Sinter-hardening alloy powder is an unsung hero in the world of materials science. This engineering marvel combines the benefits of sintering—a method used to create solid structures from powders— with the added advantages of hardening processes. This unique blend creates a material that is not only strong and durable but also easier to produce and more cost-effective than traditional methods. Whether you’re a materials scientist, an engineer, or just a curious reader, this guide will delve deep into the intricacies of sinter-hardening alloy powders, offering a comprehensive look at what makes these materials so special.
Overview of Sinter-Hardening Alloy Powder
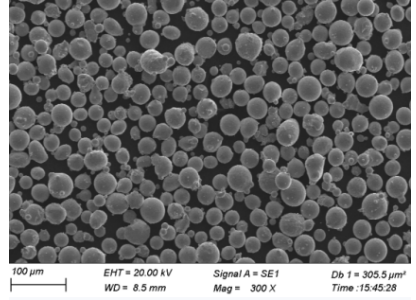
Sinter-hardening alloy powders are specialized metal powders designed to undergo hardening during the sintering process itself. This dual functionality eliminates the need for additional heat treatment, reducing production time and costs while producing components with high strength and wear resistance. These powders are predominantly used in the manufacturing of high-performance parts in the automotive, aerospace, and tooling industries.
Key Highlights:
- Versatile Applications: From automotive gears to aerospace components, sinter-hardening alloy powders are used across various industries.
- Cost-Efficient Production: The sinter-hardening process combines sintering and hardening, reducing the need for additional processing steps.
- High-Performance Characteristics: These powders offer exceptional mechanical properties, including strength, toughness, and wear resistance.
Composition of Sinter-Hardening Alloy Powder
The composition of sinter-hardening alloy powders is critical to their performance. These powders are typically composed of a base metal, such as iron, mixed with alloying elements that promote hardening during the sintering process. The selection of these elements and their concentrations are carefully balanced to achieve the desired mechanical properties.
| Metal Powder Model | Composition | Primary Alloying Elements | Notable Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| SH-42 | Iron-based | Nickel, Molybdenum | High toughness, wear resistance |
| SH-55 | Copper-based | Nickel, Chromium | Excellent corrosion resistance |
| SH-62 | Iron-based | Carbon, Manganese | Improved hardness and strength |
| SH-78 | Stainless steel | Chromium, Nickel | High corrosion resistance, good hardness |
| SH-81 | Iron-based | Chromium, Molybdenum | Superior wear resistance and hardness |
| SH-94 | Nickel-based | Molybdenum, Boron | High strength at elevated temperatures |
| SH-100 | Titanium-based | Aluminum, Vanadium | Lightweight, excellent strength-to-weight ratio |
| SH-120 | Iron-based | Silicon, Manganese | Enhanced toughness and machinability |
| SH-130 | Copper-based | Tin, Zinc | Good conductivity, moderate strength |
| SH-145 | Iron-based | Carbon, Silicon | Enhanced hardness, reduced brittleness |
Each of these powders is engineered to meet specific requirements, whether that be high wear resistance, improved toughness, or superior corrosion resistance.
Characteristics of Sinter-Hardening Alloy Powder
The characteristics of sinter-hardening alloy powders are what make them so valuable in industrial applications. These powders combine the benefits of both sintering and hardening into a single process, resulting in materials that are exceptionally strong and wear-resistant.
Mechanical Properties:
- Strength: Sinter-hardening powders produce components with high tensile and compressive strength, making them suitable for load-bearing applications.
- Toughness: These powders offer excellent toughness, allowing the material to absorb energy and resist fracture.
- Wear Resistance: The hardening elements within these powders contribute to superior wear resistance, extending the lifespan of components.
Physical Properties:
- Density: Sinter-hardening powders typically achieve high density, which contributes to their mechanical strength.
- Porosity: The sintering process can be controlled to reduce porosity, resulting in materials with a more uniform structure and better mechanical properties.
Thermal Properties:
- Heat Resistance: Certain sinter-hardening powders, especially those based on nickel or titanium, exhibit excellent heat resistance, maintaining their mechanical properties at elevated temperatures.
- Thermal Conductivity: Depending on the base metal, these powders can offer good thermal conductivity, which is beneficial in applications requiring heat dissipation.
Advantages of Sinter-Hardening Alloy Powder
Sinter-hardening alloy powders offer a range of advantages that make them the material of choice for various high-performance applications.
Cost Efficiency:
- Reduced Processing Steps: The combination of sintering and hardening in one step reduces the need for additional heat treatments, saving both time and money.
- Lower Energy Consumption: The integrated process of sinter-hardening consumes less energy compared to traditional methods that require separate sintering and hardening steps.
Enhanced Performance:
- Improved Mechanical Properties: Components made from sinter-hardening powders exhibit superior strength, toughness, and wear resistance compared to those made from traditional sintered materials.
- Consistent Quality: The controlled composition and uniform distribution of alloying elements ensure consistent quality and performance across different batches.
Versatility:
- Wide Range of Applications: From automotive parts to aerospace components, sinter-hardening powders can be used in a variety of applications, making them highly versatile.
- Customization: These powders can be tailored to meet specific requirements by adjusting the composition and processing parameters.





