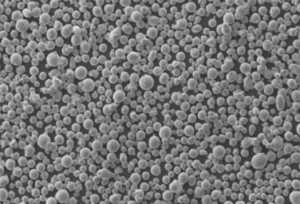
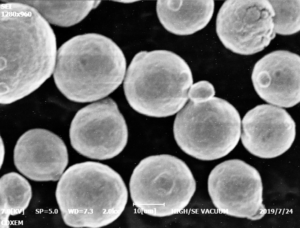
Genel Bakış Atomizasyon Tesisi
Atomizasyon tesisleri, atomizasyon işlemi yoluyla metal tozları üretme konusunda uzmanlaşmış endüstriyel tesislerdir. Bu süreç, erimiş metalin tozlar halinde katılaşan ince damlacıklar halinde parçalanmasını içerir. Bu metal tozları havacılık, otomotiv, elektronik ve katkılı üretim gibi çeşitli sektörlerde çok önemlidir.
Bir Atomizasyon Tesisinin Temel Bileşenleri
- Eritme Fırını: Metali erimiş hale getirmek için ısıtır.
- Atomizasyon Nozulu: Erimiş metali ince damlacıklar halinde kırar.
- Soğutma Odası: Damlacıkları katılaştırarak toz haline getirir.
- Toplama Sistemi: Metal tozunu toplar.
- Eleme ve Sınıflandırma Ünitesi: Tozu parçacık boyutuna göre ayırır.

Üretilen Metal Tozu Türleri
1. Paslanmaz Çelik Toz
Paslanmaz çelik tozları korozyon direnci ve mukavemeti ile bilinir. Havacılık, tıbbi cihazlar ve gıda işleme gibi sektörlerde kullanılırlar.
2. Titanyum Tozu
Titanyum tozları hafiftir ve mükemmel mukavemet ve korozyon direncine sahiptir. Havacılıkta, tıbbi implantlarda ve spor malzemelerinde çok önemlidirler.
3. Alüminyum Tozu
Alüminyum tozları hafif, güçlü ve iyi korozyon direncine sahiptir. Otomotiv ve havacılık sektörlerinde yaygın olarak kullanılırlar.
4. Bakır Tozu
Bakır tozları son derece iletkendir ve iletken mürekkepler ve kaplamalar dahil olmak üzere elektrik ve elektronik uygulamalarda kullanılır.
5. Nikel Tozu
Nikel tozları süper alaşımlarda ve bataryalarda kullanılır, yüksek mukavemet ve oksidasyon ve korozyona karşı direnç sunar.
6. Kobalt Tozu
Kobalt tozları, kesici takımlar ve havacılık motorları gibi yüksek sıcaklık ve aşınmaya dirençli uygulamalarda çok önemlidir.
7. Demir Tozu
Demir tozları otomotiv parçaları, manyetik malzemeler ve sinterlenmiş bileşenler de dahil olmak üzere çeşitli uygulamalarda kullanılır.
8. Çinko Tozu
Çinko tozları öncelikle galvanizleme için ve çinko bakımından zengin boyaların üretiminde kullanılır.
9. Tungsten Tozu
Tungsten tozları yüksek erime noktaları ve yoğunlukları nedeniyle kullanılır, bu da onları radyasyon kalkanı ve yüksek performanslı aletler gibi ağır hizmet uygulamaları için ideal hale getirir.
10. Bronz Tozu
Bakır ve kalayın bir karışımı olan bronz tozları, dekoratif eşyalarda, yataklarda ve elektrik kontaklarında kullanılır.
