Metal powders play a crucial role in various industries, providing the foundation for advanced manufacturing processes and enabling the creation of innovative products. From the automotive and aerospace sectors to electronics and healthcare, metal powders have become an indispensable resource. In this article, we will explore the world of metal powders, understanding their manufacturing process, types, applications, advantages, challenges, and future trends.
1. Introduction
Metal powders are finely divided particles of metallic substances that exhibit unique characteristics due to their small size and high surface area-to-volume ratio. They are typically produced through various manufacturing methods and can be tailored to meet specific requirements. Metal powders find applications in diverse industries, where they are used to create components, coatings, and even intricate 3D-printed objects.
2. What are Metal Powders?
Metal powder are finely ground particles of metallic elements or alloys. They are usually produced by pulverizing larger pieces of metal or by chemical or physical processes that break down bulk materials into powder form. These powders can vary in size, shape, and composition, offering a wide range of possibilities for different applications.
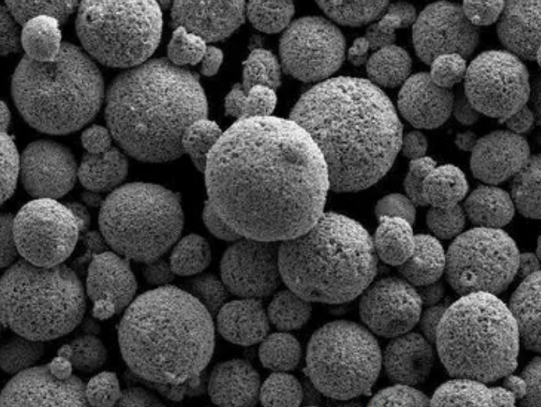

3. Manufacturing Process of Metal Powders
The production of metal powder involves several techniques, each suitable for different types of metals and desired powder characteristics. Some common manufacturing processes include:
3.1 Atomization
Atomization is one of the most widely used methods for producing metal powder. It involves the disintegration of molten metal into droplets using various techniques, such as gas atomization, water atomization, or centrifugal atomization. The droplets solidify into fine powder particles, which are then collected and processed further.
3.2 Reduction
Reduction is a process where metal oxides or salts are chemically reduced to their metallic form using a reducing agent. This method is commonly employed for the production of iron, copper, and nickel powders. The metal powder obtained through reduction can exhibit unique properties based on the specific reaction conditions.
3.3 Electrolysis
Electrolysis is primarily used to produce powders of reactive metals, such as titanium, aluminum, and magnesium. In this process, an electric current is passed through an electrolytic solution containing metal ions. The metal ions are reduced and deposited onto a cathode, resulting in the formation of metal powder.
3.4 Mechanical Methods
Mechanical methods involve mechanical alloying and milling processes. These methods typically use high-energy ball mills or attritors to grind and mix metal powders with other materials, such as ceramics or polymers. Mechanical methods can produce alloys and composite powders with enhanced properties.
3.5 Chemical Methods
Chemical methods include processes like precipitation, hydrothermal synthesis, and sol-gel synthesis. These techniques rely on the formation of metal powder through chemical reactions. Precursors or metal compounds are dissolved in a solution, and under controlled conditions, the desired metal species are precipitated or formed as a powder. Chemical methods offer the ability to precisely control the composition and morphology of the resulting powders.
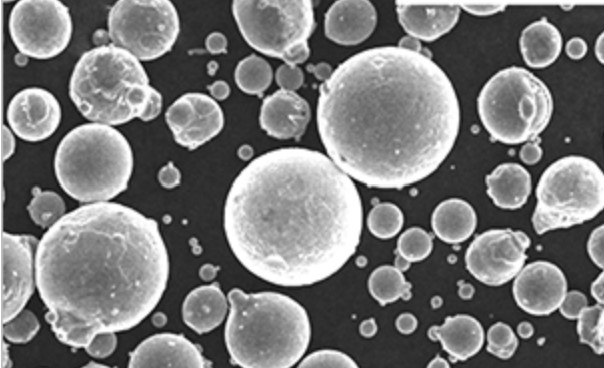
4. Types of Metal Powders
Metal powders can be classified into two main categories: ferrous metal powder and non-ferrous metal powders. Let’s explore each category in more detail:
4.1 Ferrous Metal Powders
Ferrous metal powders primarily consist of iron and iron-based alloys. These powders find extensive use in industries such as automotive, construction, and machinery. Some common ferrous metal powders include iron powder, stainless steel powder, and cast iron powder. They exhibit excellent magnetic properties, corrosion resistance, and strength, making them ideal for applications that require high-performance components.
