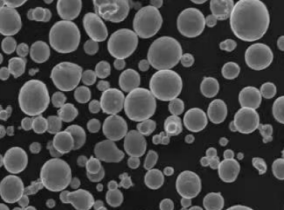
From powering advanced electronics to enhancing the performance of industrial machinery, copper alloys powder has emerged as a critical material in various industries. This article explores the world of copper alloys powder, delving into its properties, applications, production methods, and safety considerations.
Understanding Copper Alloys Powder
Copper alloys powder is a finely divided form of metals derived from copper and other elements. These alloys are meticulously engineered to leverage the advantageous properties of both copper and the alloying elements. The result is a versatile material with improved strength, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance.

Advantages of Copper Alloys Powder
Enhanced Strength and Durability
Copper alloys powder significantly boosts the mechanical properties of the materials it’s mixed with. Through careful formulation, manufacturers can tailor the strength and durability of the final product, making it suitable for various load-bearing applications.
Excellent Thermal Conductivity
One of copper’s inherent qualities is its exceptional thermal conductivity. When this property is harnessed in powder form, it becomes an invaluable component in heat exchangers, electronic devices, and other heat-sensitive applications.
Corrosion Resistance
Copper alloys powder possesses inherent corrosion resistance, making it a prime choice for environments where exposure to moisture and chemicals is a concern. This property extends the lifespan of components and reduces maintenance requirements.
Common Applications
Electronics Industry
Copper alloys powder plays a pivotal role in the miniaturization of electronic devices. Its high electrical conductivity ensures optimal performance in intricate circuits and connectors.
Automotive Sector
In automotive manufacturing, copper alloys powder finds its way into brake pads, bearings, and even engine components. Its wear resistance and thermal properties contribute to the efficiency and safety of vehicles.
Aerospace Applications
Aerospace engineers utilize copper alloys powder for its lightweight yet robust characteristics. From critical structural parts to electrical connections, this material withstands the demanding conditions of space travel.

Types of Copper Alloys Powder
Bronze Powders
Combining copper with elements like tin and aluminum results in bronze powders. These powders find application in artistic casting, bearings, and self-lubricating parts.
Brass Powders
Zinc is the key addition in brass powders, yielding materials suitable for decorative applications, corrosion-resistant coatings, and musical instruments.
Copper-Nickel Powders
Copper-nickel powders excel in marine environments due to their resistance to seawater corrosion. They are vital in naval architecture and offshore industries.
Production Methods
Atomization
Atomization involves spraying molten metal through a nozzle to create fine droplets that solidify into powder upon contact with air. This method produces spherical particles with uniform properties.
Electrolysis
Electrolysis deposits metal onto a cathode in powder form, yielding materials with controlled particle sizes and shapes.
Reduction Process
A reduction reaction produces copper alloys powder by reducing metal compounds using hydrogen or other reducing agents.
Factors Affecting Powder Characteristics
Particle Size Distribution
Particle size influences the powder’s flowability, packing density, and sintering behavior. Different applications demand specific particle size ranges.
Chemical Composition
The selection of alloying elements and their proportions directly impacts the final properties of the copper alloys powder.
Production Parameters
Variables like temperature, pressure, and gas composition during production affect the powder’s purity and morphology.
Handling and Safety Considerations
Dust Control Measures
Powder handling requires proper ventilation and dust control to minimize exposure risks.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Workers must use appropriate PPE to prevent skin and respiratory contact with powders.
Future Trends and Developments
As technology advances, copper alloys powder is poised to find new applications in emerging fields such as 3D printing, where its material properties can be harnessed for intricate designs and functional prototypes.