Metal Tozlarının Bileşimi ve Özellikleri
| Metal Tozu | Kompozisyon | Mülkler |
|---|---|---|
| Paslanmaz Çelik Toz | Fe, Cr, Ni, Mo | Korozyon direnci, yüksek mukavemet |
| Titanyum Tozu | Ti | Hafif, yüksek mukavemetli, korozyon direnci |
| Alüminyum Tozu | Al | Hafif, iyi korozyon direnci |
| Bakır Tozu | Cu | Yüksek elektriksel iletkenlik |
| Nikel Tozu | Ni | Yüksek mukavemet, oksidasyon direnci |
| Kobalt Tozu | Co | Aşınma direnci, yüksek sıcaklık kararlılığı |
| Demir Tozu | Fe | Yüksek manyetik özellikler |
| Çinko Tozu | Zn | Korozyon direnci, galvanizlemede kullanılır |
| Tungsten Tozu | W | Yüksek yoğunluk, yüksek erime noktası |
| Bronz Tozu | Cu, Sn | İyi iletkenlik, aşınma direnci |
Metal Tozlarının Uygulama Alanları
| Metal Tozu | Uygulamalar |
|---|---|
| Paslanmaz Çelik Toz | Havacılık ve uzay, tıbbi cihazlar, gıda işleme |
| Titanyum Tozu | Havacılık ve uzay, tıbbi implantlar, spor malzemeleri |
| Alüminyum Tozu | Otomotiv, havacılık ve uzay |
| Bakır Tozu | Elektrik, elektronik |
| Nikel Tozu | Süper alaşımlar, bataryalar |
| Kobalt Tozu | Kesici takımlar, havacılık ve uzay motorları |
| Demir Tozu | Otomotiv parçaları, manyetik malzemeler |
| Çinko Tozu | Galvanizleme, çinko bakımından zengin boyalar |
| Tungsten Tozu | Radyasyon kalkanı, yüksek performanslı aletler |
| Bronz Tozu | Dekoratif öğeler, rulmanlar, elektrik kontakları |
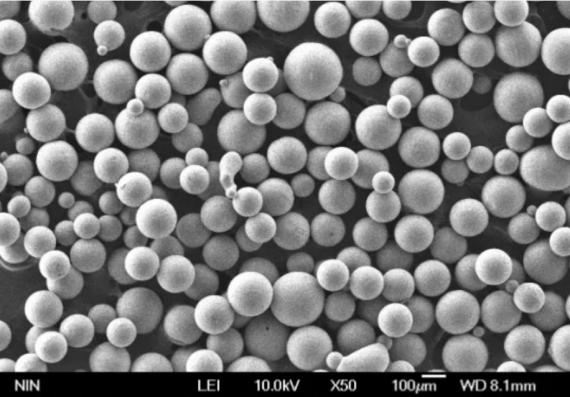
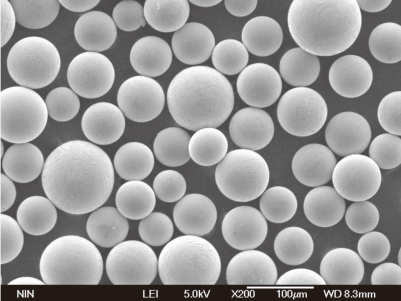

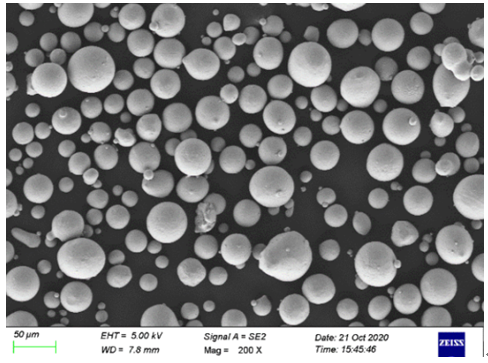
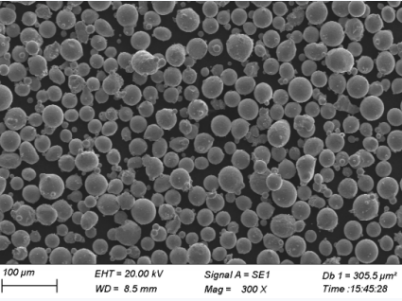
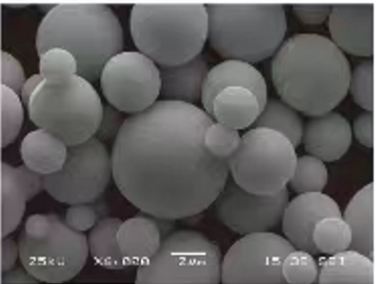
Metal Tozları için Spesifikasyonlar ve Standartlar
| Metal Tozu | Teknik Özellikler | Boyutlar (µm) | Notlar | Standartlar |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paslanmaz Çelik Toz | ASTM B214 | 1-150 | 304L, 316L | ASTM, ISO |
| Titanyum Tozu | ASTM F67, F1580 | 15-45 | CP-Ti, Ti-6Al-4V | ASTM, ISO |
| Alüminyum Tozu | ASTM B212 | 10-100 | 1100, 7075 | ASTM, ISO |
| Bakır Tozu | ASTM B833 | 5-100 | C11000 | ASTM, ISO |
| Nikel Tozu | ASTM B330 | 5-100 | Ni 200, Ni 201 | ASTM, ISO |
| Kobalt Tozu | ASTM B330 | 10-100 | Co-27, Co-28 | ASTM, ISO |
