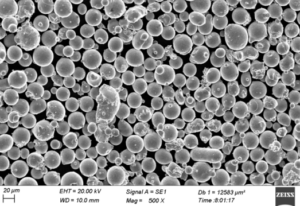
Overview of CuSnZn Powder
CuSnZn Powder, also known as Copper-Tin-Zinc Powder, is a specialized alloy powder that offers a unique combination of mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and versatility in various industrial applications. This alloy typically comprises a balanced mix of copper (Cu), tin (Sn), and zinc (Zn), which work synergistically to enhance the powder’s properties for uses in metallurgy, coatings, sintering, and brazing.
The CuSnZn alloy stands out in the metal powders category due to its balance of strength and corrosion resistance, making it popular in industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to electronics and construction. With the addition of tin, the alloy gains enhanced strength and toughness, while zinc introduces better wear resistance and anti-corrosive qualities.
Let’s dive deeper into the types, composition, characteristics, and applications of CuSnZn Powder. We’ll also examine specific models, specifications, and comparisons to help you understand where this alloy powder can fit into your projects.
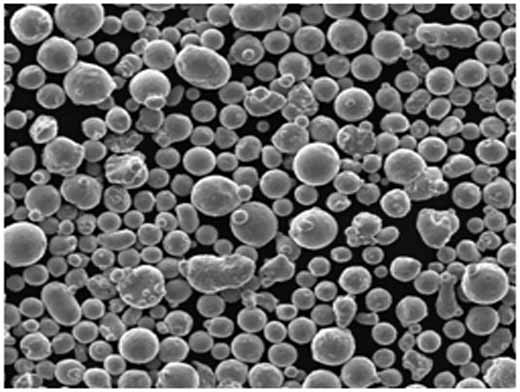
Composition and Properties of CuSnZn Powder
The composition of CuSnZn Powder varies slightly depending on the desired characteristics, but the core components remain copper, tin, and zinc in varied ratios. Each metal contributes unique properties to the alloy:
| Component | Symbol | Typical Composition Range (%) | Properties Contributed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Cu | 60-90% | High thermal/electrical conductivity, ductility |
| Tin | Sn | 5-20% | Strength, hardness, corrosion resistance |
| Zinc | Zn | 5-20% | Wear resistance, added strength, lower melting point |
Understanding the Role of Each Component
- Copper (Cu): The primary metal, copper, provides essential ductility, making the powder easy to shape and form. Its high electrical conductivity also makes it favorable for electronic applications.
- Tin (Sn): Adding tin strengthens the alloy, improves hardness, and enhances corrosion resistance, making it ideal for mechanical parts.
- Zinc (Zn): Zinc adds wear resistance and contributes to lowering the melting point, which is advantageous in applications like brazing and soldering.
Characteristics of CuSnZn Powder
The unique mix of CuSnZn Powder leads to the following notable characteristics:
| Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance to corrosion in various environments due to copper and tin content. |
| Strength | The alloy is tough and durable, making it ideal for structural and mechanical applications. |
| Wear Resistance | Zinc improves the wear resistance, suitable for high-stress components. |
| Thermal Conductivity | High thermal conductivity thanks to copper, useful in heat-sensitive applications. |
| Low Melting Point | Lower melting point than pure copper, enabling better brazing and sintering. |
Types and Grades of CuSnZn Powder
Here are some of the most common types and specific models of CuSnZn Powder, each optimized for particular industrial needs. These powders vary in terms of particle size, composition, and application.
| Model Name | Composition (Cu-Sn-Zn %) | Application | Unique Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| CuSn10Zn2 | 88-10-2 | Decorative coatings, jewelry | Excellent corrosion resistance |
| CuSn5Zn5 | 90-5-5 | Electrical contacts, low-friction coatings | High electrical conductivity |
| CuSn8Zn4 | 88-8-4 | Bearings, bushings | Improved wear resistance |
| CuSn6Zn3 | 91-6-3 | Gears, small machinery parts | Balanced strength and machinability |
| CuSn9Zn1 | 90-9-1 | Brazing and soldering | Lower melting point |
| CuSn7Zn2 | 91-7-2 | Aerospace components, heat exchangers | High thermal conductivity |
| CuSn12Zn1 | 87-12-1 | Automotive components, fasteners | Enhanced toughness |
| CuSn3Zn5 | 92-3-5 | Industrial fittings, valve seats | Good resistance to abrasive wear |
| CuSn11Zn4 | 85-11-4 | Marine equipment, propellers | Superior corrosion resistance in water |
| CuSn15Zn2 | 83-15-2 | High-stress mechanical parts | High hardness and tensile strength |
Each of these models offers slightly different strengths, making it crucial to choose the right type for specific needs.