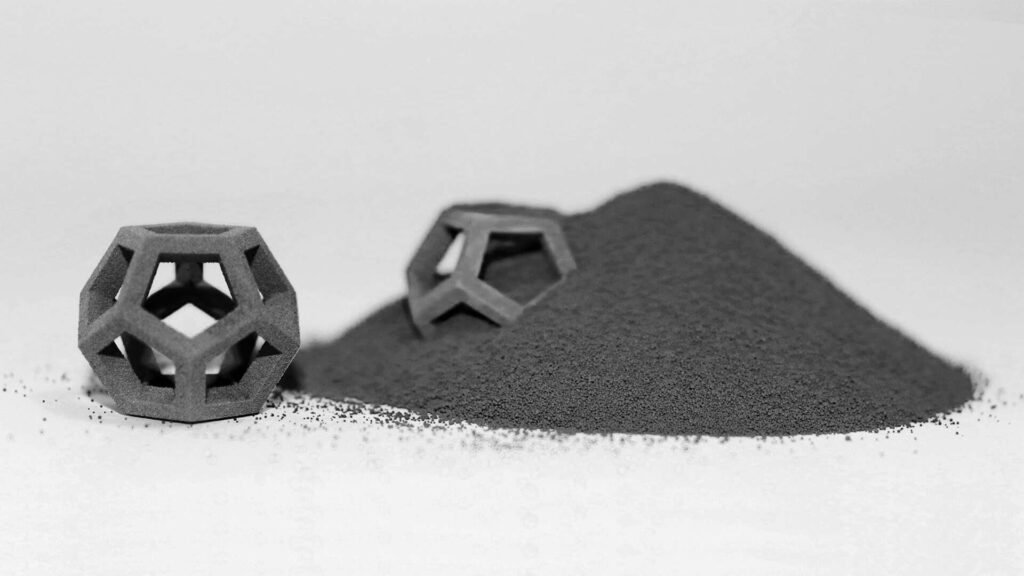

Conclusion
Copper alloys powder stands as a testament to the remarkable synergy of science and engineering. Its widespread applications, from electronics to aerospace, underscore its vital role in modern industry. As research continues and new production techniques emerge, the possibilities for this remarkable material are boundless.
FAQs
- Is copper alloys powder flammable? Copper alloys powder is not flammable, but precaution should be taken to prevent dust explosions.
- Can copper alloys powder be recycled? Yes, copper alloys powder can be recycled through suitable processes.
- Are there health risks associated with copper alloys powder? Prolonged inhalation of copper alloys powder dust can lead to health issues; thus, proper safety measures are essential.
- How are the properties of copper alloys powder tailored for specific applications? By carefully selecting alloying elements and controlling production parameters, manufacturers customize the powder’s properties.
- What role does copper alloys powder play in sustainable development? Copper alloys powder’s durability and recyclability contribute to sustainability by extending the lifespan of products and reducing waste.
know more 3D printing processes
Frequently Asked Questions (Supplemental)
1) Which Copper Alloys Powder should I choose for high-conductivity 3D‑printed heat exchangers?
- CuCrZr or CuNiSiCr. CuCrZr balances strength after aging with good thermal/electrical conductivity; CuNiSiCr offers higher softening resistance. Use gas‑atomized spherical powder, LPBF PSD ≈ 15–45 μm, low O (≤0.08 wt%) for conductivity.
2) How do oxygen and impurity levels affect Copper Alloys Powder performance?
- Elevated O and residual P/S reduce conductivity and promote porosity/soot during laser processing. Specify O ≤0.05–0.10 wt% (alloy‑dependent) for AM grades and verify via inert gas fusion; keep total impurities tightly controlled per supplier passport.
3) Can Copper Alloys Powder be binder‑jetted or used in MIM?
- Yes. Binder jetting/MIM benefit from finer PSD (D50 ≈ 12–25 μm) and narrow fines control. Debind/sinter in controlled H2/N2 or vacuum to prevent oxidation; HIP can close residual porosity for leak‑tight parts.
4) What laser wavelength works best for LPBF of copper alloys?
- Green/blue (≈515–532 nm or 450–460 nm) significantly improves absorptivity versus IR (1060–1080 nm), enabling higher density and throughput for Cu, CuCrZr, and Cu‑Ni‑Si alloys.
5) How does Copper Alloys Powder support EMI shielding applications?
- Brass and Cu‑Ni powders compounded into polymers or coatings deliver high shielding effectiveness via conductivity and permeability tuning; particle morphology and loading level drive SE and processability.
2025 Industry Trends and Data
- Green/blue laser adoption: Rapid shift for LPBF of copper alloys improves density and build rates, especially for high‑conductivity designs.
- Traceable powder passports: RFQs now request chemistry, PSD, O/N/H, inclusion ratings, lot reuse counts, and recycled content disclosure.
- Thermal management boom: EV power electronics and data center cooling drive demand for CuCrZr and OF‑Cu derivative powders for conformal‑channel heat sinks.
- ESG momentum: Argon recirculation and recycled cathode scrap integration raise recycled content to 20–40% on select copper alloy powders with published EPDs.