| Demir Tozu | ASTM B213 | 1-150 | Fe-99, Fe-100 | ASTM, ISO |
| Çinko Tozu | ASTM B852 | 5-100 | Zn-1, Zn-2 | ASTM, ISO |
| Tungsten Tozu | ASTM B777 | 1-50 | W-1, W-2 | ASTM, ISO |
| Bronz Tozu | ASTM B213 | 5-100 | CuSn8, CuSn10 | ASTM, ISO |
Metal Tozlarının Tedarikçileri ve Fiyatlandırması
| Tedarikçi | Metal Tozları | Fiyat Aralığı (kg başına) | Bölge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Höganäs AB | Paslanmaz Çelik, Demir | $10 – $100 | Avrupa, Amerika |
| GKN Hoeganaes | Titanyum, Alüminyum | $50 – $500 | Küresel |
| Sandvik Osprey | Nikel, Kobalt | $30 – $400 | Küresel |
| AMETEK | Bakır, Bronz | $20 – $150 | Amerika Kıtası |
| Marangoz | Tungsten, Çinko | $100 – $1000 | Küresel |
Metal Tozlarının Avantajları ve Sınırlamaları
| Metal Tozu | Avantajlar | Sınırlamalar |
|---|---|---|
| Paslanmaz Çelik Toz | Yüksek mukavemet, korozyon direnci | Pahalı, ağır |
| Titanyum Tozu | Hafif, biyouyumlu | Yüksek maliyet, işlenmesi zor |
| Alüminyum Tozu | Hafif, iyi termal özellikler | Çeliğe göre daha düşük mukavemet |
| Bakır Tozu | Mükemmel iletkenlik | Pahalı, oksidasyona eğilimli |
| Nikel Tozu | Yüksek sıcaklık kararlılığı, mukavemet | Maliyetli, işlenmesi zor |
| Kobalt Tozu | Aşınma direnci, yüksek sıcaklık kapasitesi | Pahalı, işlenmesi zor |
| Demir Tozu | Uygun maliyetli, manyetik özellikler | Korozyona karşı hassas |
| Çinko Tozu | Korozyon direnci, düşük maliyet | Düşük mukavemet, yüksek yük uygulamaları için uygun değildir |
| Tungsten Tozu | Yüksek yoğunluk, yüksek erime noktası | Son derece sert, işlenmesi zor |
| Bronz Tozu | İyi iletkenlik, estetik çekicilik | Orta güçte, kararabilir |
Atomizasyon Tesisinin Bileşimi
Bir atomizasyon tesisinin bileşimi, özel ihtiyaçlara ve üretilen metal tozlarının türüne bağlı olarak değişir. Bununla birlikte, temel bileşenler tipik olarak şunları içerir:
- Eritme Fırınları: Bunlar, metalin erime noktası ve özelliklerine göre seçilen indüksiyon fırınları, ark fırınları veya gaz yakıtlı fırınlar olabilir.
- Atomizasyon Odaları: Yüksek sıcaklıklara ve basınçlara dayanacak şekilde tasarlanmış, genellikle paslanmaz çelikten veya diğer ısıya dayanıklı malzemelerden yapılmıştır.
