C103 powder is a critical material in the metallurgical and engineering world, known for its exceptional properties and extensive applications. In this article, we’ll explore everything about C103 powder—its composition, characteristics, advantages, and applications. Additionally, we’ll compare specific models, their specifications, and suppliers to give you a complete picture. Let’s dive in!
Overview of C103 Powder
C103 powder is a high-performance niobium alloy primarily used in aerospace, automotive, and industrial applications. Known for its superior strength, thermal stability, and resistance to oxidation, it has become a go-to material for engineers and manufacturers aiming for high durability and performance.
Key Features of C103 Powder
- High melting point, over 4,000°F (2,204°C).
- Exceptional resistance to oxidation and thermal stress.
- Lightweight compared to traditional high-temperature alloys.
- Excellent weldability and machinability.
- Widely used in rocket nozzles, heat shields, and other critical components.
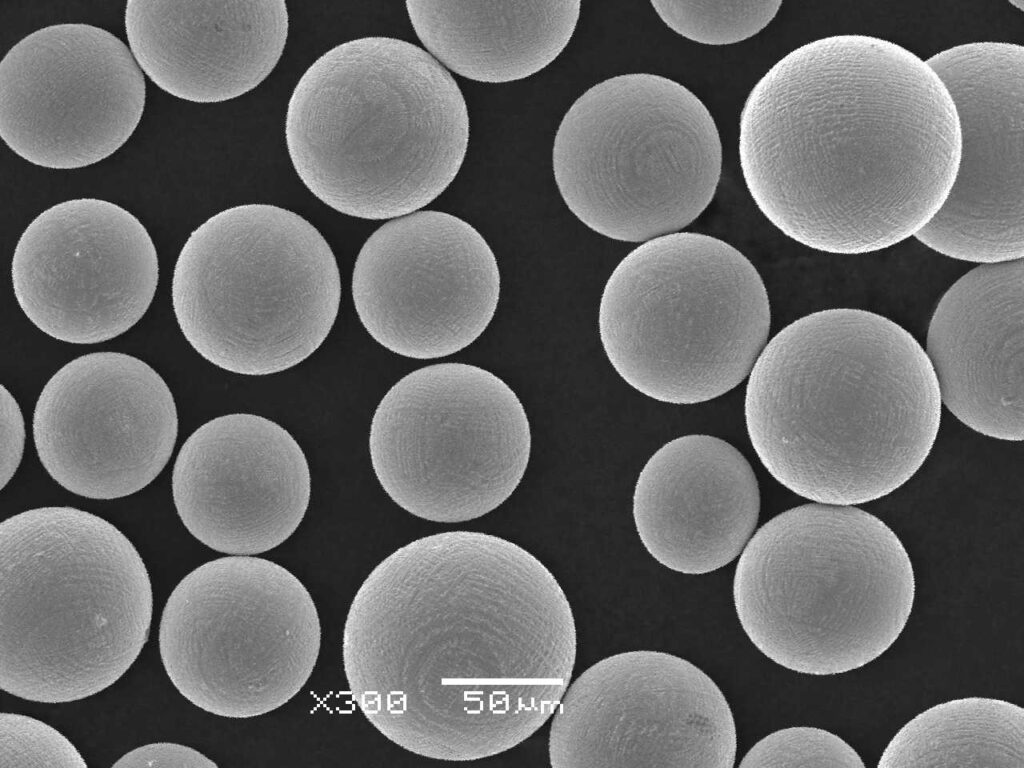

Composition of C103 Powder
C103 powder is a niobium-based alloy with specific compositions tailored to enhance its properties. Here’s a breakdown of its typical composition:
| Element | Composition (%) |
|---|---|
| Niobium (Nb) | 89–92 |
| Hafnium (Hf) | 10 |
| Titanium (Ti) | 1.0–2.0 |
| Other Elements | Trace |
The blend of hafnium and titanium enhances its thermal stability and mechanical strength, making it suitable for high-temperature environments.
Characteristics of C103 Powder
C103 powder exhibits unique properties that make it stand out compared to other metal powders. Here’s a detailed look:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | Over 4,000°F (2,204°C) for excellent heat resistance. |
| Density | Lightweight, approximately 8.6 g/cm³. |
| Thermal Conductivity | High thermal conductivity, reducing thermal gradients. |
| Oxidation Resistance | Excellent resistance up to high temperatures. |
| Machinability | Easy to machine and weld. |
These characteristics make C103 powder ideal for demanding environments, including space exploration and advanced manufacturing.
