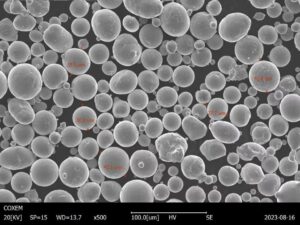
Cobalt (Co) is a crucial element in modern industries, and its powdered form has countless applications. If you’re diving into the world of metal powders, you’re likely to encounter pure cobalt powder, or “pure Co powder.” But what makes it stand out, and why is it so sought after in technical industries? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about pure Co powder — from its composition to its applications, specifications, advantages, and even the types of cobalt powder available. Whether you’re a seasoned industry professional or just beginning your research, this article will cover it all.
Overview of Pure Co Powder
Pure cobalt powder is a fine, metallic material that has become a staple in various industries like aerospace, electronics, and even healthcare. Known for its strength, wear resistance, and ability to maintain stability at high temperatures, pure Co powder has a variety of uses in both advanced and day-to-day applications. It’s also used as an alloying element, which means that it can be mixed with other metals to enhance their properties. In short, cobalt powder is an invaluable material for industries where high-performance and durability are non-negotiable.
Key Features of Pure Co Powder
- High Melting Point: Pure Co powder boasts a melting point of 1,495°C (2,723°F), making it ideal for high-temperature applications.
- Magnetic Properties: It’s ferromagnetic, meaning it can be magnetized, which is especially useful in electronics and battery technologies.
- Corrosion Resistance: The powder resists oxidation and corrosion, which is key for applications in harsh environments like jet engines or gas turbines.
- Hardness: Cobalt powder is known for its exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making it suitable for coatings and cutting tools.
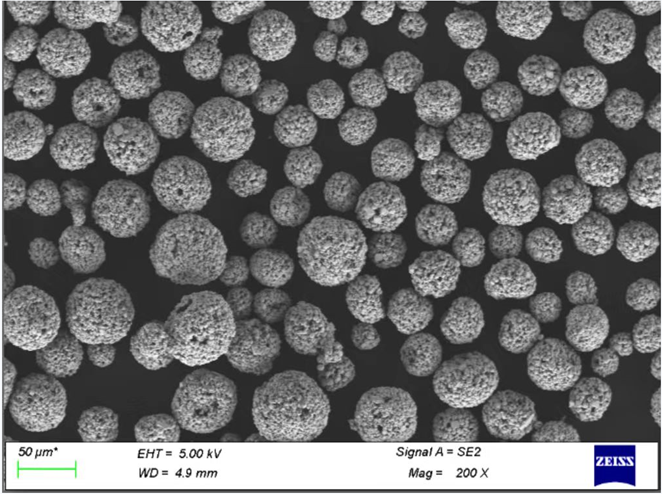
Types of Pure Cobalt Powder
Now that we have an understanding of what pure Co powder is, let’s dive into the different types available. Each type of cobalt powder is optimized for specific uses based on its composition, particle size, and manufacturing process. Here’s a table listing different cobalt powders, including specific models and their properties.
| Type | Description | Applications | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cobalt Powder – Ultra-Fine | Composed of extremely small particles, typically less than 1 micron in size. | Used in 3D printing, electronics, and fine coating applications. | High surface area, ideal for detailed surface treatments. |
| Cobalt Carbonyl Powder | Made from cobalt carbonyl, offering very pure cobalt content. | Excellent for magnetic materials and chemical catalysts. | High purity and uniformity, excellent for electronic applications. |
| Cobalt Electrolytic Powder | Electrolytic process creates high-purity powder with larger particle sizes. | Battery technologies, superalloys. | Excellent chemical stability and electrical conductivity. |
| Cobalt Spherical Powder | Created through atomization, forming highly spherical particles. | Metal injection molding, 3D printing, powder metallurgy. | Excellent flowability, crucial for additive manufacturing. |
| Cobalt Acetate Powder | Derived from cobalt acetate and used in organic synthesis. | Catalysts, chemical synthesis, and dyes. | Very fine, uniform powder with good solubility in organic solvents. |
| Cobalt Alloy Powder | Combined with other elements such as chromium or nickel for enhanced properties. | Aerospace components, superalloys. | High corrosion and oxidation resistance. |
| Cobalt Nanoparticles | Nanoscale particles of cobalt offering exceptional surface area. | Used in high-tech applications like magnetic storage devices. | Enhanced magnetic properties at the nanoscale. |
| Cobalt Oxide Powder | Powder made from cobalt oxides, rather than pure cobalt. | Catalysts, pigments, glass production. | Used in environments that require both oxidation and reduction. |
| Cobalt Sulfide Powder | Combines cobalt and sulfur, used mainly in battery and catalysis applications. | Energy storage devices like lithium-ion batteries. | Highly reactive for battery technologies. |
| Cobalt-Chromium Alloy Powder | Alloy powder used in medical and dental prosthetics. | Dental and orthopedic implants. | Biocompatible, corrosion-resistant, and wear-resistant. |
Each of these powders serves unique purposes and exhibits distinct properties, making it crucial to understand which one suits your particular needs.