- Soğutma Sistemleri: Bunlar, belirli metal tozu için gereken soğutma hızına bağlı olarak su soğutmalı, gaz soğutmalı veya hava soğutmalı olabilir.
- Toplama Sistemleri: Genellikle ince tozları verimli bir şekilde toplamak için siklonlar, torba filtreler ve hazneler içerir.
- Eleme ve Sınıflandırma Üniteleri: Tozları parçacık boyutuna göre ayırmak için titreşimli elekler veya santrifüjlü sınıflandırıcılar kullanın.
Atomizasyon Tesisinin Özellikleri
Atomizasyon tesisleri birkaç temel özellik ile karakterize edilir:
- Üretim Kapasitesi: Küçük seri üretimden büyük ölçekli endüstriyel çıktılara kadar çeşitlilik gösterir.
- Esneklik: Çok çeşitli metal tozları üretebilir.
- Verimlilik: Minimum atık ile yüksek verim.
- Hassasiyet: Tutarlı partikül boyutu ve dağılımına sahip tozlar üretir.
- Güvenlik: Yüksek sıcaklık ve basınçlarla başa çıkmak için gelişmiş güvenlik özellikleriyle donatılmıştır.
Avantajları Atomizasyon Tesisi
Verimlilik ve Verimlilik
Atomizasyon tesisleri yüksek verimlilik için tasarlanmıştır ve ham maddeden maksimum verim elde edilmesini sağlar. Bu da daha az atıkla daha fazla metal tozu üretilmesi anlamına gelir.
Çok Yönlülük
Bu tesisler, farklı endüstriyel ihtiyaçları karşılayan çok çeşitli metal tozları üretebilir. İster havacılık ve uzay uygulamaları için paslanmaz çeliğe, ister elektrikli bileşenler için bakıra ihtiyacınız olsun, bir atomizasyon tesisi bunun üstesinden gelebilir.
Yüksek Kalite
Üretilen tozlar yüksek kalitede, homojen partikül boyutunda ve mükemmel saflıktadır. Bu da onları çeşitli yüksek teknoloji endüstrilerindeki zorlu uygulamalar için uygun hale getirir.
Ölçeklenebilirlik
Atomizasyon tesisleri, araştırma ve geliştirme için küçük ölçekli üretimden büyük ölçekli endüstriyel üretime kadar farklı üretim gereksinimlerini karşılayacak şekilde ölçeklendirilebilir.
Uygun Maliyetli
İlk kurulum maliyeti yüksek olabilir,
uzun vadeli faydalar ve verimlilik, atomizasyon tesislerini metal tozu üretimi için uygun maliyetli bir çözüm haline getirmektedir.
Atomizasyon Tesisinin Dezavantajları
Yüksek İlk Yatırım
Bir atomizasyon tesisi kurmak önemli bir sermaye yatırımı gerektirir. Ekipman, kurulum ve altyapı maliyeti önemli olabilir.
Karmaşık Operasyon
Bir atomizasyon tesisinin işletimi karmaşıktır ve kalifiye personel gerektirir. Verimli ve güvenli çalışmayı sağlamak için uygun eğitim ve deneyim şarttır.
Bakım
Tesisin sorunsuz çalışmasını sağlamak için düzenli bakım çok önemlidir. Bu, işletme maliyetlerini artırabilir ve özel bir bakım ekibi gerektirir.
Enerji Tüketimi
Atomizasyon prosesleri, özellikle de tungsten veya titanyum gibi yüksek erime noktalı metalleri içerenler, yoğun enerji gerektirir. Bu da yüksek işletme maliyetlerine yol açabilir.
