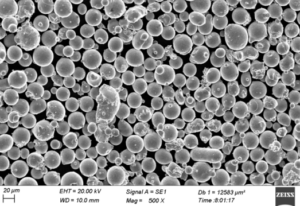
Welcome to the world of EB 3D printing system! If you’re diving into this realm, you’re likely seeking to understand what makes EB 3D printing tick, how it stacks up against other technologies, and what specific materials are best suited for your projects. Let’s explore this fascinating technology in depth, covering everything from its fundamentals to the nitty-gritty details of metal powders, and why it might just be the game-changer you’re looking for.
Overview of EB 3D Printing System
Electron Beam (EB) 3D printing, also known as Electron Beam Melting (EBM), is an advanced additive manufacturing process that uses a high-energy electron beam to melt and fuse metal powders layer by layer, creating complex geometries with high precision and excellent material properties. Unlike traditional methods, EB 3D printing allows for the creation of intricate designs that are otherwise impossible or extremely costly to produce.
Key Details:
- Technology: Additive Manufacturing
- Process: Electron Beam Melting
- Materials: Primarily Metal Powders
- Applications: Aerospace, Medical Implants, Automotive, Tooling, and more
- Advantages: High precision, complex geometries, superior material properties
- Limitations: High initial cost, limited material choices, requires vacuum environment
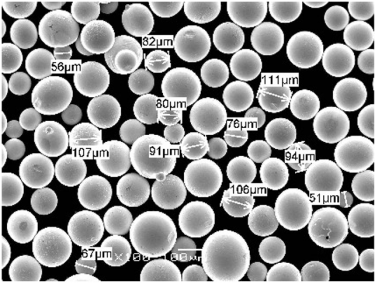
Types and Characteristics of Metal Powders for EB 3D Printing
Choosing the right metal powder is crucial for the success of EB 3D printing. Below is a detailed table of specific metal powder models, their compositions, and key characteristics.
| Metal Powder Model | Composition | Properties | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V | Ti-6Al-4V | High strength, lightweight | Widely used in aerospace and medical implants |
| Inconel 718 | Ni-Cr-Fe | High-temperature resistance | Suitable for turbine blades and high-stress components |
| CoCrMo | Co-Cr-Mo | Excellent wear resistance | Ideal for dental and orthopedic implants |
| 316L Stainless Steel | Fe-Cr-Ni-Mo | Corrosion-resistant | Used in marine and medical applications |
| AlSi10Mg | Al-Si-Mg | Lightweight, good thermal properties | Popular in automotive and aerospace industries |
| Maraging Steel (1.2709) | Fe-Ni-Mo-Co | High strength, good hardness | Used for tooling and high-performance parts |
| Copper (Cu) | Pure Copper | Excellent thermal and electrical conductivity | Applications in electronics and heat exchangers |
| Niobium (Nb) | Pure Niobium | High melting point, good ductility | Used in superconductors and aerospace components |
| Tantalum (Ta) | Pure Tantalum | Corrosion-resistant, high melting point | Suitable for chemical processing equipment |
| Hastelloy X | Ni-Cr-Fe-Mo | Oxidation-resistant, high strength | Ideal for gas turbine engines and industrial furnaces |
Applications of EB 3D Printing System
EB 3D printing’s unique capabilities make it suitable for a variety of high-performance applications. Let’s look at some of the primary uses of this technology.
| Application | Industry | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace Components | Aerospace | Turbine blades, structural components |
| Medical Implants | Medical | Hip and knee implants, dental prosthetics |
| Automotive Parts | Automotive | Engine components, lightweight structures |
| Tooling and Molds | Manufacturing | Injection molds, die-casting tools |
| Heat Exchangers | Electronics | Efficient cooling solutions |
| Superconducting Materials | Energy | Superconducting magnets and components |
| Chemical Processing Equipment | Industrial | Corrosion-resistant components |
Specifications, Sizes, Grades, Standards
Understanding the specifications, sizes, grades, and standards of metal powders is essential for ensuring compatibility and performance in EB 3D printing.
| Metal Powder | Particle Size Range | Grade | Standards |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V | 15-45 µm | Grade 5 | ASTM F2924 |
| Inconel 718 | 15-53 µm | AMS 5662 | ASTM B637 |
| CoCrMo | 10-45 µm | ASTM F75 | ASTM F1537 |
| 316L Stainless Steel | 15-45 µm | 316L | ASTM A276 |
| AlSi10Mg | 20-63 µm | DIN 3.2381 | ISO 3522 |
| Maraging Steel (1.2709) | 15-45 µm | 1.2709 | AMS 6520 |
| Copper (Cu) | 10-45 µm | Cu-ETP | ASTM B170 |
| Niobium (Nb) | 20-60 µm | R04200 | ASTM B392 |
| Tantalum (Ta) | 15-45 µm | R05200 | ASTM B365 |
| Hastelloy X | 15-53 µm | UNS N06002 | ASTM B572 |






Suppliers and Pricing Details
Finding the right supplier is critical for maintaining the quality and consistency of your EB 3D printing materials. Here is a list of reputable suppliers along with their pricing details.