Applications of Sinter-Hardening Alloy Powder
Sinter-hardening alloy powders are used in a wide range of applications due to their exceptional mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness.
| Industry | Common Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Gears, transmission components, engine parts | High strength, wear resistance, cost-effective production |
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, structural components | Lightweight, high-temperature resistance |
| Tooling | Cutting tools, dies, molds | Superior hardness, extended tool life |
| Electronics | Heat sinks, connectors | Good thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance |
| Medical | Implants, surgical instruments | Biocompatibility, strength, corrosion resistance |
| Oil & Gas | Drill bits, valves, seals | High wear resistance, corrosion resistance |
| Consumer Goods | Watches, jewelry, high-end appliances | Aesthetic appeal, durability |
| Industrial Machinery | Bearings, gears, fasteners | High load-bearing capacity, wear resistance |
| Defense | Armor, weapon components | High strength, impact resistance |
| Energy | Fuel cells, battery components | High efficiency, long lifecycle |
These applications highlight the versatility and performance of sinter-hardening alloy powders across different industries.
Specifications, Sizes, Grades, and Standards
When selecting sinter-hardening alloy powders, it’s important to consider the specifications, sizes, grades, and standards that apply to your specific application.
| Metal Powder Model | Particle Size Range (μm) | Grade | Standard Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|
| SH-42 | 10-50 | A2 | ASTM B783, MPIF 35 |
| SH-55 | 15-45 | B3 | ISO 5755, DIN 3572 |
| SH-62 | 20-60 | A1 | ASTM B783, ISO 4499 |
| SH-78 | 5-30 | C1 | ASTM B243, MPIF 35 |
| SH-81 | 25-70 | B1 | ISO 4499, DIN 30910 |
| SH-94 | 15-45 | A3 | ASTM B312, MPIF 35 |
| SH-100 | 10-40 | C2 | ISO 5755, ASTM B312 |
| SH-120 | 10-50 | A2 | MPIF 35, DIN 30910 |
| SH-130 | 20-60 | B2 | ISO 5755, ASTM B243 |
| SH-145 | 15-55 | C1 | ASTM B243, ISO 5755 |
Choosing the right grade and standard is crucial for ensuring the material meets the necessary performance criteria for your application.
Suppliers and Pricing Details
Understanding the market for sinter-hardening alloy powders can help you make informed purchasing decisions. Below are some of the key suppliers and general pricing information for these powders.
| Supplier | Location | Metal Powder Model | Price Range (per kg) | Delivery Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Metal Powders | United States | SH-42, SH-55 | $20 – $50 | 2-4 weeks |
| Global Powders Ltd. | United Kingdom | SH-62, SH-78 | $25 – $60 | 3-6 weeks |
| Metallurgical Solutions | Germany | SH-81, SH-94 | $30 – $70 | 4-8 weeks |
| PowderTech | China | SH-100, SH-120 | $15 – $40 | 3-5 weeks |
| Eastern Alloys | Japan | SH-130, SH-145 | $35 – $75 | 2-5 weeks |
Prices can vary depending on the supplier, the quantity ordered, and the specific requirements of your application.
Pros and Cons of Sinter-Hardening Alloy Powder
While sinter-hardening alloy powders offer numerous advantages, they also come with certain limitations. Understanding these can help you make the best decision for your specific needs.
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Production Process | Combines sintering and hardening, reducing production steps | Requires precise control of sintering conditions |
| Cost | Lower overall cost due to reduced processing steps | Initial investment in sintering equipment can be high |
| Mechanical Properties | High strength, wear resistance, and toughness | Limited to specific alloy compositions |
| Versatility | Suitable for a wide range of applications | May not be suitable for all high-temperature applications |
| Customization | Can be tailored to specific requirements | Custom powders can be more expensive than standard grades |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower energy consumption due to combined process | May not achieve the same properties as separately hardened materials |
These pros and cons illustrate the trade-offs involved in using sinter-hardening alloy powders, helping you make an informed decision based on your specific requirements.
FAQ
To wrap up, here are some frequently asked questions about sinter-hardening alloy powders, presented in a convenient table format for quick reference.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is sinter-hardening alloy powder? | Sinter-hardening alloy powder is a metal powder designed to undergo hardening during the sintering process, eliminating the need for additional heat treatment. |
| What are the key benefits of using sinter-hardening powders? | They offer cost-effective production, high strength, wear resistance, and can be tailored to specific applications. |
| In which industries are sinter-hardening powders commonly used? | Automotive, aerospace, tooling, electronics, medical, oil & gas, and consumer goods industries. |
| How is sinter-hardening different from traditional sintering? | Sinter-hardening combines sintering and hardening in one step, reducing production time and improving material properties. |
| Can sinter-hardening powders be customized? | Yes, they can be tailored by adjusting the composition and processing parameters to meet specific application requirements. |
| What are the limitations of sinter-hardening alloy powders? | They may require precise control of sintering conditions and may not be suitable for all high-temperature applications. |
| How does the cost of sinter-hardening powders compare to traditional powders? | Sinter-hardening powders can be more cost-effective due to the reduced processing steps, but the initial investment in equipment can be high. |
| Are sinter-hardening powders environmentally friendly? | They can be more energy-efficient due to the combined process, reducing the overall environmental impact of production. |
| What are some common metal powder models available? | Examples include SH-42, SH-55, SH-62, SH-78, SH-81, SH-94, SH-100, SH-120, SH-130, and SH-145. |
| Where can I purchase sinter-hardening alloy powders? | Sinter-hardening powders can be purchased from suppliers such as Advanced Metal Powders, Global Powders Ltd., and PowderTech. |
Conclusion
Sinter-hardening alloy powders represent a significant advancement in materials science, offering a unique combination of strength, durability, and cost-efficiency. Whether you’re developing high-performance automotive components or cutting-edge aerospace parts, these powders provide a versatile and reliable solution. By understanding the composition, characteristics, advantages, and applications of sinter-hardening alloy powders, you can make informed decisions that will help you optimize your production processes and achieve superior results.