Metal Tozlarının Karşılaştırılması: Artıları ve Eksileri
| Metal Tozu | Artıları | Eksiler |
|---|---|---|
| Paslanmaz Çelik Toz | Güçlü, korozyona dayanıklı | Pahalı, ağır |
| Titanyum Tozu | Hafif, yüksek mukavemetli | Çok pahalı, işlenmesi zor |
| Alüminyum Tozu | Hafif, iyi korozyon direnci | Diğer metallere kıyasla daha zayıf |
| Bakır Tozu | Mükemmel iletkenlik | Pahalı, oksidasyona eğilimli |
| Nikel Tozu | Güçlü, yüksek sıcaklık dayanımı | Yüksek maliyet, işlenmesi zor |
| Kobalt Tozu | Dayanıklı, ısıya dayanıklı | Pahalı, işlenmesi zor |
| Demir Tozu | Uygun fiyatlı, manyetik | Korozyona eğilimli |
| Çinko Tozu | Ucuz, korozyona dayanıklı | Zayıf, yüksek stresli kullanımlar için uygun değil |
| Tungsten Tozu | Çok yoğun, yüksek erime noktası | Son derece sert, işlenmesi zor |
| Bronz Tozu | İyi iletkenlik, estetik | Orta güçte, kararabilir |
SSS
Atomizasyon tesisi nedir?
Bir atomizasyon tesisi, erimiş metali ince damlacıklara ayırarak metal tozları üreten ve daha sonra toz formunda katılaşan endüstriyel bir tesistir.
Bir atomizasyon tesisinin temel bileşenleri nelerdir?
Temel bileşenler arasında eritme fırınları, atomizasyon nozulları, soğutma odaları, toplama sistemleri ve eleme ve sınıflandırma üniteleri bulunmaktadır.
Atomizasyon tesisleri tarafından üretilen metal tozları hangi endüstrilerde kullanılır?
Havacılık, otomotiv, elektronik ve eklemeli üretim gibi sektörler büyük ölçüde metal tozlarına dayanmaktadır.
Atomizasyon tesislerini kullanmanın avantajları nelerdir?
Avantajları arasında yüksek verimlilik, toz üretiminde çok yönlülük, yüksek kaliteli tozlar, ölçeklenebilirlik ve uzun vadede maliyet etkinliği yer almaktadır.
Üretilen başlıca metal tozu türleri nelerdir?
Ana tipler arasında paslanmaz çelik, titanyum, alüminyum, bakır, nikel, kobalt, demir, çinko, tungsten ve bronz tozları bulunur.
Metal tozları bir atomizasyon tesisinde nasıl sınıflandırılır?
Metal tozları, tozları parçacık boyutuna göre ayıran eleme ve sınıflandırma üniteleri kullanılarak sınıflandırılır.
Bir atomizasyon tesisini işletmenin zorlukları nelerdir?
Zorluklar arasında yüksek ilk yatırım, karmaşık işletim, bakım ihtiyaçları ve yüksek enerji tüketimi yer almaktadır.
Atomizasyon işlemi nasıl çalışır?
Atomizasyon prosesi metalin eritilmesini, ardından erimiş metalin bir atomizasyon nozülü kullanılarak ince damlacıklar halinde parçalanmasını ve ardından damlacıkların soğutularak toz formunda katılaştırılmasını içerir.
Atomizasyon tesisleri tüm metaller için kullanılabilir mi?
Atomizasyon tesisleri çok çeşitli metal tozları üretebilirken, proses parametrelerinin her bir metalin spesifik özelliklerine göre ayarlanması gerekir.
Atomizasyon tesislerinde üretilen metal tozları için maliyet aralığı nedir?
Maliyet, metal tozunun türüne bağlı olarak kilogram başına 10 ila 1000 dolar arasında değişebilir.
Sonuç
Atomizasyon tesisleri çeşitli endüstriler için gerekli olan yüksek kaliteli metal tozları üreterek modern üretimde çok önemli bir rol oynamaktadır. Yüksek ilk yatırım ve operasyonel karmaşıklıklara rağmen, verimlilik, çok yönlülük ve ölçeklenebilirlik avantajları onları değerli bir varlık haline getirmektedir. İster havacılık, ister otomotiv veya elektronik sektöründe olun, bu tesislerde üretilen tozlar ürünlerinizin ve yeniliklerinizin ayrılmaz bir parçasıdır.