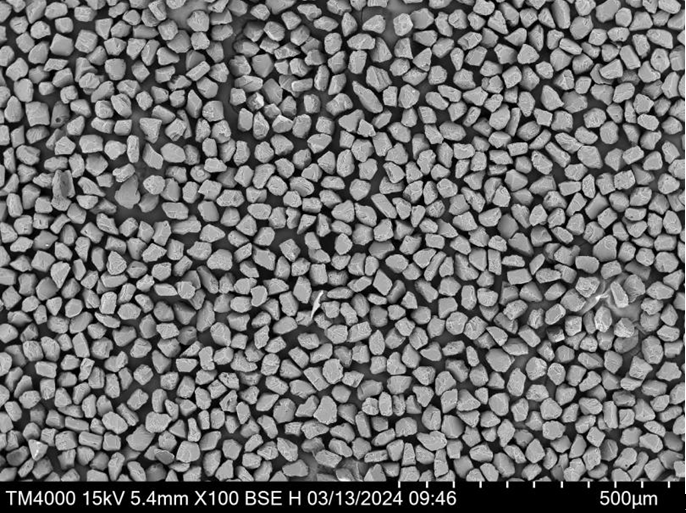








Applications of CuSnZn Powder
CuSnZn Powder’s versatility makes it suitable across a wide array of applications:
| Application | Details |
|---|---|
| Automotive Industry | Bearings, bushings, gears, due to wear resistance and durability. |
| Aerospace Industry | Components in engines and structural parts requiring high strength and corrosion resistance. |
| Electronics | Electrical contacts, connectors, and heat dissipation materials. |
| Marine Engineering | Propellers, marine fittings, due to superior corrosion resistance. |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Bearings, bushings, low-friction coatings for machinery. |
| Jewelry and Decorative Arts | Used for aesthetic coatings, jewelry due to attractive color and durability. |
| Brazing and Soldering | Low melting point alloys that provide strong bonding in metal joints. |
| Heat Exchangers | High thermal conductivity is beneficial for efficient heat transfer. |
Specifications of CuSnZn Powder Models
| Model | Particle Size Range (µm) | Density (g/cm³) | Melting Point (°C) | Hardness (HV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuSn10Zn2 | 20-45 | 7.6 | 980 | 120 |
| CuSn5Zn5 | 15-50 | 7.7 | 990 | 110 |
| CuSn8Zn4 | 25-60 | 7.5 | 970 | 130 |
| CuSn6Zn3 | 10-40 | 7.65 | 980 | 125 |
| CuSn9Zn1 | 5-30 | 7.8 | 950 | 115 |
| CuSn7Zn2 | 20-60 | 7.7 | 960 | 130 |
| CuSn12Zn1 | 15-45 | 7.6 | 940 | 140 |
| CuSn3Zn5 | 20-55 | 7.75 | 930 | 110 |
| CuSn11Zn4 | 25-70 | 7.6 | 920 | 135 |
| CuSn15Zn2 | 10-50 | 7.5 | 910 | 145 |
Advantages and Limitations of CuSnZn Powder
| Feature | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Highly resistant to corrosion in marine and industrial environments. | Less resistant than some other alloys in extreme acidic conditions. |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent wear resistance, especially with added zinc. | Higher zinc content can lead to brittleness in some applications. |
| Thermal Conductivity | Efficient in heat transfer, useful for electronics and heat exchangers. | Not as high as pure copper or copper-aluminum alloys in thermal applications. |
| Strength and Hardness | Provides a good balance of strength and hardness, ideal for load-bearing parts. | May be softer than steel-based alloys, limiting use in extremely high-stress applications. |
| Machinability | Easily machinable with standard tools, reducing production costs. | Higher tin or zinc content can reduce machinability due to increased brittleness. |
| Cost | Generally more affordable than pure copper or specialized alloys. | Prices fluctuate with market demand for copper, tin, and zinc. |
Leading Suppliers and Pricing Information
| Supplier | Country | Average Price (per kg) | Grades Available |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABC Metals | USA | $25 – $40 | CuSn10Zn2, CuSn5Zn5 |
| Global Alloy Ltd. | Germany | $28 – $45 | CuSn8Zn4, CuSn6Zn3 |
| Alloy World | Japan | $30 – $42 | CuSn7Zn2, CuSn12Zn1 |
| Metals R Us | UK | $27 – $38 | CuSn3Zn5, CuSn11Zn4 |
| CopperCraft | China | $20 – $35 | CuSn9Zn1, CuSn15Zn2 |

FAQ
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is CuSnZn Powder used for? | It is widely used in automotive, aerospace, marine, and electronic industries due to its corrosion resistance. |
| Can CuSnZn Powder replace pure copper? | In many cases, yes. It offers similar thermal conductivity but with added strength and corrosion resistance. |
| What is the typical price range? | Prices vary between $20 – $45 per kg, depending on composition and supplier. |
| Is CuSnZn Powder good for brazing? | Absolutely, the low melting point makes it an excellent choice for brazing and soldering applications. |
| What is the main advantage of this alloy? | The alloy offers a balanced blend of strength, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. |