Applications of C103 Powder
C103 powder finds extensive use in industries requiring high-temperature performance. Here’s how it’s utilized:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Rocket nozzles, thrusters, and heat shields due to its heat resistance and lightweight properties. |
| Automotive | High-performance engine components for extreme operating conditions. |
| Industrial Equipment | Components in furnaces and reactors exposed to extreme heat and corrosion. |
| Medical | Surgical tools and implants owing to its biocompatibility. |
| Energy Sector | Turbines and heat exchangers, where thermal stress is a concern. |
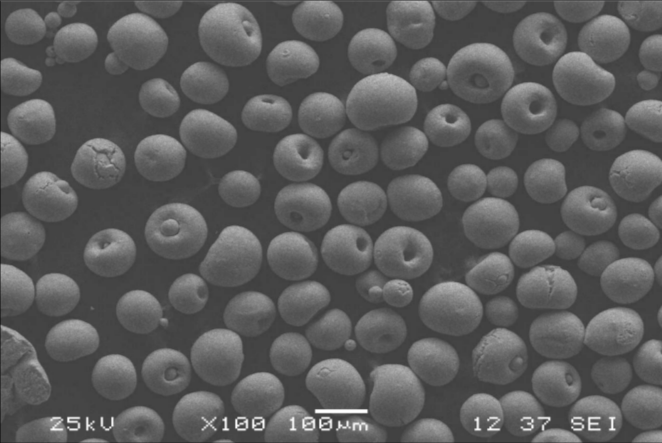
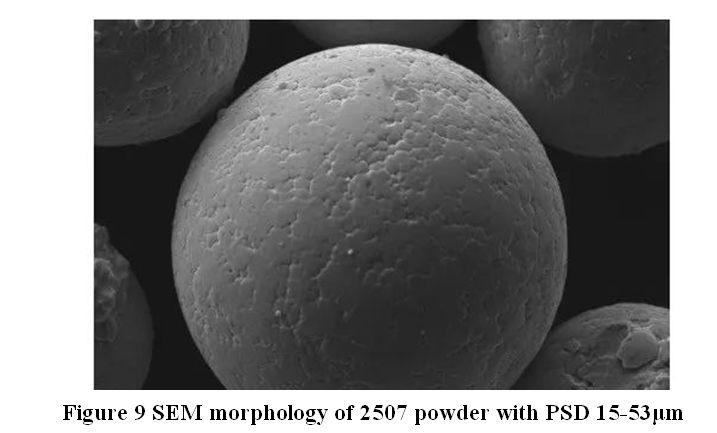


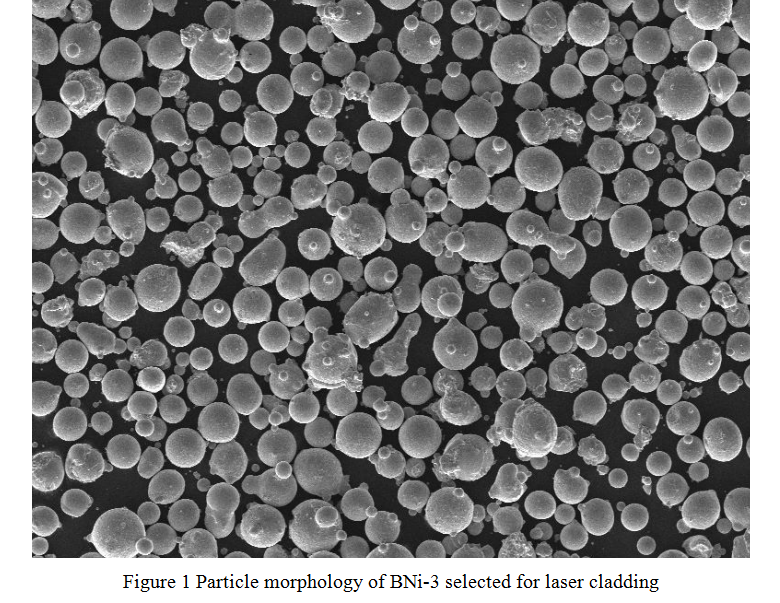
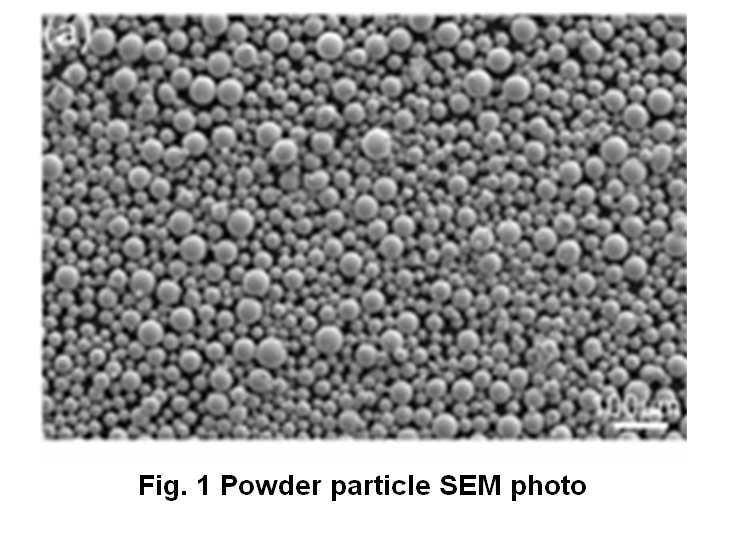


Specific Models of C103 Powder
C103 powder is available in various grades and models designed for specific applications. Below are ten notable models:
| Model | Description |
|---|---|
| C103-SF | High-purity grade for aerospace and critical applications requiring superior performance. |
| C103-HT | Heat-treated variant for enhanced thermal resistance and mechanical strength. |
| C103-AM | Optimized for additive manufacturing processes like 3D printing. |
| C103-WL | Weldable grade ensuring seamless joining in complex structures. |
| C103-CF | Corrosion-resistant grade suitable for harsh environments. |
| C103-LP | Low-porosity powder designed for smooth surface finishes. |
| C103-B | Budget-friendly option for industrial-grade applications. |
| C103-MD | Medical-grade powder adhering to stringent biocompatibility standards. |
| C103-NH | Non-hafnium variant for specific cost and performance trade-offs. |
| C103-XT | Experimental grade for cutting-edge research and custom applications. |
Each model is tailored to meet unique demands, ensuring versatility across industries.
Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards
Understanding the technical details is crucial for selecting the right C103 powder model. Here’s a detailed table:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Particle Size | Available in sizes ranging from 15–150 microns. |
| Purity | Typically 99.5% or higher for high-performance grades. |
