppliers known for quality and reliability.

FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What metals can be atomized using gas atomizers? | Common metals include aluminum,titanium, steel, nickel, and various alloys. |
| How does gas atomization compare to water atomization? | Gas atomization generally produces higher purity and more uniform particle sizes compared to water atomization. |
| What is the typical particle size range for gas-atomized powders? | The particle size can range from 1 to 150 micrometers, depending on the atomizer and process parameters. |
| What gases are commonly used in gas atomization? | Nitrogen and argon are the most commonly used gases due to their inert properties, reducing oxidation and contamination. |
| Is gas atomization environmentally friendly? | While gas atomization is generally cleaner than other methods, it can still have a significant energy and gas consumption footprint. |
| Can gas atomizers produce nano-sized powders? | Yes, specialized atomizers like the NanoSpray 500 are designed to produce nano-sized particles. |
| What industries benefit the most from gas-atomized powders? | Aerospace, automotive, medical, and additive manufacturing industries benefit greatly from the high quality of gas-atomized powders. |
| How do I maintain a gas atomizer? | Regular maintenance includes cleaning the nozzles, checking gas lines, and ensuring the crucible is free from contaminants. |
| What is the cost range for gas atomizers? | Gas atomizers can range from $100,000 to several million dollars, depending on the size and capabilities. |
| Are there any safety concerns with gas atomization? | Yes, handling high-pressure gases and molten metals requires stringent safety protocols to prevent accidents and ensure operator safety. |
Conclusion
Gas atomization is a sophisticated and highly effective method for producing high-quality metal powders essential for a variety of advanced applications. By understanding the different types of gas atomizers, their components, advantages, and applications, you can make informed decisions about which technology best suits your needs. Whether you are in aerospace, automotive, medical, or additive manufacturing, choosing the right gas atomizer can significantly enhance your production capabilities and product quality.