Composition of Pure Co Powder
The composition of pure Co powder can vary slightly depending on the production process and intended application. Generally, it contains nearly 100% cobalt, but there are times when trace elements or additives are included to modify its properties for specific industrial uses.
Common Additives in Cobalt Powder
- Nickel (Ni): Often added to enhance corrosion resistance and toughness.
- Chromium (Cr): Improves wear and oxidation resistance, particularly in high-temperature environments.
- Iron (Fe): Sometimes included in small amounts to adjust the powder’s magnetic properties.
| Cobalt Powder Composition | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Cobalt (Co) | 98% – 100% |
| Nickel (Ni) | 0% – 1% |
| Chromium (Cr) | 0% – 1% |
| Iron (Fe) | 0% – 0.5% |
While these additives are minimal, their impact on the final properties of the powder can be significant.
Characteristics of Pure Co Powder
When evaluating cobalt powder for your application, there are several key characteristics to consider:
1. Particle Size Distribution
Cobalt powder is available in a variety of particle sizes, ranging from submicron (nano) to larger particles. The size distribution of the powder influences how it behaves in processes like powder metallurgy and additive manufacturing.
- Fine Powder (Nanoparticles): Used in high-precision industries like electronics.
- Coarser Powder: Ideal for thermal spraying and metal injection molding.
2. Surface Area
The surface area of cobalt powder can directly impact its reactivity and effectiveness, especially in catalytic applications.
- Higher Surface Area: Increases the reactivity, which is ideal for catalysis.
- Lower Surface Area: More stable, better for structural applications.
3. Purity
Purity is a critical factor, especially for high-end applications like superalloys, where contaminants can compromise performance. Pure cobalt powders typically exceed 99% purity, ensuring minimal impurities like sulfur, phosphorus, or oxygen.
4. Magnetic Properties
One of the standout features of cobalt powder is its magnetic properties. Pure cobalt has ferromagnetic properties, which makes it invaluable in the production of permanent magnets and other electronic components.
5. Thermal Stability
With a high melting point and excellent thermal stability, cobalt powders are often used in environments that operate at extreme temperatures, such as jet engines or high-temperature gas turbines.
| Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|
| Particle Size Distribution | Fine to coarse (submicron to microns) |
| Surface Area | Varies depending on particle size, typically from 0.1m²/g to 5m²/g |
| Purity | 99% or higher, depending on production method |
| Magnetic Properties | Ferromagnetic |
| Thermal Stability | High-temperature resistance, up to 1,495°C |

Applications of Pure Co Powder
Pure cobalt powder finds use in a variety of industries, from aerospace and automotive to medical and electronics. Below is a table showcasing its most common applications and the key benefits it brings to each sector.