- Binder jetting maturation: Debind/sinter/HIP playbooks achieve 99.0–99.5% density in Cu‑based heat exchanger cores and RF components.
| KPI (Copper Alloys Powder & AM), 2025 | 2023 Baseline | 2025 Typical/Target | Why it matters | Sources/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPBF CuCrZr density (as‑built, green/blue) | 98.5–99.3% | 99.3–99.8% | Mechanical + leak‑tightness | OEM/peer‑reviewed data |
| Build‑rate improvement (green vs IR) | — | +10–30% | Throughput | AMUG/Formnext 2024–2025 |
| Electrical conductivity of LPBF CuCrZr (IACS) | 70–80% | 80–90% post‑age | Thermal/electric performance | Vendor app notes |
| Chamber O2 during Cu alloy LPBF (ppm) | ≤1000 | 100–300 | Oxide/soot control | Machine vendor guidance |
| Binder‑jet Cu alloy final density with HIP | 98–99% | 99–99.5% | Reliability, leak rate | OEM notes |
| Recycled content disclosed in powder lots | Limited | 20–40% | ESG, cost | EPD/LCA reports |
Standards and references:
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (metal powder characterization), 52904 (LPBF practice): https://www.iso.org
- ASTM B822/B214 (PSD), B212/B213 (density/flow), E1019 (O/N/H), B923 (metal powder density by helium pycnometry): https://www.astm.org
- ASM Handbook: Copper and Copper Alloys; Additive Manufacturing: https://dl.asminternational.org
- NIST AM Bench datasets: https://www.nist.gov/ambench
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Green‑Laser LPBF of CuCrZr Cold Plates for EV Inverters (2025)
- Background: An EV Tier‑1 required high‑conductivity cold plates with conformal microchannels and low leak rates.
- Solution: Gas‑atomized CuCrZr powder (15–45 μm, O ≤0.06 wt%); 515 nm LPBF with optimized gas flow and contour strategies; aging heat treatment; internal abrasive flow finishing.
- Results: Density 99.6%; conductivity 85–88% IACS after age; helium leak rate <1×10⁻⁹ mbar·L/s; build time −22% vs. IR‑laser baseline; first‑pass yield +13%.
Case Study 2: Binder‑Jetted Cu‑Ni RF Waveguide Sections with Sinter‑HIP (2024)
- Background: A telecom OEM sought lightweight, corrosion‑resistant RF sections with integrated mounting features.
- Solution: Cu‑10Ni powder (D50 ≈ 18 μm) for BJ; debind/sinter in H2‑N2 with carbon control; HIP consolidation; bead blast + electropolish.
- Results: Final density 99.2–99.4%; surface roughness Ra 3.2–3.8 μm; RF insertion loss improved 8% vs. machined brass baseline; part cost −15% at 3k units/year.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Ian Gibson, Additive Manufacturing Scholar, University of Texas at Arlington
- Viewpoint: “Green and blue lasers have turned copper alloys from ‘difficult’ into production‑ready for thermal management—powder cleanliness and gas‑flow design are still critical.”
- Dr. Martina Zimmermann, Head of Additive Materials, Fraunhofer IWM
- Viewpoint: “Powder passports tied to in‑situ layer imaging reduce qualification time for copper alloys powder, especially when recycled content is introduced.”
- Dr. James E. Cotter, Electronics Packaging Consultant (ex‑TI)
- Viewpoint: “For EMI/RF parts, alloy selection and post‑finish dictate performance as much as geometry—Cu‑Ni mixes offer corrosion robustness without sacrificing conductivity too much.”
Affiliation links:
- University of Texas at Arlington: https://www.uta.edu
- Fraunhofer IWM: https://www.iwm.fraunhofer.de
- Texas Instruments (background): https://www.ti.com
Practical Tools/Resources
- Standards/QC: ISO/ASTM 52907; ASTM B822/B214/B212/B213; ASTM E1019 for O/N/H; ASTM B193 (resistivity of copper)
- Metrology: LECO inert‑gas fusion for O/N/H (https://www.leco.com); eddy‑current conductivity meters; laser diffraction PSD; SEM for morphology/satellites; CT for porosity/leak paths
- Design/simulation: Ansys Additive/Simufact Additive for scan strategy and distortion; Ansys Fluent or COMSOL for thermal fluid design of cold plates; nTopology for lattice and channel generators
- Databases: Senvol Database (https://senvol.com/database); MatWeb (https://www.matweb.com); NIST AM Bench datasets
- ESG/traceability: Environmental Product Declarations (EPD) guidance; Responsible Minerals Initiative (https://www.responsiblemineralsinitiative.org)
Last updated: 2025-08-22
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs; introduced 2025 trends with KPI table and standards; provided two case studies (green‑laser LPBF CuCrZr cold plates; binder‑jet Cu‑Ni RF sections); added expert viewpoints with affiliations; compiled standards, metrology, simulation, and ESG resources for Copper Alloys Powder.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ISO/ASTM standards update, OEMs issue new oxygen/PSD specs for copper alloys powder, or new datasets on green/blue laser performance and binder‑jet densification are published.