4.2 Non-Ferrous Metal Powders
Non-ferrous metal powders encompass a wide range of metallic elements and alloys other than iron. Aluminum, copper, titanium, nickel, and bronze are some examples of non-ferrous metal powder. These powders offer unique properties such as lightweight, high conductivity, excellent thermal stability, and corrosion resistance. They are widely utilized in industries like aerospace, electronics, and biomedical, where specific material characteristics are critical.
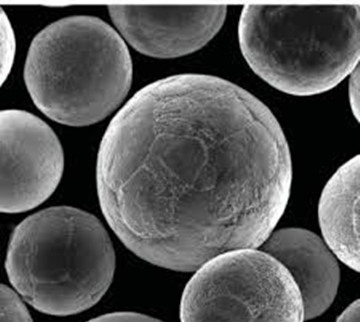
5. Applications of Metal Powders
Metal powders find numerous applications across various industries due to their versatile nature. Let’s explore some of the key sectors where metal powders are extensively used:
5.1 Automotive Industry
The automotive industry relies heavily on metal powders for manufacturing components such as engine parts, gears, bearings, and brake systems. Metal powders provide excellent strength, wear resistance, and dimensional accuracy, contributing to the overall performance and efficiency of vehicles.
5.2 Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace sector, metal powders are utilized in the production of lightweight components that can withstand extreme conditions. Powder metallurgy techniques enable the fabrication of complex shapes and structures, including turbine blades, rocket engine parts, and structural components, ensuring optimal performance and fuel efficiency.
5.3 Electronics Industry
Metal powder play a vital role in the electronics industry, where they are used for electrical contacts, conductive coatings, and soldering applications. The high electrical conductivity of metals facilitates efficient energy transfer and ensures reliable performance in electronic devices and circuits.
5.4 Medical Industry
In the medical field, metal powders find applications in the manufacturing of implants, surgical instruments, and dental prosthetics. Metals like titanium and cobalt-chromium alloys are biocompatible and offer excellent mechanical properties, making them ideal for implants that need to integrate with the human body while providing durability and strength.
5.5 Additive Manufacturing
Metal powders have revolutionized the field of additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing. By selectively fusing metal powders layer by layer, intricate and complex geometries can be created with high precision. This technology has opened up new possibilities in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare, allowing for customized and lightweight designs.

6. Advantages of Using Metal Powders
The utilization of metal powder offers several advantages over traditional manufacturing methods. Let’s explore some of these advantages:
6.1 Design Flexibility
Metal powders allow for the production of complex and intricate shapes that are difficult to achieve through conventional manufacturing techniques. This design flexibility opens up possibilities for innovative and lightweight product designs, improving overall performance.
6.2 Cost Efficiency
Powder metallurgy techniques often result in less material waste compared to traditional machining methods. The ability to create near-net-shape components reduces material costs and minimizes machining requirements, leading to cost savings in production.
6.3 Material Properties
By carefully selecting metal powders and adjusting processing parameters,manufacturers can tailor the material properties of metal powders to meet specific application requirements. This customization includes controlling the composition, porosity, density, and mechanical properties of the final product, ensuring optimal performance and functionality.
6.4 Waste Reduction
Powder metallurgy techniques promote sustainable manufacturing practices by minimizing material waste. The ability to recycle and reuse excess powders further reduces environmental impact, making metal powder a greener alternative to traditional manufacturing processes.
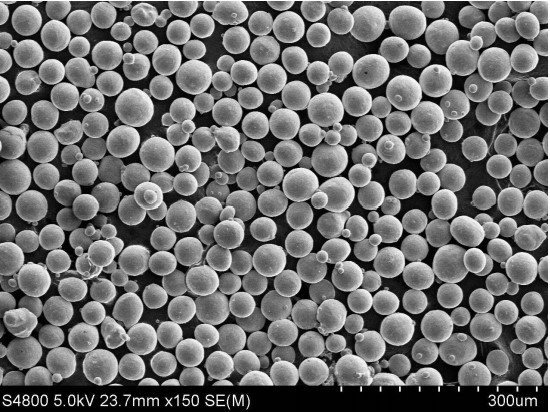

7. Challenges in Working with Metal Powders
While metal powders offer numerous benefits, there are certain challenges associated with their handling and processing. Let’s discuss some of the key challenges:
7.1 Safety Concerns
Metal powder can pose safety risks due to their flammable and explosive nature. Proper safety measures, including adequate ventilation, dust control, and fire prevention protocols, must be implemented in manufacturing facilities to ensure a safe working environment.