| Industry | Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Jet engine components, superalloys. | High thermal resistance, durability under extreme conditions. |
| Medical | Dental and orthopedic implants, prosthetics. | Biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, wear resistance. |
| Electronics | Permanent magnets, magnetic storage devices, sensors. | Strong magnetic properties, electrical conductivity. |
| Battery Technologies | Lithium-ion batteries, cathodes for rechargeable batteries. | High energy storage capacity, longevity. |
| Catalysts | Used in the petroleum and chemical industries for refining. | High surface area, enhances catalytic reactions. |
| Powder Metallurgy | Production of high-strength metal components through sintering. | Excellent flowability and compaction. |
Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards of Pure Co Powder
When selecting cobalt powder for a particular application, it’s essential to know its specifications. Below is a table outlining the most important specifications, including sizes, grades, and applicable industry standards.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Particle Size | Typically ranges from 0.1 to 100 microns. |
| Purity | Usually 99% or higher, depending on the production method. |
| Grades | Commercially available in various grades like ASTM F75, ASTM B838. |
| Density | Varies based on particle size and shape, generally between 8.9 to 9.1 g/cm³ |
| Industry Standards | ASTM F75, ISO 5832-4, AMS 4775, for cobalt alloys and medical applications. |

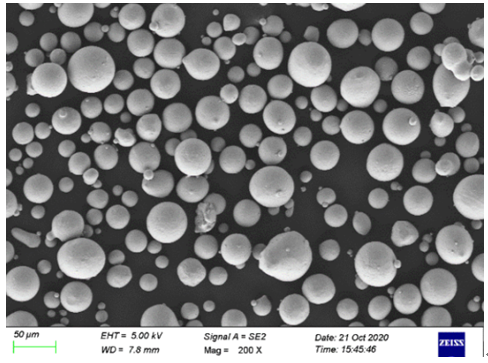
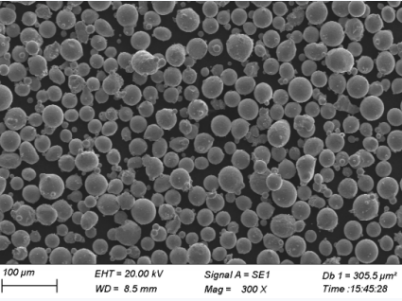



Suppliers and Pricing of Pure Co Powder
Pricing for pure cobalt powder can vary significantly depending on factors like purity, particle size, and the supplier. Below is a table of typical suppliers and their pricing information.
| Supplier | Product | Purity | Particle Size | Price (per kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| American Elements | Ultra-Fine Cobalt Powder | 99.8% | 0.5-5 microns | $500 – $800 |
| Alfa Aesar | Electrolytic Cobalt Powder | 99.5% | 10-50 microns | $400 – $600 |
| Nanografi | Cobalt Nanoparticles | 99.9% | <100 nm | $1,200 – $1,800 |
| Stanford Advanced Materials | Spherical Cobalt Powder | 99.7% | 15-45 microns | $450 – $700 |
| Inframat | Cobalt Carbonyl Powder | 99.9% | 1-10 microns | $600 – $900 |
Advantages and Limitations of Pure Co Powder
While pure Co powder is a versatile and widely-used material, it comes with its own set of advantages and limitations. Let’s break them down in the table below:
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| High thermal and corrosion resistance | Expensive compared to other metals |
| Magnetic properties for electronic uses | Toxicity concerns in specific environments |
| Excellent wear resistance for tooling | Requires careful handling due to safety |
| Ideal for high-performance alloys | Difficult to source in large quantities |

FAQ
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is pure Co powder used for? | It is used in industries like aerospace, electronics, medical implants, and batteries. |
| Is cobalt powder magnetic? | Yes, cobalt is ferromagnetic, making it useful in magnetic and electronic applications. |
| Is cobalt powder toxic? | Inhalation or prolonged exposure to cobalt powder can be toxic, requiring proper safety measures. |
| What’s the price range of cobalt powder? | Prices vary based on purity and particle size, typically between $400 and $1,800 per kg. |
| Can cobalt powder be used in 3D printing? | Yes, certain types like spherical cobalt powder are ideal for 3D printing applications. |
| How is cobalt powder produced? | Methods include electrolytic processes, carbonyl decomposition, and atomization. |
Conclusion
Pure cobalt powder, with its high-performance characteristics, remains an essential material for various industries. Whether you’re looking at its thermal resistance, magnetic properties, or use in critical applications like batteries and aerospace components, cobalt powder offers unmatched versatility. Understanding the different types, characteristics, and suppliers will help you make informed decisions for your projects, ensuring you get the best material for your needs.