| Standards | Meets ASTM B365 and AMS7852 specifications. |
| Packaging | Supplied in vacuum-sealed containers to preserve quality. |
Comparison of C103 Powder Models
| Feature | C103-SF | C103-HT | C103-AM | C103-WL | C103-CF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | High | Very High | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Machinability | Easy | Moderate | Easy | Easy | Easy |
| Cost | High | High | Moderate | Moderate | Low |
| Best For | Aerospace | Industrial | 3D Printing | Welded Parts | Corrosive Environments |
This table simplifies decision-making by highlighting key features of different models.
Suppliers and Pricing Details
Below is a snapshot of some suppliers and pricing for C103 powder:
| Supplier | Region | Price Range (per kg) | Specialization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Alloys Inc. | USA | $1,500–$2,000 | Aerospace-grade powders. |
| PowderTech Ltd. | Europe | $1,200–$1,800 | Customizable particle sizes. |
| NiobiumPro | Asia | $1,000–$1,600 | Bulk orders and industrial applications. |
| MetalMasters | Global | $1,300–$1,900 | Medical and automotive-grade powders. |
Prices may vary based on quantity and customization.
Advantages and Limitations of C103 Powder
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | Can withstand extreme heat, making it ideal for aerospace. | Expensive compared to other metal powders. |
| Machinability | Easy to process and weld, reducing manufacturing complexities. | Requires expertise for proper handling and application. |
| Durability | High strength and corrosion resistance. | Limited suppliers globally, leading to longer lead times. |

FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is C103 powder used for? | Primarily for aerospace applications, heat exchangers, and medical devices. |
| How is it processed? | Typically via powder metallurgy, 3D printing, or traditional fabrication methods. |
| What makes it unique? | Its niobium-based composition offers unmatched heat resistance and lightweight properties. |
| Is it expensive? | Yes, it’s pricier than conventional powders due to its specialized properties. |
| How does it compare to other alloys? | C103 excels in thermal resistance but might fall short in affordability and availability. |