7.2 Handling and Storage
Metal powders require careful handling and storage to prevent contamination, oxidation, and moisture absorption. Specialized equipment and controlled environments are necessary to maintain the quality and integrity of the powders throughout the manufacturing process.
7.3 Contamination
Contamination of metal powders can negatively impact the quality and properties of the final product. Cross-contamination from foreign particles or improper cleaning of equipment can introduce impurities, affecting the performance and reliability of the manufactured components.
7.4 Post-Processing
After the initial manufacturing stage, metal powder often require additional post-processing steps, such as sintering, heat treatment, and surface finishing. These processes can be time-consuming and add complexity to the overall production cycle, requiring careful planning and quality control.

8. Future Trends in Metal Powder Technology
The field of metal powder technology continues to evolve, driven by ongoing research and advancements in manufacturing techniques. Some of the future trends in metal powder technology include:
- Nanomaterials: The development of nanoscale metal powders opens up new possibilities for enhanced material properties, improved performance, and innovative applications in fields such as electronics, energy storage, and catalysis.
- Powder Recycling: Increasing emphasis on sustainability and circular economy principles drives the development of efficient powder recycling methods. Recycling excess powders and metal scrap reduces waste and minimizes the environmental footprint of the manufacturing industry.
- Advanced Alloy Development: Researchers are actively exploring the development of new alloy compositions and powder formulations to achieve superior mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties. Advanced alloys open doors to applications that require specific material characteristics beyond what traditional metals can offer.
- Powder Characterization Techniques: Advancements in powder characterization techniques enable manufacturers to gain deeper insights into powder properties, such as particle size distribution, shape, and surface characteristics. This knowledge aids in optimizing manufacturing processes and achieving consistent product quality.
9. Conclusion
Metal powders have revolutionized modern industries, offering a versatile and customizable solution for manufacturing processes. From automotive and aerospace to electronics and healthcare, metal powder find applications in diverse sectors, enabling the production of high-performance components and innovative products. While challenges exist in handling and processing metal powders, ongoing research and technological advancements continue to drive the industry forward, paving the way for exciting future possibilities.
FAQs
1. Are metal powders safe to work with?
Metal powders require proper safety protocols and handling to ensure a safe working environment. Measures such as ventilation, dust control, and fire prevention are crucial in handling metal powder.
2. Can metal powders be recycled?
Yes, metal powder can be recycled. Recycling excess powders and metal scrap reduces waste and promotes sustainable manufacturing practices.
3. What are some common applications of metal powder in the automotive industry?
Metal powder are extensively used in the automotive industry for manufacturing components such as engine parts, gears, bearings, and brake systems. They offer excellent strength, wear resistance, and dimensional accuracy, contributing to the overall performance and efficiency of vehicles.
4. How are metal powder used in additive manufacturing?
Metal powder are a key material in additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing. They are selectively fused layer by layer to create complex and customized geometries with high precision. This technology allows for the production of lightweight designs and enables the manufacturing of intricate components in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare.
5. What are the advantages of using metal powder in manufacturing?
Using metal powder in manufacturing offers several advantages, including design flexibility, cost efficiency, tailored material properties, and waste reduction. Metal powder allow for the production of complex shapes, reduce material waste, enable customization of material properties, and promote sustainable manufacturing practices.
Additional FAQs on Metal Powders
1) How do particle size and morphology affect performance in different processes?
- LPBF prefers spherical powders D10–D90 ≈ 15–45 μm for flow and packing; binder jetting often uses 5–25 μm; press-and-sinter favors irregular particles for mechanical interlocking. Sphericity improves flow but can reduce green strength in pressing.
2) What are the most critical quality controls for AM-grade metal powders?
- PSD (laser diffraction), flowability (Hall/Carney), apparent/tap density, interstitials (O/N/H), moisture, morphology (SEM), contamination (ICP-OES), and reuse genealogy tracking.
3) Can recycled/used metal powder be blended back safely?
- Yes, with controlled blend-back ratios (e.g., 20–50%), sieving, PSD/interstitial checks, and periodic tensile/fatigue coupons. Retire lots when specs or part quality drift.
4) Which atomization route should I choose for stainless vs. titanium?
- Gas atomization suits steels/Ni alloys for cost and throughput; plasma/electrode (PA/PREP/EIGA) are preferred for reactive alloys (Ti, TiAl) due to lower oxygen and higher sphericity.
5) What standards govern metal powders for additive manufacturing?
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (feedstock), material-specific standards like ASTM F2924/F3001 (Ti), F3184 (CoCr), F3055 (Ni alloys), plus facility safety via NFPA 484 for combustible metals.