| Supplier | Metal Powder | Price (per kg) | Website |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Powders | Ti-6Al-4V, Inconel 718 | $300 – $500 | advancedpowders.com |
| Sandvik Materials | 316L Stainless Steel, AlSi10Mg | $200 – $400 | home.sandvik |
| Carpenter Technology | CoCrMo, Maraging Steel | $350 – $600 | cartech.com |
| GKN Additive | Copper, Niobium | $150 – $350 | gknadditive.com |
| LPW Technology | Tantalum, Hastelloy X | $400 – $700 | lpwtechnology.com |
Comparing Pros and Cons of EB 3D Printing
It’s important to weigh the advantages and limitations of EB 3D printing against other additive manufacturing technologies. Here’s a detailed comparison.
| Aspect | EB 3D Printing | Compared to Other Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | High | Similar to SLM, better than FDM |
| Material Properties | Superior | Better than most AM techniques |
| Speed | Moderate | Faster than SLS, slower than DMLS |
| Initial Cost | High | Higher than SLM and FDM |
| Operational Cost | Moderate | Similar to SLM, lower than DMLS |
| Complexity of Designs | Very high | Superior to FDM, comparable to SLM |
| Material Choices | Limited | More restricted than SLM and DMLS |
| Post-Processing | Minimal | Less than SLS, similar to DMLS |
| Vacuum Requirement | Yes | Unique to EB, not needed in SLM/FDM |
Composition of EB 3D Printing System
The composition of the EB 3D printing system involves several key components, each playing a vital role in the process.
- Electron Beam Gun: Generates the electron beam for melting the metal powder.
- Vacuum Chamber: Maintains a controlled environment free of contaminants.
- Powder Dispenser: Ensures even distribution of metal powder.
- Build Platform: Supports the part being printed and moves as layers are added.
- Control System: Manages the entire printing process, from beam control to powder spreading.
Characteristics of EB 3D Printing System
Understanding the unique characteristics of EB 3D printing is essential for harnessing its full potential.
- High Energy Density: The electron beam can melt high-melting-point metals with precision.
- Vacuum Environment: Essential for preventing oxidation and ensuring material integrity.
- Layer-by-Layer Fusion: Enables the creation of complex geometries with fine details.
- Minimal Thermal Stress: Reduces warping and residual stresses in printed parts.
Advantages of EB 3D Printing System
Why should you consider EB 3D printing? Here are some compelling reasons:
- Superior Material Properties: Achieves excellent mechanical properties and material homogeneity.
- Complex Geometries: Capable of producing intricate designs and internal structures.
- Reduced Waste: Uses only the necessary amount of material, minimizing waste.
- Less Post-Processing: Typically requires less finishing work compared to other methods.
Limitations of EB 3D Printing System
No technology is without its downsides. Here are some limitations to consider:
- High Initial Cost: The equipment and setup costs can be prohibitive for small businesses.
- Material Limitations: Fewer material choices compared to other AM methods.
- Vacuum Requirement: The need for a vacuum environment can complicate the setup.
- Speed: Slower than some other 3D printing methods, particularly for large parts.
FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is EB 3D printing? | A high-energy additive manufacturing process using electron beams to melt metal powders layer by layer. |
| Which industries use EB 3D printing? | Mainly aerospace, medical, automotive, and manufacturing industries. |
| What materials can be used? | Primarily metal powders like Ti-6Al-4V, Inconel 718, and 316L Stainless Steel. |
| How does it compare to SLM? | Offers superior material properties and precision but has fewer material choices. |
| What are the main advantages? | High precision, excellent material properties, and ability to create complex geometries. |
| What are the main limitations? | High initial cost, limited material choices, and requirement for a vacuum environment. |
| Is post-processing required? | Typically minimal compared to other methods like SLS and DMLS. |
| What are common applications? | Turbine blades, medical implants, engine components, and tooling. |
| How is the electron beam generated? | Using an electron beam gun within a vacuum chamber. |
| What is the typical cost of metal powders? | Prices range from $150 to $700 per kg, depending on the material. |
Conclusion
The EB 3D printing system stands out in the additive manufacturing landscape for its ability to produce high-quality, complex metal parts with precision and excellent material properties. While it comes with higher costs and some material limitations, the benefits it offers in terms of reduced waste, minimal post-processing, and superior mechanical properties make it an attractive choice for industries where performance and quality are paramount. Whether you’re in aerospace, medical, or any other high-tech field, understanding the nuances of EB 3D printing can help you make informed decisions about your manufacturing processes.