2025 Industry Trends in Metal Powders
- Qualification at scale: In‑situ monitoring tied to powder passports reduces CT burden for recurring geometries.
- Copper and aluminum growth: Blue/green laser LPBF expands high‑reflectivity metals for e‑mobility and thermal management.
- Binder jetting maturity: Higher densities via sinter/HIP playbooks for steels, Ni, and copper; larger parts at lower cost.
- Sustainability: EPDs, recycled content disclosure, and closed-loop powder handling adopted by aerospace/medical OEMs.
- Supply resilience: Dual‑sourcing and regional atomization capacity added to mitigate geopolitical and logistics risks.
| 2025 Metric (Metal Powders) | Typical Range/Value | Why it matters | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| LPBF powder PSD target | D10–D90 ≈ 15–45 μm | Stable recoating and density | ISO/ASTM 52907 |
| Relative density after LPBF + HIP (common alloys) | 99.5–99.9% | Structural reliability | Peer-reviewed AM/OEM notes |
| Oxygen spec (Ti‑6Al‑4V ELI powder) | ≤0.13 wt% O | Ductility/fatigue | ASTM F136/F3001 |
| Binder‑jetted density after sinter/HIP (steels/Ni/Cu) | 95–99% | Cost-effective large parts | Vendor case data |
| Typical reuse blend-back in serial AM | 20–50% recycled | Cost and consistency | Industry benchmarks |
| Price band, AM‑grade powders (alloys vary) | ~$20–$500/kg | Budgeting | Supplier quotes/trackers |
Authoritative references and further reading:
- ISO/ASTM AM standards: https://www.astm.org and https://www.iso.org
- NFPA 484 (combustible metals): https://www.nfpa.org
- NIST AM Bench and datasets: https://www.nist.gov
- ASM Handbook: Powder Metallurgy; Additive Manufacturing: https://www.asminternational.org
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Multi‑Laser LPBF of Copper Powders for EV Inverter Cold Plates (2025)
Background: An EV OEM sought higher thermal performance with pure copper components, historically difficult due to reflectivity and spatter.
Solution: Deployed green-laser LPBF with high-sphericity gas‑atomized copper powder (15–45 μm), inline O2/H2O monitoring, and optimized scan strategy.
Results: Build yield +22%, porosity <0.2%; heat exchanger showed 12–15% lower thermal resistance vs. machined baseline; powder reuse at 30% with stable PSD and oxygen.
Case Study 2: Binder‑Jetted 17‑4PH Metal Powders for Large Tooling Inserts (2024)
Background: A tooling supplier needed rapid, low‑cost conformal‑cooled inserts.
Solution: Used fine gas‑atomized 17‑4PH powder for binder jetting, followed by sinter + HIP and machining of critical surfaces.
Results: Final density 97–98.5%, cycle time reduction 35%, mold cooling improved part ejection time by 18%; powder scrap reduced by 40% via closed‑loop sieving.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. John Hart, Professor of Mechanical Engineering, MIT
Key viewpoint: “Powder passports that link PSD and interstitials with in‑situ build data are enabling statistically defensible part acceptance at production volumes.” - Dr. Laura Schmidt, Head of Additive Manufacturing, Fraunhofer IAPT
Key viewpoint: “Blue/green laser adoption is unlocking copper and aluminum powders for production, not just prototypes.” - Dr. Brent Stucker, AM standards contributor and industry executive
Key viewpoint: “Binder jetting plus mature sinter/HIP recipes is a credible path for large, cost‑sensitive metal parts with industrial‑grade properties.”
Citations for expert profiles:
- MIT: https://meche.mit.edu
- Fraunhofer IAPT: https://www.iapt.fraunhofer.de
- ASTM AM CoE: https://amcoe.org
Practical Tools and Resources
- Standards and safety
- ISO/ASTM 52907; ASTM F2924/F3001/F3055/F3184; NFPA 484
- Powder characterization and QC
- LECO O/N/H analyzers: https://www.leco.com
- Laser diffraction PSD, SEM morphology at accredited labs
- Apparent/tap density (ASTM B212/B329)
- Design and simulation
- Ansys Additive, Simufact Additive; nTopology for lattices and conformal cooling
- Market and data
- Senvol Database (machines/materials): https://senvol.com/database
- NIST AM Bench datasets: https://www.nist.gov
Last updated: 2025-08-21
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs, 2025 trends with metrics table and sources, two recent metal powder case studies, expert viewpoints with citations, and curated tools/resources.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ISO/ASTM standards update, major OEMs release new copper/aluminum AM parameter sets, or significant powder price/availability shifts occur.

